The impact of the coronavirus or COVID-19 has been unprecedented and of a scale that can only be rivaled by the 1918 Spanish Flu. Dwarfing the SARS epidemic of 2003 and the Swine Flu Pandemic of 2009 by a large margin, the novel Coronavirus has infected over 300,000 individuals and has claimed over 16,000 lives. Designated as a pandemic by the WHO, the Coronavirus has wreaked havoc on our healthcare facilities, overwhelming them to levels that have been unforeseen to date.
See also – Telemedicine Tools To Combat Against Corona Virus
With alarming infection rates even in developed countries, this virus is spreading faster than containment measures can kick in to control it.
A prime example of accelerated medical research
The coronavirus pandemic has added much-needed fuel to the medical research industry, with companies pumping in both money and scientific resources to help curb and manage this pandemic. As an example, an experimental COVID-19 vaccine developed by Moderna Therapeutics has already reached a level where human trials are being conducted by the NIH for review. This vaccine has come in days rather than months, taking merely 63 days after China released the genetic sequence of the virus in mid-January to reach stability levels that can initiate human trials. This has been made possible using mRNA, which uses a genetic form of the genome of the virus, which prompts cells to process it and rally up the immune system to generate a response and target it for destruction. This method does not involve “growing” the virus, which can sometimes take many months to reach levels where production can begin.
The overburdened healthcare system
However, as cases arise, the shortfall of medical workers and experts has started to show up. Hospitals and clinics are severely overwhelmed, impacting care and reducing the number of patients a doctor can take care of or even advise. As OPDs have closed nearly everywhere in the world, people have few options except queuing outside hospital emergency centers and being there is a big risk factor on its own.
Technology to the rescue – again
Around the world, telemedicine had gained some importance in the early 2000s but lost impetus somewhere down the line due to a lack of interest in patients and the medical community. As the coronavirus pandemic overwhelms our medical systems, hospitals and clinics have either run out or do not have patient footfall due to lockdowns, hampering aid to those in need. Telemedicine or telemedicine has come to the rescue of both patients and doctors by providing an alternative means of communicating with each other. This also helps patients with unrelated ailments such as diabetes to get care despite lockdowns being in place.
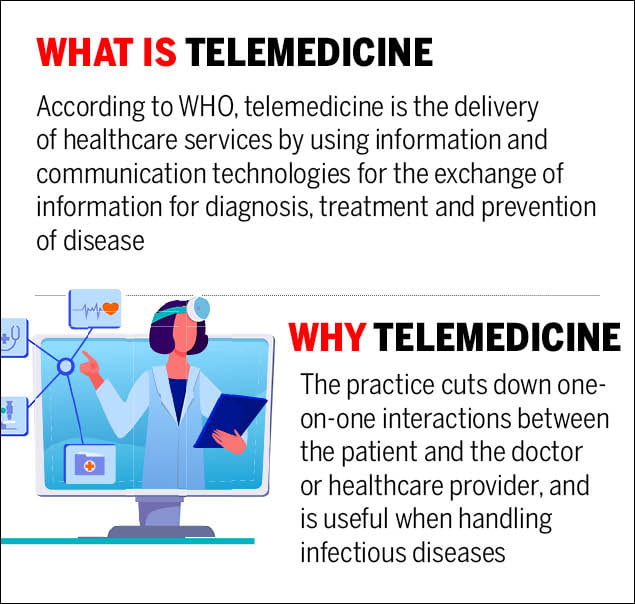
What is telemedicine? How does it work?
Telemedicine is using alternative methods of communication, like video conferencing, video chat, phones and instant messaging to provide medical care to patients remotely. Although telemedicine or telemedicine cannot replace a traditional healthcare setting, it can reduce the burden on healthcare providers immensely. telemedicine provides real-time responses from healthcare professionals, ensuring that patient concerns can be addressed. In India, programs like ICMR-AROGYASREE, NeHA, and VRCs have helped patients get access to care, no matter how remote the location may be. In countries like the USA, telemedicine is now covered by Medicare, ensuring that millions of patients can now use telemedicine to help reduce exposure during regular health check-ups and clinic visits.
Is telemedicine the right approach for combating the COVID-19 pandemic?
Telemedicine helps to bridge the gap between people, healthcare providers, and health systems. This ensures that patients can stay at home and communicate with medical care workers remotely, helping to reduce the spread of the virus to the masses and medical workers unless it is necessary. Telemedicine has also been given the right push by this outbreak, helping governments and healthcare providers to test the system in a way that can never be replicated in a lab. This real-world test will determine the future of telemedicine, but we’re sure that for the current pandemic, this is a solution that can assist doctors in helping thousands more than they could on the ground. According to a recent survey by Software Advice, telemedicine adoption rates have skyrocketed in the US and over 80% of patients now prefer providers that offer telemedicine instead of regular clinic visits for routine checkups.
What does a typical telemedicine system comprise of?
Telemedicine involves the usage of IVRs, knowledgebases and informational videos for self-care of non-critical patients and most recently, mobile apps to ensure that patients have access to the information or support they need at their fingertips. A more direct method of telemedicine is the usage of videoconferencing to help doctors assist each other and to diagnose patients that cannot visit the clinic personally. This helps doctors overseas and in less-affected regions to help and assess patients that an overwhelmed hospital might not be able to cater to, ensuring that patient care continues 24/7 with doctors around the world being available on call.
How is telemedicine different from Telemetry?
Telemetry is the capability to remotely measure data that would otherwise require physical presence to collate. As an example, health workers dealing with patients in quarantine can remotely monitor their data, reducing exposure levels and enhancing the quality of care. Telemedicine involves the interaction of doctors with patients to provide endpoint, contactless care.
Can prescriptions be issued by telemedicine professionals?
Although most international telemedicine services can issue prescriptions so patients can get medication that they need, the rules might be different in some countries. Please ensure that you check the website of your local health department for more details.
I am a doctor and I would like to offer telemedicine services for my setup
You’re in luck. Volumetree is an experienced software development company that has global exposure in developing apps and services for the medical industry. A recent example is the development of online nurse management and onboarding platform for the largest nursing services provider in South Africa. Volumetree can help you develop a platform to help those in need, thereby reducing the burden on public health services, and helping your patients take care of their regular visits without having to step out of their homes.
Infrastructural challenges and limitations of telemedicine
Although telemedicine is considered a godsend by many, the existing infrastructure was dependent on clinics and hospitals to function. With a massive expected influx, many systems around the world have reported infrastructural challenges and difficulties in coping with the large number of users thronging the system. Although these can be worked out with scalability, telemedicine will take some time before it is completely streamlined. Problems were recently noticed by patients using services like Amwell and Penn medicine, however, bottlenecks are being addressed by all telemedicine services globally.
Are there any legal or regulatory issues with telemedicine while dealing with COVID-19?
Telemedicine is a relatively nascent field that had to evolve rapidly in the wake of this pandemic. There is not much information available about regulatory norms and it is best to consult the local health department for more information. Here are some guidelines that can help you take care of the requirements so that you can be better prepared to launch your service in your home country
- Check insurance provider coverage and assess if insurance can cover telemedicine in your region
- If your country has region-limited licensing for doctors and other medical workers, ensure that you are not violating any regulatory norms.
- Ensure that both your clinic and the patients being treated are adhering to all technology and medico-legal requirements in their respective regions.
- Ensure compliance with governmental regulation of prescription of controlled substances.
- Ensure that remote physicians can be reliably screened before bringing them onboard.
- Ensure that your communication tools comply with privacy laws.
- Ensure that clinical services, billings, ordering, and follow-up comply with local laws.
- Ensure that if you are providing care to patients overseas, your clinic must comply with regulations in that country.
Telemedicine is considered to be the best tool for combating COVID-19 internationally as it can bring together medical care workers from around the world to combat this deadly and highly infectious disease. Volumetree is committed to the betterment of mankind by creating solutions that can help medical health professionals reach the widest possible audience. Our world-class team had anticipated disruptions and were ready to take on the challenge of business continuity. We planned in time to ensure our availability to attend to your needs at all times. Together, we can help the world combat this disease better.






