In today’s mobile-dominated world, creating an app for your business is as important as the business itself. Most people prefer using mobile apps compared to websites due to their ease of use. Personalization is the norm today when it comes to great mobile apps. Around the world, app developers are focusing their energies on showcasing location and preference-specific products and information to their users to ensure that user retention is high.
Growing at a CAGR of over 27%, it is estimated that the global location-based services market will reach $61 billion by 2022 and over $150 billion by 2026. With governments now increasingly investing in location-based apps to combat the recent Coronavirus pandemic, the time is right for your app to gear up and be ready for a slice of the location-based app pie.
What is a location-based app?
Mobile phones dominate our lives today, and so much so that they have replaced entire sets of appliances in one go. From alarm clocks to watches to newspapers to recipe books to calendars, mobile phone apps can give you nearly everything you need at your fingertips.
However, with the plethora of information and products available on the internet today, users would rather use targeted and specified content and products than see an entire range. For example, users of a grocery app in Northern India might not be interested in canned fish, or South Indian food, or news from Africa.
Location-based apps use your current location or your location preferences to reduce the clutter in your feed or searches and provide you with relevant products and services.
Some examples of such apps include:
- Apps for tracking and combating the Coronavirus pandemic like TraceTogether and CoronaKavach
- Weather apps like Accuweather or Weather.com
- Newsfeeds like Google News or others
- Social Media and dating apps like Facebook, Tinder, Instagram and WhatsApp
- Travel/Tourism apps like MakeMyTrip, Via, ScoutMyTrip, Uber or Ola
- Navigation apps like Google Maps and Garmin
- On-demand home services like UrbanCompany
- Personal assistants like Siri, Google
- Gaming apps like Pokemon Go and PUBG
- Fitness tracking apps like FitBit, Google Fit, Apple Watch or Strava
- Food-related apps like Swiggy, Zomato, Tasty
And many more.
See also: How to create an app like Zomato
How do location-based apps work?
Location-based apps are based on geolocation. Geolocation is the geographical location of a user based on the latitude and longitude of where your mobile is. Therefore, if your mobile last updated its location to New Delhi, all the recommendations of location-based apps would be of that location. According to a recent survey by Geomarketing.com, over 90% of mobile phone users keep location services on. This means that if you create a location-based app, nearly 90 out of those 100 users are your potential clients.
These apps collect location-based data in the following ways:
Using GPS
GPS or Global Positioning System-based location services leverage data from satellites orbiting the earth, fetching location and time details using radio signals sent out by these satellites. Using signals from a minimum of 3 satellites, a GPS device uses trilateration to calculate your exact location. Routing, landmarks and other information can be gathered similarly by using your relative location on a map.
Using cellular networks
Towers put up by cellular (mobile) networks can provide approximate location data by applying triangulation to data gathered from multiple mobile towers. This is not as accurate as a GPS-driven location.
Many apps use a combination of GPS and Cellular location data to further fine-tune the location of a device.
IP-based location
IP-based location tracking uses IP information of any device connected to the internet to provide the geographical location.
Wi-Fi-based location
Similar to GPS, WPS or WiFi Positioning System leverages active WiFi hotspot data to determine the location of a device according to signal strength.
Getting location indoors
GPS signals indoors are usually weak. Indoor positioning systems leverage the power of NFC tags, Bluetooth beacons powered by BLE and Wi-Fi access points to get your exact location – a true use case for IoT.
Technology giants Apple and Google have brought out BLE based devices called iBeacon and Eddystone that leverage the power of BLE and beacons to get signals and access to information and services in the beacon’s vicinity.
Geofencing
Geofencing involves capturing the user’s location when they enter a geofenced perimeter, prompting a response, such as a discount coupon or a push notification with other instructions. Geofencing is increasingly being used by companies that wish to monitor employee movement or customer movement in a particular location. Governments are using geofencing powered by BLE devices to combat the COVID-19 pandemic.
Why create a location-based app?
Location-based apps have many advantages. Most companies use the capabilities of geolocation-based apps to provide various services to their customers. Some of the most important use cases include:
Enhancing Marketing
Marketing teams can leverage geolocation and gamification to target incentives and devise campaigns based on this information to open up new avenues of customer interaction. A new marketing trend is to involve users in marketing by letting them add assessments, recommendations, and rankings for products and services.
Leveraging Social networks
The dynamic nature of location-based apps leverages social network profiles to deduce out the intrinsic nature of the user. These apps help the user share their lifestyle and daily routine too, allowing others to follow influencers and enhance a brand’s fan following.