such a wonderful and amazing blog and I’m very happy to read this blog.
very informative posts and advice :)
I always was interested in this subject and still am, thanks for putting up.
I’m not sure why but this website is loading incredibly slow for me. Is anyone else having this problem or is it a problem on my end? I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
Rattling great info can be found on website. “The only thing you take with you when you’re gone is what you leave behind.” by John Allston.
I consider something truly interesting about your web blog so I saved to my bookmarks.
What i do not realize is in truth how you’re no longer actually a lot more well-preferred than you may be right now. You’re so intelligent. You understand therefore significantly on the subject of this matter, made me in my opinion consider it from numerous numerous angles. Its like women and men are not fascinated until it is something to do with Woman gaga! Your personal stuffs excellent. All the time maintain it up!
I like what you guys are usually up too. Such clever work and reporting! Keep up the excellent works guys I’ve included you guys to my blogroll.
Thank you for sharing superb informations. Your website is very cool. I am impressed by the details that you?¦ve on this website. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for extra articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found just the information I already searched all over the place and just could not come across. What a perfect website.
My brother recommended I may like this web site. He was totally right. This submit truly made my day. You can not believe just how a lot time I had spent for this info! Thank you!
I am often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has really peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information.
Greetings from California! I’m bored to death at work so I decided to check out your website on my iphone during lunch break. I enjoy the information you present here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m amazed at how quick your blog loaded on my mobile .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyhow, superb site!
Great blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A design like yours with a few simple tweeks would really make my blog stand out. Please let me know where you got your theme. Thank you
I am not sure where you are getting your info, but good topic. I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more. Thanks for magnificent information I was looking for this info for my mission.
Hello, i think that i saw you visited my blog thus i came to “return the favor”.I am trying to find things to improve my web site!I suppose its ok to use a few of your ideas!!
I just couldn’t depart your web site before suggesting that I actually enjoyed the standard information a person provide for your visitors? Is going to be back often to check up on new posts
I have read some good stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how much effort you put to make such a magnificent informative website.
I gotta bookmark this website it seems invaluable invaluable
naturally like your web site but you need to check the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I to find it very bothersome to inform the truth on the other hand I will surely come again again.
Sweet blog! I found it while searching on Yahoo News. Do you have any tips on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Appreciate it
It’s hard to find knowledgeable people on this topic, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
That is the correct weblog for anyone who needs to find out about this topic. You realize a lot its almost arduous to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You undoubtedly put a brand new spin on a subject thats been written about for years. Nice stuff, just nice!
Hiya, I am really glad I’ve found this information. Nowadays bloggers publish only about gossips and internet and this is actually frustrating. A good blog with exciting content, that’s what I need. Thanks for keeping this website, I will be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Cant find it.
I genuinely appreciate your work, Great post.
Thank you for sharing excellent informations. Your website is so cool. I am impressed by the details that you have on this blog. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for more articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found simply the info I already searched everywhere and just could not come across. What a perfect website.
Some really nice stuff on this website , I enjoy it.
Забота о жилище – это забота о спокойствии. Теплосберегающая облицовка – это не только стильный внешний вид, но и обеспечение теплового комфорта в вашем уютном уголке. Наша команда, бригада мастеров, предлагаем вам сделать ваш дом в прекрасное место обитания.
Наши улучшения – это не просто теплоизоляция, это творческое воплощение с каждым шагом. Мы стремимся к идеальному балансу между внешним видом и практической ценностью, чтобы ваш дом преобразился не только пригодным для жизни, но и шикарным.
И самое существенное – приемлемая цена! Мы уверены, что высококачественные услуги не должны быть дорогим удовольствием. [url=https://ppu-prof.ru/]Строительные расценки на утепление фасадов[/url] начинается всего начиная с 1250 руб/м².
Применение современных технологий и материалов высокого качества позволяют нам создавать тепловую обработку, которая обеспечивает долговечность и надежность. Оставьте в прошлом холодные стены и лишние затраты на отопление – наше утепление станет вашим надежным препятствием перед холодом.
Подробнее на [url=https://ppu-prof.ru/]веб-сайте компании[/url]
Не откладывайте на потом заботу о счастье в вашем уголке. Обращайтесь к опытным строителям, и ваше жилье станет настоящим художественным творчеством, которое принесет вам тепло и удовлетворение. Вместе мы создадим жилище, в котором вам будет по-настоящему уютно!
Awsome article and right to the point. I am not sure if this is actually the best place to ask but do you folks have any thoughts on where to employ some professional writers? Thank you :)
Переутомились застывать зимой и перевыплачивать за отопление?
Утепление фасада – решение проблемы!
Компания “Тепло и уют” с 2010 года предлагает квалифицированные услуги по теплообеспечению фасадов зданий любой сложности. За это время мы зарекомендовали себя как стойкий и ответственный партнер, о чем свидетельствуют многочисленные отзывы наших клиентов.
Почему стоит выбрать нас?
доступные цены. [url=https://stroystandart-kirov.ru/]Утепление фасадов в москве цена[/url] от 1350 руб/м2.
практичность и опытность. Наши бригады имеют обширный опыт работы в сфере инсуляции фасадов. Мы используем только аттестованные материалы и современные технологии, что гарантирует высочайшее качество работ.
Частный подход. Мы подберем для вас лучшее решение с учетом ваших потребностей и бюджета.
Бесплатная консультация и выезд замерщика. Наши специалисты бесплатно проконсультируют вас по всем вопросам термоизоляции фасада и произведут аккуратные замеры.
Наш сайт: [url=https://stroystandart-kirov.ru/]http://stroystandart-kirov.ru[/url]
Гарантия качества. Мы предоставляем гарантию на все виды работ.
Звоните нам сегодня и получите бесплатную консультацию!
Мы сделаем ваш дом теплым, теплым и экономичным!
Изнурены застывать зимой и избыточно платить за отопление?
Термоизоляция фасада – решение проблемы!
Компания “Тепло и уют” с 2010 года предлагает компетентные услуги по термоизоляции фасадов зданий любой сложности. За это время мы зарекомендовали себя как прочный и сознательный партнер, о чем свидетельствуют многочисленные отзывы наших клиентов.
Почему стоит выбрать нас?
доступные цены. [url=https://stroystandart-kirov.ru/]Утепление фасада расценка[/url] от 1350 руб/м2.
опытность и мастерство. Наши бригады имеют огромный опыт работы в сфере теплообеспечения фасадов. Мы используем только сертифицированные материалы и современные технологии, что гарантирует высокое качество работ.
Индивидуальный подход. Мы подберем для вас лучшее решение с заметанием ваших потребностей и бюджета.
Бесплатная консультация и выезд замерщика. Наши специалисты бесплатно проконсультируют вас по всем вопросам термоизоляции фасада и произведут аккуратные замеры.
Наш сайт: [url=https://stroystandart-kirov.ru/]веб-сайте[/url]
Уверенность качества. Мы предоставляем уверенность на все виды работ.
Звоните нам сегодня и получите бесплатную консультацию!
Мы сделаем ваш дом уютным, теплым и экономичным!
You got a very fantastic website, Gladiolus I observed it through yahoo.
Thanks , I have recently been looking for information about this topic for ages and yours is the best I have discovered till now. But, what about the bottom line? Are you sure about the source?
It is in reality a nice and useful piece of information. I am satisfied that you simply shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Valuable info. Lucky me I found your web site by chance, and I am stunned why this coincidence did not took place in advance! I bookmarked it.
Appreciate it for this tremendous post, I am glad I found this site on yahoo.
Its such as you learn my mind! You seem to understand a lot approximately this, such as you wrote the e book in it or something. I think that you could do with a few to power the message house a little bit, but instead of that, that is magnificent blog. A fantastic read. I will certainly be back.
Дорогие Клиенты!
Подносим вам последнее элемент в мире декора домашней обстановки – шторы плиссе. Если вы желаете к великолепию в всякой стороне вашего дома, то эти перила будут выдающимся решением для вас.
Что делает шторы плиссе столькими неповторимыми? Они объединяют в себе в себе изысканность, функциональность и эффективность. Благодаря эксклюзивной формации, новаторским тканям, шторы плиссе идеально гармонизируются с для любого другого комнатки, будь то гостинка, спальня, кухня или профессиональное место.
Закажите [url=https://tulpan-pmr.ru]шторы гофре плиссе[/url] – совершите уют и красоту в вашем доме!
Чем манят шторы плиссе для вас? Во-первых, их своеобразный бренд, который присоединяет к очарование и вкус вашему обстановке. Вы можете отыскивать из разнообразных текстур, оттенков и стилей, чтобы акцентировать оригинальность вашего дома.
Кроме того, шторы плиссе предлагают полный круг функциональных вариантов. Они могут регулировать уровень освещения в месте, преграждать от солнечных лучей, предоставлять закрытость и формировать уютную среду в вашем доме.
Наш ресурс: [url=https://tulpan-pmr.ru]www.tulpan-pmr.ru[/url]
Мы поддержим вам подобрать шторы плиссе, какие замечательно подойдут для вашего дизайна!
The very core of your writing while appearing reasonable at first, did not really work very well with me personally after some time. Somewhere throughout the sentences you actually managed to make me a believer unfortunately only for a short while. I however have a problem with your jumps in logic and one would do well to help fill in those breaks. In the event you can accomplish that, I will certainly end up being impressed.
hello!,I like your writing very much! share we communicate more about your article on AOL? I require an expert on this area to solve my problem. May be that’s you! Looking forward to see you.
We’re a bunch of volunteers and opening a new scheme in our community. Your website provided us with valuable information to work on. You’ve done an impressive task and our entire group might be thankful to you.
I was very pleased to find this web-site.I wanted to thanks for your time for this wonderful read!! I definitely enjoying every little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you blog post.
I got what you intend,saved to favorites, very decent site.
I like this post, enjoyed this one appreciate it for putting up.
I have been reading out many of your articles and i must say pretty good stuff. I will surely bookmark your website.
Thank you for all your valuable labor on this blog. Kate take interest in engaging in internet research and it’s really easy to understand why. Many of us know all concerning the dynamic form you present important information on your website and in addition strongly encourage contribution from others about this matter while our own princess is without a doubt understanding a lot. Take pleasure in the remaining portion of the year. You’re conducting a tremendous job.
I do not even know the way I stopped up here, however I believed this publish used to be good. I do not recognize who you are but definitely you are going to a famous blogger in the event you aren’t already ;) Cheers!
You are a very capable individual!
Мы компания специалистов по поисковой оптимизации, специализирующихся на продвижении сайтов в поисковых системах.
Мы получили заметные достижения и предлагаем вам воспользоваться нашим опытом и знаниями.
Что мы можем вам предложить:
• [url=https://seo-prodvizhenie-ulyanovsk1.ru/]комплексный аудит сайта цена[/url]
• Комплексный анализ вашего сайта и разработка индивидуальной стратегии продвижения.
• Оптимизация контента и технических аспектов вашего сайта для максимальной эффективности.
• Систематический мониторинг и анализ результатов с целью улучшения вашего онлайн-присутствия.
Подробнее [url=https://seo-prodvizhenie-ulyanovsk1.ru/]https://seo-prodvizhenie-ulyanovsk1.ru/[/url]
Результаты наших клиентов уже видны: рост посещаемости, улучшение позиций в поисковых системах и, конечно, рост бизнеса. У нас есть возможность предоставить вам бесплатную консультацию, для того чтобы обсудить ваши требования и разработать стратегию продвижения, соответствующую вашим целям и финансовым возможностям.
Не упустите возможность повысить эффективность вашего бизнеса в интернете. Свяжитесь с нами сегодня же.
I was more than happy to find this net-site.I needed to thanks to your time for this excellent learn!! I positively enjoying every little little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you weblog post.
Some truly nice stuff on this site, I enjoy it.
I have been exploring for a bit for any high-quality articles or blog posts in this kind of space . Exploring in Yahoo I ultimately stumbled upon this web site. Reading this info So i am satisfied to exhibit that I have a very good uncanny feeling I discovered exactly what I needed. I most indisputably will make certain to don’t overlook this site and give it a look on a continuing basis.
I’d forever want to be update on new posts on this website , saved to bookmarks! .
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this site. Thank you, I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your website?
I too conceive thence, perfectly indited post! .
I am usually to running a blog and i actually appreciate your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for brand spanking new information.
I enjoy the efforts you have put in this, regards for all the great content.
I genuinely enjoy reading on this web site, it contains great posts.
Hello there, I found your web site by means of Google whilst searching for a comparable subject, your site got here up, it seems great. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
What is FlowForce Max? FlowForce Max Advanced Formula is a holistic blend designed to promote optimal prostate health
I think you have remarked some very interesting points, regards for the post.
I was just seeking this info for some time. After 6 hours of continuous Googleing, at last I got it in your site. I wonder what is the lack of Google strategy that do not rank this kind of informative sites in top of the list. Usually the top sites are full of garbage.
After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
I discovered your weblog web site on google and check a number of of your early posts. Continue to keep up the very good operate. I just additional up your RSS feed to my MSN Information Reader. Looking for forward to reading extra from you in a while!…
I do agree with all of the ideas you have presented in your post. They’re very convincing and will certainly work. Still, the posts are very short for starters. Could you please extend them a little from next time? Thanks for the post.
Thank you for another informative website. Where else could I get that kind of information written in such an ideal way? I’ve a project that I am just now working on, and I’ve been on the look out for such information.
Keep functioning ,remarkable job!
I have recently started a web site, the info you provide on this web site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
Very interesting details you have mentioned, regards for putting up.
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz respond as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know where u got this from. appreciate it
I really appreciate this post. I have been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You’ve made my day! Thank you again
WONDERFUL Post.thanks for share..more wait .. …
Lovely just what I was looking for.Thanks to the author for taking his time on this one.
Hi there, I found your website by way of Google at the same time as looking for a related topic, your website came up, it appears good. I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
There is evidently a bunch to know about this. I assume you made various good points in features also.
PBN sites
We shall create a system of private blog network sites!
Pros of our PBN network:
We carry out everything SO THAT GOOGLE does not comprehend that this A self-owned blog network!!!
1- We buy web domains from separate registrars
2- The leading site is hosted on a VPS server (Virtual Private Server is high-speed hosting)
3- The remaining sites are on different hostings
4- We attribute a distinct Google account to each site with verification in Search Console.
5- We make websites on WordPress, we don’t use plugins with assistance from which Trojans penetrate and through which pages on your websites are created.
6- We refrain from reproduce templates and utilise only individual text and pictures
We never work with website design; the client, if desired, can then edit the websites to suit his wishes
I have recently started a blog, the info you offer on this site has helped me greatly. Thanks for all of your time & work.
It is really a great and useful piece of info. I am glad that you shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Lovely blog! I am loving it!! Will come back again. I am taking your feeds also
As soon as I detected this website I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
Thank you for sharing superb informations. Your website is so cool. I am impressed by the details that you’ve on this web site. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for more articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched everywhere and just could not come across. What a perfect web-site.
I got what you intend, appreciate it for posting.Woh I am lucky to find this website through google.
Perfect piece of work you have done, this internet site is really cool with good information.
I admire your piece of work, appreciate it for all the good articles.
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this site. Thank you, I?¦ll try and check back more often. How frequently you update your website?
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
There are definitely numerous details like that to take into consideration. That could be a great level to bring up. I supply the thoughts above as general inspiration but clearly there are questions like the one you bring up the place the most important thing will be working in honest good faith. I don?t know if finest practices have emerged around things like that, however I’m sure that your job is clearly identified as a fair game. Both girls and boys feel the influence of just a second’s pleasure, for the remainder of their lives.