Communication and pins
Pinning service or landmark locations along with feedback helps others to decide if they wish to use this service. This also involves providing incentives for users by giving coupons or VIP status. Advertising also benefits from this by providing targeted advertisements and reaching a customer when they are “in the moment”.
Showcasing the power of AR
Using AR to super-impose physical objects based on geolocation is one capability of these apps. This was showcased in Pokémon Go, where users could point their phones at scenes and have location-based annotations.
Usage in emergencies
The government of Singapore has used the power of BLE, Geofencing, AI, the community and a location-based app called TraceTogether to combat and contain the novel Coronavirus epidemic. Emergencies like the COVID-19 pandemic require monitoring of confirmed cases.
Read here: Top telemedicine tools to combat against Coronavirus
Installing the app on phones of all users helped them stay away from infection-hotspots and study the pattern of those infected, including things like breaking quarantine protocols and using public service, etc. AI helps users self-diagnose themselves and contact emergency services for testing if they are infected. A similar app has also been developed by the government of India called CoronaKavach, which works similarly.
10 Steps to consider while creating a location-based app
1. Studying the market
Possibly the most important step before thinking of creating any product would be to study the market, know your competition better and understand what your users need. This will ensure that the rest of the phases of development work seamlessly.
2. Deciding on in-house development vs outsourcing
This is an important aspect that you must consider before you create the app. An in-house team offers better flexibility, but also has fixed costs that rake up the final cost of your app. If you do not have a team already, you will end up splurging on IT infrastructure, team salaries and talent management. Outsourcing your app to development companies like Volumetree that already have the infrastructure and the talent in place is a better option if you do not have these things in place.
3. Finding the right development partner
Companies like Volumetree have a lot of experience in user research, functionality assessment, and user experience design. This gives them a distinctive edge over other low-priced alternatives as they ensure that your app is created the way your users would want it to be. A good development partner also ensures that the rest of the app development and release process is streamlined and simplified for you.
4. Choosing the right tech stack
Using the wrong tools in the right app is a recipe for disaster. Things might not work as intended or you might end up trying to exploit a functionality that might not be legal or available in your target region. Using the services of a good development partner like Volumetree mitigates these problems as they are aware of these challenges through experience and domain expertise.
5. Being focused on security
Security and privacy are major concerns while creating a location-based app. As various countries might have multiple regulations in place that can affect your app, companies like Volumetree ensure that your app is completely focused on the safety, security, and privacy of your users. The app should also be safe from data theft, data loss and ransomware attacks using multi-factor authentication, encryption and other technologies.
6. Testing the waters – creating a prototype
Creating a prototype is a good way to see the look and feel of the app. You also get to gather feedback for users and make important changes at the outset, rather than doing them later.
7. Beautification – making a good user experience
The user interface and experience of an app must be innovative, minimalistic and functional, rather than going all out and adding all the elements possible in one go. Great design always goes a long way in ensuring that users prefer your app over others.
8. Getting down and dirty: Developing the app
Developing the app involves coding the entire application and bringing all the elements together to create a cohesive system.
9. Testing the app
Testing an app is as important as thinking of creating it. A well-tested app is stable, enhances the trust of the user in the app and ensures user retention.
10. Showing off your new toy – release and marketing
Once testing is complete, it is time to release your app, making it available on the app stores and your website. This is a great time to indulge yourself in marketing your app well, ensuring that all your potential users know that you are now “out there”.
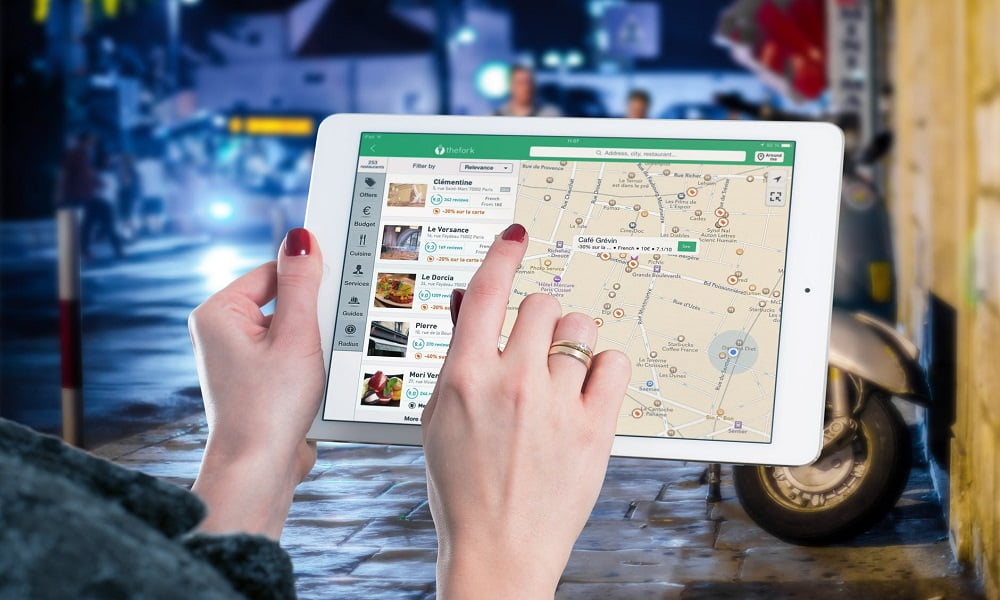
Top features of a location-based app
Depending upon their use case, location-based apps must include some basic features that include:
- Map integration
If your location-based app has route planning or showcases the distance between two cities, you must integrate maps to ensure users get the information they need.