Understanding COSC Certification and Its Importance in Watchmaking
COSC Certification and its Stringent Standards
Controle Officiel Suisse des Chronometres, or the Controle Officiel Suisse des Chronometres, is the official Swiss testing agency that attests to the precision and accuracy of wristwatches. COSC certification is a symbol of superior craftsmanship and trustworthiness in chronometry. Not all timepiece brands follow COSC validation, such as Hublot, which instead sticks to its own demanding standards with movements like the UNICO calibre, reaching equivalent precision.
The Science of Precision Timekeeping
The central system of a mechanized watch involves the mainspring, which delivers power as it unwinds. This mechanism, however, can be prone to environmental elements that may impact its precision. COSC-certified mechanisms undergo demanding testing—over 15 days in various conditions (five positions, three temperatures)—to ensure their resilience and dependability. The tests measure:
Typical daily rate accuracy between -4 and +6 secs.
Mean variation, highest variation rates, and impacts of temperature changes.
Why COSC Certification Is Important
For watch fans and connoisseurs, a COSC-validated timepiece isn’t just a item of technology but a demonstration to lasting quality and accuracy. It represents a timepiece that:
Presents outstanding dependability and accuracy.
Ensures confidence of quality across the complete design of the watch.
Is likely to hold its value more effectively, making it a smart choice.
Well-known Chronometer Manufacturers
Several renowned brands prioritize COSC accreditation for their timepieces, including Rolex, Omega, Breitling, and Longines, among others. Longines, for instance, provides collections like the Archive and Spirit, which showcase COSC-accredited mechanisms equipped with advanced substances like silicone balance suspensions to enhance resilience and performance.
Historic Background and the Evolution of Chronometers
The notion of the chronometer dates back to the requirement for accurate chronometry for navigational at sea, emphasized by John Harrison’s work in the 18th century. Since the official establishment of COSC in 1973, the certification has become a standard for judging the accuracy of high-end timepieces, sustaining a legacy of excellence in horology.
Conclusion
Owning a COSC-validated watch is more than an aesthetic choice; it’s a commitment to excellence and precision. For those appreciating accuracy above all, the COSC certification provides peacefulness of thoughts, ensuring that each certified watch will perform reliably under various circumstances. Whether for individual contentment or as an investment, COSC-accredited watches stand out in the world of watchmaking, carrying on a legacy of meticulous timekeeping.
F*ckin¦ amazing things here. I¦m very happy to peer your post. Thank you a lot and i’m having a look ahead to contact you. Will you please drop me a e-mail?
Very interesting topic, regards for posting. “Nothing is more wretched than the mind of a man conscious of guilt.” by Titus Maccius Plautus.
Pretty! This was a really wonderful post. Thank you for your provided information.
Utterly composed subject material, Really enjoyed studying.
En Son Zamanın En Fazla Popüler Kumarhane Platformu: Casibom
Casino oyunlarını sevenlerin artık duymuş olduğu Casibom, nihai dönemde adından sıkça söz ettiren bir şans ve kumarhane sitesi haline geldi. Ülkemizdeki en başarılı bahis web sitelerinden biri olarak tanınan Casibom’un haftalık bazda cinsinden değişen giriş adresi, alanında oldukça yenilikçi olmasına rağmen itimat edilir ve kar getiren bir platform olarak tanınıyor.
Casibom, yakın rekabeti olanları geride bırakıp eski bahis sitelerinin üstünlük sağlamayı başarmayı sürdürüyor. Bu pazarda uzun soluklu olmak önemli olsa da, oyunculardan etkileşimde olmak ve onlara erişmek da aynı kadar değerli. Bu durumda, Casibom’un 7/24 servis veren gerçek zamanlı destek ekibi ile rahatlıkla iletişime geçilebilir olması önemli bir artı getiriyor.
Hızla artan oyuncuların kitlesi ile dikkat çekici Casibom’un arkasındaki başarılı faktörleri arasında, sadece ve yalnızca bahis ve canlı olarak casino oyunlarına sınırlı olmayan geniş bir servis yelpazesi bulunuyor. Spor bahislerinde sunduğu geniş seçenekler ve yüksek oranlar, oyuncuları cezbetmeyi başarmayı sürdürüyor.
Ayrıca, hem atletizm bahisleri hem de kumarhane oyunlar katılımcılara yönlendirilen sunulan yüksek yüzdeli avantajlı ödüller da ilgi çekici. Bu nedenle, Casibom hızla sektörde iyi bir tanıtım başarısı elde ediyor ve büyük bir oyuncu kitlesi kazanıyor.
Casibom’un kazandıran ödülleri ve tanınırlığı ile birlikte, platforma üyelik nasıl sağlanır sorusuna da değinmek gereklidir. Casibom’a hareketli cihazlarınızdan, bilgisayarlarınızdan veya tabletlerinizden internet tarayıcı üzerinden rahatça erişilebilir. Ayrıca, web sitesinin mobil cihazlarla uyumlu olması da büyük önem taşıyan bir fayda sağlıyor, çünkü artık pratikte herkesin bir akıllı telefonu var ve bu telefonlar üzerinden kolayca erişim sağlanabiliyor.
Hareketli tabletlerinizle bile yolda canlı bahisler alabilir ve maçları gerçek zamanlı olarak izleyebilirsiniz. Ayrıca, Casibom’un mobil uyumlu olması, memleketimizde kumarhane ve kumarhane gibi yerlerin meşru olarak kapatılmasıyla birlikte bu tür platformlara erişimin büyük bir yolunu oluşturuyor.
Casibom’un emin bir casino platformu olması da önemli bir fayda getiriyor. Lisanslı bir platform olan Casibom, duraksız bir şekilde keyif ve kazanç elde etme imkanı getirir.
Casibom’a üye olmak da oldukça basittir. Herhangi bir belge gereksinimi olmadan ve ücret ödemeden web sitesine rahatça üye olabilirsiniz. Ayrıca, web sitesi üzerinde para yatırma ve çekme işlemleri için de çok sayıda farklı yöntem vardır ve herhangi bir kesim ücreti alınmamaktadır.
Ancak, Casibom’un güncel giriş adresini takip etmek de elzemdir. Çünkü canlı iddia ve casino platformlar popüler olduğu için hileli platformlar ve dolandırıcılar da görünmektedir. Bu nedenle, Casibom’un sosyal medya hesaplarını ve güncel giriş adresini periyodik olarak kontrol etmek gereklidir.
Sonuç olarak, Casibom hem itimat edilir hem de kar getiren bir kumarhane sitesi olarak dikkat çekiyor. Yüksek promosyonları, geniş oyun seçenekleri ve kullanıcı dostu mobil uygulaması ile Casibom, kumarhane sevenler için ideal bir platform sağlar.
로드스탁과의 레버리지 방식의 스탁: 투자 전략의 새로운 영역
로드스탁에서 제공하는 레버리지 스탁은 주식 시장의 투자의 한 방법으로, 큰 이익율을 목적으로 하는 투자자들을 위해 매력적인 선택입니다. 레버리지 사용을 이용하는 이 전략은 투자자가 자신의 자금을 넘어서는 금액을 투입할 수 있도록 함으로써, 주식 시장에서 더욱 큰 힘을 행사할 수 있는 방법을 제공합니다.
레버리지 스탁의 원리
레버리지 방식의 스탁은 원칙적으로 투자금을 대여하여 운용하는 방법입니다. 예를 들어, 100만 원의 자금으로 1,000만 원 상당의 주식을 사들일 수 있는데, 이는 투자자가 일반적인 자본보다 훨씬 훨씬 더 많은 증권을 사들여, 주식 가격이 올라갈 경우 상응하는 더욱 큰 이익을 얻을 수 있게 합니다. 하지만, 증권 가격이 내려갈 경우에는 그 손해 또한 커질 수 있으므로, 레버리지를 사용할 때는 조심해야 합니다.
투자 전략과 레버리지
레버리지는 특히 성장 잠재력이 큰 사업체에 적용할 때 효과적입니다. 이러한 사업체에 큰 비율을 통해 투입하면, 잘 될 경우 막대한 수입을 얻을 수 있지만, 반대의 경우 많은 리스크도 감수하게 됩니다. 그러므로, 투자자들은 자신의 리스크 관리 능력을 가진 장터 분석을 통해 통해, 일정한 회사에 얼마만큼의 투자금을 투자할지 결정해야 합니다.
레버리지 사용의 이점과 위험 요소
레버리지 스탁은 높은 이익을 약속하지만, 그만큼 상당한 위험성 수반합니다. 주식 시장의 변동은 예측이 어렵기 때문에, 레버리지를 사용할 때는 언제나 시장 경향을 면밀히 주시하고, 손해를 최소로 줄일 수 있는 계획을 세워야 합니다.
맺음말: 세심한 고르기가 필요
로드스탁을 통해 공급하는 레버리지 스탁은 강력한 투자 도구이며, 적절히 이용하면 큰 수입을 가져다줄 수 있습니다. 그렇지만 상당한 리스크도 신경 써야 하며, 투자 결정이 충분한 데이터와 조심스러운 고려 후에 실시되어야 합니다. 투자하는 사람의 금융 상황, 위험 수용 능력, 그리고 장터 상황을 반영한 조화로운 투자 방법이 핵심입니다.
Wow, wonderful weblog structure! How lengthy have you ever been running a blog for? you make running a blog glance easy. The entire look of your site is excellent, let alone the content material!
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Your website is very useful. Thanks for sharing.
Just wanna comment that you have a very decent internet site, I like the style and design it actually stands out.
Effective Backlinks in Blogs and Comments: Increase Your SEO
Backlinks are crucial for enhancing search engine rankings and enhancing website visibility. By integrating backlinks into weblogs and comments prudently, they can significantly enhance targeted traffic and SEO performance.
Adhering to Search Engine Algorithms
Today’s backlink placement tactics are finely tuned to align with search engine algorithms, which now prioritize website link high quality and relevance. This guarantees that links are not just abundant but meaningful, directing end users to helpful and pertinent content material. Website owners should focus on incorporating backlinks that are contextually suitable and enhance the general articles good quality.
Advantages of Utilizing Fresh Donor Bases
Utilizing current donor bases for backlinks, like those maintained by Alex, offers substantial advantages. These bases are regularly refreshed and consist of unmoderated sites that don’t pull in complaints, guaranteeing the hyperlinks positioned are both powerful and agreeable. This approach will help in maintaining the efficacy of hyperlinks without the risks associated with moderated or problematic resources.
Only Authorized Resources
All donor sites used are sanctioned, keeping away from legal pitfalls and conforming to digital marketing requirements. This determination to utilizing only sanctioned resources assures that each backlink is legitimate and trustworthy, thereby building trustworthiness and reliability in your digital presence.
SEO Impact
Expertly put backlinks in blogs and remarks provide over just SEO rewards—they improve user experience by linking to appropriate and high-quality content. This technique not only satisfies search engine criteria but also entails consumers, leading to far better visitors and improved online engagement.
In essence, the right backlink technique, specifically one that employs fresh and dependable donor bases like Alex’s, can alter your SEO efforts. By focusing on quality over amount and adhering to the most recent criteria, you can ensure your backlinks are both powerful and efficient.
Wonderful work! This is the type of information that should be shared around the internet. Shame on the search engines for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my site . Thanks =)
Woh I like your blog posts, saved to bookmarks! .
Kantorbola situs slot online terbaik 2024 , segera daftar di situs kantor bola dan dapatkan promo terbaik bonus deposit harian 100 ribu , bonus rollingan 1% dan bonus cashback mingguan . Kunjungi juga link alternatif kami di kantorbola77 , kantorbola88 dan kantorbola99
Проверка данных бумажников за выявление наличия нелегальных денег: Охрана личного криптовалютного портфеля
В мире криптовалют становится все важнее необходимее соблюдать безопасность собственных финансов. Постоянно обманщики и криминальные элементы разрабатывают новые способы обмана и мошенничества и угонов виртуальных средств. Один из ключевых способов обеспечения безопасности становится анализ кошелька за выявление наличия нелегальных средств передвижения.
Почему так важно и проверять личные криптовалютные кошельки для хранения электронных денег?
Прежде всего, вот это обстоятельство необходимо для обеспечения безопасности своих финансовых средств. Множество участники рынка находятся в зоне риска потери денег своих собственных денег вследствие несправедливых подходов или угонов. Проверка данных кошелька способствует предотвращению обнаружить в нужный момент сомнительные манипуляции и предотвратить.
Что предлагает вашему вниманию наша фирма?
Мы оказываем послугу проверки данных цифровых кошельков для хранения электронных денег и переводов средств с намерением идентификации происхождения финансовых средств и дать детального отчета о результатах. Наши платформа проанализировать данные пользователя для обнаружения незаконных манипуляций и оценить риск для личного финансового портфеля. Благодаря нашей системе проверки, вы будете способны предотвратить возможные с государственными органами и обезопасить себя от непреднамеренного участия в незаконных операций.
Как происходит процесс?
Наша фирма-разработчик работает с ведущими аудиторскими фирмами структурами, как например Cure53, для того, чтобы обеспечить и точность наших проверок данных. Мы внедряем современные технологии и техники анализа данных для выявления наличия потенциально опасных манипуляций. Данные пользователей наших заказчиков обрабатываются и хранятся в специальной базе данных согласно высокими стандартами безопасности и конфиденциальности.
Ключевой запрос: “проверить свои USDT на чистоту”
В случае если вы хотите проверить надежности ваших USDT-кошельков, наша компания предоставляет возможность провести бесплатный анализ первых пяти кошельков. Просто введите свой кошелек в указанное место на нашем онлайн-ресурсе, и мы вышлем вам подробную информацию о статусе вашего кошелька.
Обеспечьте безопасность своих активы уже сегодня!
Не рискуйте становиться жертвой мошенников злоумышленников или стать неприятном положении незаконных сделок с ваших средствами. Дайте вашу криптовалюту специалистам, которые окажут поддержку, вам и вашим финансам обезопасить криптовалютные средства и предотвратить возможные проблемы. Примите первый шаг к обеспечению безопасности защите личного цифрового портфеля сразу же!
Осмотр Tether для прозрачность: Как защитить свои криптовалютные средства
Каждый день все больше индивидуумов заботятся к секурити их электронных средств. Постоянно дельцы предлагают новые схемы кражи электронных средств, и также держатели криптовалюты становятся страдающими их афер. Один из способов обеспечения безопасности становится проверка кошельков в наличие противозаконных средств.
С каким намерением это потребуется?
Преимущественно, чтобы защитить личные активы от шарлатанов и также украденных денег. Многие участники встречаются с вероятностью утраты их финансов в результате мошеннических сценариев или хищений. Проверка кошельков помогает определить подозрительные транзакции и предотвратить возможные убытки.
Что наша команда предоставляем?
Мы предлагаем сервис анализа криптовалютных бумажников и операций для определения начала фондов. Наша платформа исследует информацию для выявления противозаконных действий и также оценки угрозы для вашего счета. Благодаря этой проверке, вы сможете избегнуть проблем с регуляторами и защитить себя от участия в противозаконных переводах.
Каким образом это работает?
Мы сотрудничаем с ведущими проверочными компаниями, такими как Certik, для того чтобы предоставить аккуратность наших тестирований. Мы применяем передовые технологии для определения потенциально опасных операций. Ваши данные проходят обработку и сохраняются в соответствии с высокими нормами безопасности и приватности.
Каким образом проверить личные USDT в прозрачность?
Если хотите проверить, что ваши USDT-кошельки нетронуты, наш подход предоставляет бесплатную проверку первых пяти бумажников. Легко введите положение вашего бумажника на на нашем веб-сайте, и наш сервис предоставим вам детальный доклад об его статусе.