- Notifications
Push notifications are essential for every location-based app. These notifications keep the user updated and can easily send alerts about upcoming sunrise and sunset times, moon phases, bad weather, traffic jams, etc.
- Analytics
AI and IoT-driven location-based apps can now provide a better and more personalized user experience to their users. From better navigation to targeted ads to informing customers about sales in the vicinity or even offering mini-contests to build engagement with nearby customers, AI has opened up more avenues for location-based apps than ever before.
- Community
Community building is a fantastic way to build a brand. Apps can easily leverage location information to announce events and provide helpful information in a localized community.
- Feedback and support
Your customers might often run into roadblocks or have suggestions that can significantly improve your location-based app. Offering avenues for feedback and support is an excellent way to keep your customers hooked for good.
- Filters
Customers demand the power of choice. From telemarketing to social media, nearly every avenue you can think of uses the power of filters to get targeted information to customers. Filters can help your customers keep out notifications they do not need and improve satisfaction levels.
- AR or Augmented Reality
AR is trending with many location-based gaming apps such as Pokémon Go and others, and this helps these apps to provide an immersive experience to their players.
Cost of developing a location-based app
The cost of developing a location-based app can vary greatly depending on the features that you choose. A locaion-based app with basic features can cost between $10,000 to $15,000 per platform. Your basic app development cost will depend on:
- Features—Adding features will rake up development costs significantly. An MVP with few basic features can cost much less than a full-fledged app with a host of features.
- Platforms—The platform you choose will determine the cost of developing your app. Usually, developing an app for both iOS and Android together may cost a bit less than developing for a different platform at a later stage. Conduct your market research well to understand the most-used platform for your target group.
- Developer location—the location of your development company can significantly impact development costs. For example, a developer in the US will charge between $100-$150 per hour for developing a location-based app. Considering the time to develop such an app can range from 500-800 hours, you are looking at a figure between $75,000 to $120,000. Comparatively, a developer in India might charge between $50-$75 per hour, dropping your development cost to range between $35,000 to $65,000.
At Volumetree, our vast talent pool and global reach will help you achieve the perfect price-feature ratio. Our world-class developers, designers, testers and UX experts will help you create an outstanding app—without breaking the bank.
Here’s what impacts the cost of a location-based app:
Third-party service integration
Integrating third-party services such as maps, geofencing, and others can significantly rake up the cost of the app. This cost will include licensing and integration fees in addition to the development cost of the app.
- Design time: 20 hours
- Backend development: 50 hours
- Front-end development: 50 hours
Vendor registration
If you are offering services such as delivery or home care, adding vendor profiles will add to the cost of your app.
- Design time: 10 hours
- Backend development: 15 hours
- Front-end development: 30 hours
Gamification
Gamification using AR is an additional add-on feature for a location-based app. Adding this feature requires skill and will come at an additional cost.
- Design time: 50 hours
- Backend development: 100 hours
- Front-end development: 120 hours
Payment gateway integration
Location-based shopping or services require payment gateway integrations to ensure that users can pay for products or services online.
- Design time: 10 hours
- Backend development: 15 hours
- Front-end development: 15 hours
Analytics
In-app analytics are essential to gather product usage metrics and find areas of improvement for your location-based app.
- Design time: 15 hours
- Backend development: 35 hours
- Front-end development: 25 hours
Location-based apps are largely considered to be “the future” of apps being created today. As companies increasingly focus their energies on relevancy and consumer location while marketing and advertising, it is important that your app considers this at the outset. Companies like Volumetree can help you by providing the talent and the vision to create location-based apps that can help your idea reach the market, fast.