Защитите свои фонды уже сейчас!
Не подвергайте опасности подвергнуться дельцов или попасть в неблагоприятную обстановку из-за незаконных операций. Свяжитесь с нашей команде, чтобы предохранить ваши электронные активы и предотвратить затруднений. Совершите первый шаг к безопасности криптовалютного портфеля уже сегодня!
Осмотр Тетер на прозрачность: Каковым способом защитить свои цифровые состояния
Все больше людей обращают внимание для безопасность их криптовалютных активов. День ото дня дельцы разрабатывают новые способы разграбления электронных денег, а также владельцы криптовалюты являются пострадавшими их обманов. Один из техник защиты становится проверка кошельков в наличие нелегальных финансов.
С каким намерением это потребуется?
Прежде всего, с тем чтобы обезопасить свои активы против дельцов или украденных денег. Многие специалисты сталкиваются с риском потери своих активов из-за мошеннических сценариев либо хищений. Тестирование кошельков позволяет выявить непрозрачные операции а также предотвратить возможные потери.
Что наша команда предоставляем?
Мы предоставляем сервис тестирования криптовалютных бумажников и операций для обнаружения начала фондов. Наша система анализирует информацию для выявления противозаконных операций и также оценки угрозы вашего портфеля. Из-за этой проверке, вы сможете избежать недочетов с регуляторами а также защитить себя от участия в незаконных операциях.
Как происходит процесс?
Мы работаем с первоклассными аудиторскими агентствами, наподобие Kudelsky Security, с целью обеспечить точность наших тестирований. Мы применяем новейшие техники для определения опасных операций. Ваши информация обрабатываются и хранятся согласно с высокими нормами безопасности и конфиденциальности.
Как проверить личные USDT на чистоту?
В случае если вы желаете проверить, что ваши USDT-кошельки чисты, наш сервис обеспечивает бесплатное тестирование первых пяти кошельков. Легко передайте адрес вашего кошелька на нашем сайте, и мы предоставим вам полную информацию доклад о его статусе.
Защитите ваши активы уже сегодня!
Не рискуйте стать жертвой обманщиков или оказаться в неприятную ситуацию вследствие нелегальных операций. Обратитесь к нашему агентству, для того чтобы сохранить свои криптовалютные финансовые ресурсы и избежать проблем. Предпримите первый шаг к сохранности вашего криптовалютного портфеля уже сейчас!
грязный usdt
Проверка Tether в нетронутость: Как обезопасить свои электронные средства
Каждый день все больше граждан заботятся на безопасность своих криптовалютных активов. Постоянно обманщики придумывают новые способы кражи цифровых денег, и держатели цифровой валюты являются жертвами своих афер. Один из техник защиты становится проверка кошельков для присутствие незаконных денег.
Для чего это потребуется?
Преимущественно, для того чтобы защитить собственные финансы от обманщиков и похищенных монет. Многие вкладчики встречаются с риском потери своих финансов из-за мошеннических механизмов или кражей. Анализ кошельков помогает выявить подозрительные транзакции а также предотвратить возможные убытки.
Что мы предлагаем?
Мы предлагаем услугу анализа цифровых бумажников или операций для выявления источника средств. Наша технология проверяет информацию для обнаружения незаконных транзакций или оценки опасности вашего портфеля. Из-за этой проверке, вы сможете избежать проблем с регуляторами или обезопасить себя от участия в противозаконных операциях.
Как это действует?
Наша фирма сотрудничаем с ведущими аудиторскими фирмами, наподобие Cure53, для того чтобы гарантировать аккуратность наших проверок. Мы применяем передовые технологии для обнаружения потенциально опасных транзакций. Ваши информация обрабатываются и хранятся согласно с высокими стандартами безопасности и конфиденциальности.
Как проверить свои Tether на прозрачность?
В случае если вы желаете проверить, что ваша USDT-кошельки нетронуты, наш сервис обеспечивает бесплатное тестирование первых пяти кошельков. Просто вбейте адрес собственного бумажника на на нашем веб-сайте, и наш сервис предоставим вам полную информацию отчет об его статусе.
Защитите вашими фонды прямо сейчас!
Не рискуйте подвергнуться шарлатанов или попадать в неприятную ситуацию по причине незаконных операций. Обратитесь за помощью к нам, чтобы обезопасить ваши криптовалютные средства и избежать сложностей. Примите первый шаг к сохранности вашего криптовалютного портфеля прямо сейчас!
Situs kantor bola merupakan penyedia permainan slot online gacor dengan RTP 98% , mainkan game slot online mudah menang di situs kantorbola . tersedia fitur deposit kilat menggunakan QRIS Kantorbola .
Как убедиться в чистоте USDT
Анализ бумажников за присутствие нелегальных финансовых средств: Защита вашего электронного финансового портфеля
В мире цифровых валют становится все важнее все более необходимо гарантировать секретность личных финансовых активов. Постоянно жулики и киберпреступники создают совершенно новые схемы мошенничества и воровства электронных финансов. Одним из важных инструментов защиты является проверка кошелька по выявление наличия неправомерных средств передвижения.
Почему вот важно проверить личные электронные кошельки?
В первую очередь, вот данный факт необходимо для защиты своих финансов. Большинство инвесторы сталкиваются с риском утраты своих собственных финансов из-за недоброжелательных планов или угонов. Проверка кошелька способствует обнаружить в нужный момент подозрительные действия и предотвратить возможные.
Что предлагает вашему вниманию наша фирма?
Мы оказываем послугу проверки данных цифровых кошельков для хранения криптовалюты и транзакций с целью обнаружения источника средств и выдачи детального доклада. Компания предлагает технология проверяет данные пользователя для обнаружения подозрительных манипуляций и оценить риск для вашего портфеля. Благодаря нашей системе проверки, вы сможете предотвратить с регуляторными органами и защитить от непреднамеренного участия в нелегальных операций.
Как осуществляется процесс?
Наши компания работает с ведущими аудиторскими организациями организациями, вроде Kudelsky Security, для того чтобы дать гарантию и адекватность наших проверок кошельков. Мы используем новейшие и подходы анализа данных для выявления небезопасных действий. Персональные данные наших пользователей обрабатываются и хранятся в соответствии с высокими стандартами безопасности.
Основной запрос: “проверить свои USDT на чистоту”
В случае если вы хотите проверить безопасности ваших USDT-кошельков, наша компания оказывает шанс бесплатной проверки первых 5 кошельков. Достаточно просто адрес своего кошелька в соответствующее окно на нашем сайте проверки, и мы предоставим вам подробную информацию о статусе вашего кошелька.
Обезопасьте свои активы уже сегодня!
Избегайте риска оказаться жертвой мошенников или оказаться неприятной ситуации незаконных действий с вашими собственными деньгами. Дайте вашу криптовалюту профессиональным консультантам, которые помогут, вам и вашим финансам защититься криптовалютные активы и предотвратить возможные проблемы. Совершите первый шаг к обеспечению безопасности к безопасности личного цифрового портфеля прямо сейчас!
usdt не чистое
Тестирование Tether в чистоту: Каким образом защитить собственные цифровые активы
Каждый день все больше индивидуумов заботятся для надежность их криптовалютных активов. Постоянно дельцы изобретают новые схемы кражи цифровых денег, а также владельцы криптовалюты являются жертвами их интриг. Один способов сбережения становится проверка бумажников на присутствие нелегальных денег.
Зачем это полезно?
В первую очередь, для того чтобы защитить свои финансы от шарлатанов и также похищенных монет. Многие вкладчики встречаются с вероятностью утраты личных фондов из-за мошеннических сценариев либо краж. Осмотр кошельков способствует выявить подозрительные действия и также предотвратить возможные потери.
Что наша команда предлагаем?
Наша компания предоставляем услугу тестирования криптовалютных кошельков или операций для обнаружения источника средств. Наша система анализирует информацию для обнаружения нелегальных операций или оценки риска для вашего счета. Вследствие этой проверке, вы сможете избежать проблем с регуляторами и также обезопасить себя от участия в незаконных переводах.
Каким образом это работает?
Мы работаем с лучшими аудиторскими агентствами, например Cure53, для того чтобы обеспечить точность наших проверок. Мы применяем передовые технологии для выявления опасных операций. Ваши информация обрабатываются и хранятся в соответствии с высокими нормами безопасности и конфиденциальности.
Как проверить свои Tether для чистоту?
Если вам нужно подтвердить, что ваши USDT-кошельки чисты, наш сервис предоставляет бесплатную проверку первых пяти кошельков. Просто вбейте адрес собственного кошелька в нашем сайте, а также наш сервис предоставим вам подробный отчет о его положении.
Гарантируйте безопасность для вашими активы уже сейчас!
Не подвергайте риску стать жертвой шарлатанов или оказаться в неприятную ситуацию по причине незаконных сделок. Обратитесь за помощью к нам, чтобы сохранить ваши криптовалютные активы и предотвратить затруднений. Примите первый шаг для безопасности криптовалютного портфеля уже сейчас!
Тетер – является устойчивая цифровая валюта, связанная к валюте страны, подобно американский доллар. Это делает данную криптовалюту особенно известной у трейдеров, так как данный актив предлагает стабильность курса в в условиях волатильности криптовалютного рынка. Однако, как и другая вид криптовалюты, USDT изложена опасности использования с целью легализации доходов и поддержки неправомерных сделок.
Промывка средств через криптовалюты превращается все более и более распространенным в большей степени путем с целью скрытия происхождения средств. Воспользовавшись различные приемы, дельцы могут стараться легализовывать незаконно завоеванные деньги через обменники криптовалют или миксеры средств, для того чтобы сделать их происхождение менее прозрачным.
Именно для этой цели, анализ USDT на чистоту становится значимой мерой предосторожности для того чтобы владельцев криптовалют. Доступны для использования специализированные платформы, которые проводят проверку сделок и счетов, для того чтобы определить подозрительные транзакции и нелегальные источники средств. Данные услуги способствуют участникам избежать непреднамеренной участи в преступной деятельности и предотвратить блокировку аккаунтов со со стороны надзорных органов.
Проверка USDT на чистоту также как и помогает защитить себя от финансовых потерь. Владельцы могут быть убеждены что их активы не ассоциированы с нелегальными сделками, что снижает риск блокировки аккаунта или перечисления денег.
Поэтому, в условиях возрастающей сложности криптовалютной среды важно принимать действия для обеспечения надежности своих финансовых ресурсов. Экспертиза USDT на чистоту с использованием специальных платформ становится одним из способов предотвращения отмывания денег, предоставляя владельцам криптовалют дополнительный уровень и безопасности.
Проверка USDT на чистоту
Анализ Тетер для чистоту: Каким образом обезопасить свои цифровые состояния
Каждый день все больше пользователей заботятся в секурити личных цифровых активов. День ото дня обманщики предлагают новые способы кражи криптовалютных средств, или держатели цифровой валюты становятся страдающими их обманов. Один из подходов защиты становится проверка кошельков в наличие незаконных денег.
Зачем это важно?
Преимущественно, для того чтобы защитить собственные финансы от мошенников а также украденных денег. Многие вкладчики сталкиваются с риском потери их финансов по причине мошеннических схем или краж. Анализ бумажников помогает выявить подозрительные действия а также предотвратить возможные потери.
Что наша команда предоставляем?
Мы предлагаем услугу тестирования криптовалютных бумажников и операций для выявления начала денег. Наша платформа анализирует данные для обнаружения нелегальных операций и также оценки опасности для вашего счета. Вследствие этой проверке, вы сможете избегать проблем с регулированием и также предохранить себя от участия в нелегальных операциях.
Как это действует?
Мы работаем с первоклассными аудиторскими агентствами, такими как Cure53, для того чтобы предоставить точность наших проверок. Мы используем новейшие технологии для выявления опасных операций. Ваши информация обрабатываются и сохраняются в соответствии с высокими нормами безопасности и конфиденциальности.
Как проверить свои Tether в нетронутость?
При наличии желания убедиться, что ваши USDT-кошельки чисты, наш сервис предоставляет бесплатную проверку первых пяти кошельков. Просто вбейте местоположение личного кошелька в на нашем веб-сайте, и также наш сервис предоставим вам детальный доклад о его положении.
Защитите вашими активы уже сейчас!
Не рискуйте подвергнуться дельцов либо попадать в неблагоприятную обстановку из-за противозаконных транзакций. Свяжитесь с нашему сервису, чтобы предохранить ваши криптовалютные финансовые ресурсы и избежать сложностей. Сделайте первый шаг к безопасности вашего криптовалютного портфеля уже сейчас!
бормашини
такери за пирони
акумулаторни резачки
изработване на сайтове
cá cược thể thao
https://rg777.app/cup-c1-202324/
הימורים מקוונים הם חוויה מרגש ופופולרי ביותר בעידן המקוון, שמביאה מיליוני אנשים מכל
רחבי העולם. ההימורים המקוונים מתרחשים על אירועים ספורטיים, תוצאות פוליטיות ואפילו תוצאות מזג האוויר ונושאים נוספים. אתרי ה הימורים הווירטואליים מזמינים את מי שמעוניין להמר על תוצאות מתאימות וליהנות חוויות ייחודיות ומרתקות.
ההימורים המקוונים הם כבר חלק מהותי מתרבות האנושית לא מעט זמן והיום הם לא רק רק חלק נפרד מהפעילות הכלכלית והתרבותית, אלא כמו כן מספקים תשואות וחוויות מרתקות. משום שהם נגישים מאוד ונוחים לשימוש, הם מובילים את כולם ליהנות מהמשחק ולהנציח רגעי עסקה וניצחון בכל זמן ובכל מקום.
טכנולוגיות דיגיטליות והימורים הפכו להיות הפופולריים ביותר מעניינת ופופולרית. מיליוני אנשים מכל כל רחבי העולם משתתפים בהימורים, כוללים סוגים שונים של הימורים. הימורים מקוונים מציעים למשתתפים חוויה ייחודית ומרתקת, שמתאימה לכל גיל וכישור בכל זמן ובכל מקום.
אז מה נותר אתה מחכה למה? אל תהסס והצטרף עכשיו והתחיל לחוות את ההתרגשות וההנאה מהמשחקים ברשת.
שרף כיוונים: המדריכים המלא לסחר פרחי קנאביס באמצעות הטלגרמה
טלגראס הוראות היא פורטל ידע ומשלחי לסחר ב פרחי קנאביס במקום האפליקציה הניידת הנפוצה המשלוח.
האתר מספק את כלל המידע הקישורות והמסמכים העדכוני לקבוצות העוקבות וערוצים המומלצים מומלצות לקריאה לרכישת קנאביס בטלגרם בארץ ישראל.
כמו כן, האתר הרשמי מציעה מדריכים מפורטת לאיך להתארגן באמצעות בטלגראס ולרכוש קנאביס בקלות הזמנה ובמהירות רבה.
בעזרת ההוראות, גם כן המשתמשים משתמשים בטלגרם יוכלו להירשם לעולם השרף בהטלגרמה בצורה מוגנת ומאובטחת.
ההאוטומטיזציה של הפרח מאפשר למשתמשי הערוץ לבצע פעולות שונות ומגוונות כמו השקת פרחי קנאביס, קבלה תמיכה, בדיקת הקיימות והוספת ביקורות על פריטים. כל זאת בצורה נוחה לשימוש ופשוטה דרך האפליקציה.
כאשר כשם הדבר בשיטות תשלום, הקנאביס משתמשת בשיטות ה מוכרות כגון כסף מזומן, כרטיסים של אשראי וקריפטוֹמוֹנֵדָה. חשוב ללציין כי ישנה לבדוק ולוודא את ההוראות והחוקים המקומיים בארץ שלך ללפני ביצוע רכישה.