Hello there, just became aware of your blog through Google,
and found that it is really informative.
I’m gonna watch out for brussels. I will
be grateful if you continue this in future.
Many people will be benefited from your writing.
Cheers!
Hi my loved one! I wish to say that this post is awesome, nice written and include approximately all important infos. I¦d like to see more posts like this .
Thanks so much for giving everyone an extraordinarily superb possiblity to read in detail from this site. It is always so excellent plus packed with a lot of fun for me personally and my office acquaintances to visit your blog really three times per week to find out the latest tips you have got. And lastly, I am at all times motivated with all the very good opinions you give. Some two tips in this posting are absolutely the most effective we’ve ever had.
It¦s actually a cool and helpful piece of information. I am happy that you shared this useful information with us. Please stay us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
You really make it seem so easy together with your presentation however I find this topic to be actually something that I believe I might by no means understand. It seems too complex and very wide for me. I’m taking a look ahead in your subsequent put up, I will try to get the dangle of it!
At this time it appears like Drupal is the top blogging platform available right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
Great work! That is the kind of info that are meant to be shared around the net. Disgrace on Google for no longer positioning this publish higher! Come on over and consult with my web site . Thanks =)
I’d constantly want to be update on new articles on this site, saved to bookmarks! .
I like what you guys are up too. Such smart work and reporting! Carry on the excellent works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my web site :).
There is noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made certain nice points in features also.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Heya i’m for the first tjme here. I founjd this board and I find It really useful & it helped mee out a lot.
I hope to give something back annd aid others like you helped me.
Here is my homepage :: https://Sites.Google.com/view/vavada-online-casino
Hmm it looks like yoyr website atee myy first comment (it was super long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I wrote and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog.
I ass well am an aspiringg blog blogger but I’m still new
to everything. Do you have any tips for rokokie
blog writers? I’d really appreciate it.
Also visit my web site … https://Sites.google.com/view/start-playing-online-casino
whoah this blog is great i love studying your posts. Stay up the good paintings! You know, lots of individuals are looking round for this info, you could help them greatly.
Pingback: สูตรสล็อต pg ใช้ได้จริง 2024
Some truly wonderful information, Sword lily I found this.
My brother suggested I might like this web site. He was entirely right. This post actually made my day. You cann’t imagine just how much time I had spent for this information! Thanks!
This is very attention-grabbing, You are an excessively skilled blogger. I have joined your feed and look ahead to looking for more of your magnificent post. Additionally, I have shared your site in my social networks!
I am not real wonderful with English but I get hold this really easygoing to translate.
Superb website you have here but I was wondering if you knew of any discussion boards that cover the same topics discussed here? I’d really like to be a part of group where I can get feed-back from other experienced individuals that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Kudos!
Hi! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any suggestions?
What Is Sugar Defender? Sugar Defender is made of natural plant-based ingredients and minerals that support healthy blood sugar levels.
I have read some good stuff here. Certainly worth bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how much effort you put to create such a wonderful informative web site.
Lovely just what I was searching for.Thanks to the author for taking his time on this one.
Just desire to say your article is as astounding. The clarity in your post is just great and i could assume you’re an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission let me to grab your RSS feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please continue the enjoyable work.
It?¦s really a cool and helpful piece of information. I am glad that you simply shared this useful information with us. Please stay us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
I real delighted to find this web site on bing, just what I was searching for : D also bookmarked.
Dead indited content, appreciate it for entropy.
Pingback: วิเคราะห์บอลวันนี้
Greetings I am so happy I found your webpage, I really found you by accident, while I was searching on Bing for something else, Regardless I am here now and would just like to say many thanks for a incredible post and a all round exciting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to look over it all at the moment but I have bookmarked it and also added in your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a great deal more, Please do keep up the awesome job.
Its wonderful as your other posts : D, thankyou for posting. “It takes less time to do things right than to explain why you did it wrong.” by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow.
top 10 online pharmacy in india http://indiaph24.store/# pharmacy website india
reputable indian online pharmacy
I’ll right away clutch your rss as I can not in finding your email subscription hyperlink or newsletter service. Do you have any? Kindly allow me know so that I may subscribe. Thanks.
Oh my goodness! an incredible article dude. Thank you Nevertheless I am experiencing subject with ur rss . Don’t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anyone getting identical rss downside? Anybody who knows kindly respond. Thnkx