טלגרם מציע הטבות מרכזיים כגון פרטיות ובטיחות מוגברים, תקשורת מהירה וגמישות גבוהה. בנוסף, הוא מאפשר גישה להקהל גלובלית רחבה ומציע מגוון של תכונות ויכולות.
בסיכום, הטלגרמה הנחיות היה המקום האידיאלי ללמצוא את כל המידע והקישורים לסחר ב פרחי קנאביס בפני מהירה מאוד, בבטוחה ונוחה מאוד דרך הטלגרמה.
digital auto insurance claims in nigeria
Africa’s Best Embedded Insurance Infrastructure. Get Octamile’s embedded Insurance and claims automation SaaS. Boost sales and reduce costs with the best digital Insurance solutions for leading Insurers, B2C and app businesses in Africa. Get a quote today.
Backlink pyramid
Sure, here’s the text with spin syntax applied:
Backlink Pyramid
After numerous updates to the G search mechanism, it is required to utilize different methods for ranking.
Today there is a approach to attract the focus of search engines to your site with the support of incoming links.
Links are not only an effective promotional instrument but they also have organic traffic, straight sales from these sources perhaps will not be, but transitions will be, and it is advantageous visitors that we also receive.
What in the end we get at the final outcome:
We show search engines site through backlinks.
Prluuchayut natural click-throughs to the site and it is also a signal to search engines that the resource is used by users.
How we show search engines that the site is profitable:
Backlinks do to the principal page where the main information.
We make backlinks through redirections reliable sites.
The most CRUCIAL we place the site on sites analyzers distinct tool, the site goes into the memory of these analyzers, then the acquired links we place as redirects on blogs, forums, comment sections. This essential action shows search engines the MAP OF THE SITE as analysis tool sites present all information about sites with all keywords and headings and it is very POSITIVE.
All data about our services is on the website!
Creating exclusive articles on Medium and Telegraph, why it is required:
Created article on these resources is better ranked on low-frequency queries, which is very important to get natural traffic.
We get:
natural traffic from search engines.
natural traffic from the internal rendition of the medium.
The platform to which the article refers gets a link that is profitable and increases the ranking of the webpage to which the article refers.
Articles can be made in any amount and choose all low-frequency queries on your topic.
Medium pages are indexed by search engines very well.
Telegraph pages need to be indexed separately indexer and at the same time after indexing they sometimes occupy spots higher in the search algorithms than the medium, these two platforms are very beneficial for getting traffic.
Here is a hyperlink to our services where we provide creation, indexing of sites, articles, pages and more.
Great V I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs and related information ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, web site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Nice task..
link building
Backlink creation is just just as efficient currently, just the instruments to operate in this area have got shifted.
You can find several choices regarding backlinks, our team utilize a few of them, and these approaches operate and are actually examined by our team and our customers.
Not long ago we conducted an trial and it transpired that low-volume searches from one website ranking nicely in online searches, and the result doesnt require being your website, you can use social networking sites from web2.0 collection for this.
It additionally it is possible to partially transfer mass through web page redirects, offering an assorted link profile.
Go to our web page where our company’s offerings are actually provided with detailed explanations.
Thank you for the sensible critique. Me and my neighbor were just preparing to do some research about this. We got a grab a book from our local library but I think I learned more clear from this post. I am very glad to see such fantastic info being shared freely out there.
Creating hyperlinks is just equally effective at present, just the tools for working in this area have got changed.
There are many possibilities regarding backlinks, our team utilize some of them, and these methods operate and are actually tested by our team and our clientele.
Not long ago our company conducted an experiment and it turned out that low-volume searches from one domain name ranking effectively in search results, and the result doesnt require being your own website, it is possible to make use of social media from the web 2.0 collection for this.
It additionally it is possible to partly shift mass through website redirects, providing a diverse backlink profile.
Visit to our website where our services are actually provided with comprehensive overview.
как разорвать контракт сво контрактнику
С началом СВО уже спустя полгода была объявлена первая волна мобилизации. При этом прошлая, в последний раз в России была аж в 1941 году, с началом Великой Отечественной Войны. Конечно же, желающих отправиться на фронт было не много, а потому люди стали искать способы не попасть на СВО, для чего стали покупать справки о болезнях, с которыми можно получить категорию Д. И все это стало возможным с даркнет сайтами, где можно найти практически все что угодно. Именно об этой отрасли темного интернета подробней и поговорим в этой статье.
反向連結金字塔
G搜尋引擎在多次更新後需要使用不同的排名參數。
今天有一種方法可以使用反向連結吸引G搜尋引擎對您的網站的注意。
反向連接不僅是有效的推廣工具,也是有機流量。
我們會得到什麼結果:
我們透過反向連接向G搜尋引擎展示我們的網站。
他們收到了到該網站的自然過渡,這也是向G搜尋引擎發出的信號,表明該資源正在被人們使用。
我們如何向G搜尋引擎表明該網站具有流動性:
個帶有主要訊息的主頁反向鏈接
我們透過來自受信任網站的重新导向來建立反向連接。
此外,我們將網站放置在独立的網路分析器上,網站最終會進入這些分析器的缓存中,然後我們使用產生的連結作為部落格、論壇和評論的重新导向。 這個重要的操作向G搜尋引擎顯示了網站地圖,因為網站分析器顯示了有關網站的所有資訊以及所有關鍵字和標題,這很棒
有關我們服務的所有資訊都在網站上!
Pirámide de backlinks
Aquí está el texto con la estructura de spintax que propone diferentes sinónimos para cada palabra:
“Pirámide de enlaces de retorno
Después de varias actualizaciones del motor de búsqueda G, necesita aplicar diferentes opciones de clasificación.
Hay una manera de llamar la atención de los motores de búsqueda a su sitio web con backlinks.
Los enlaces de retorno no sólo son una herramienta eficaz para la promoción, sino que también tienen tráfico orgánico, las ventas directas de estos recursos más probable es que no será, pero las transiciones será, y es tráfico potencial que también obtenemos.
Lo que vamos a obtener al final en la salida:
Mostramos el sitio a los motores de búsqueda a través de backlinks.
Conseguimos visitas orgánicas hacia el sitio, lo que también es una señal para los buscadores de que el recurso está siendo utilizado por la gente.
Cómo mostramos los motores de búsqueda que el sitio es líquido:
1 enlace se hace a la página principal donde está la información principal
Hacemos enlaces de retroceso a través de redirecciones de sitios de confianza
Lo más vital colocamos el sitio en una herramienta independiente de analizadores de sitios, el sitio entra en la caché de estos analizadores, luego los enlaces recibidos los colocamos como redirecciones en blogs, foros, comentarios.
Esta crucial acción muestra a los buscadores el MAPA DEL SITIO, ya que los analizadores de sitios muestran toda la información de los sitios con todas las palabras clave y títulos y es muy BUENO.
¡Toda la información sobre nuestros servicios en el sitio web!
Just wanna remark that you have a very nice web site, I like the design and style it actually stands out.
I’m impressed, I need to say. Actually hardly ever do I encounter a weblog that’s each educative and entertaining, and let me tell you, you may have hit the nail on the head. Your thought is excellent; the issue is something that not enough individuals are speaking intelligently about. I’m very completely satisfied that I stumbled throughout this in my search for one thing referring to this.
взлом кошелька
Как охранять свои данные: остерегайтесь утечек информации в интернете. Сегодня сохранение информации становится всё более важной задачей. Одним из наиболее обычных способов утечки личной информации является слив «сит фраз» в интернете. Что такое сит фразы и как предохранить себя от их утечки? Что такое «сит фразы»? «Сит фразы» — это сочетания слов или фраз, которые бывают используются для входа к различным онлайн-аккаунтам. Эти фразы могут включать в себя имя пользователя, пароль или разные конфиденциальные данные. Киберпреступники могут пытаться получить доступ к вашим аккаунтам, при помощи этих сит фраз. Как охранить свои личные данные? Используйте сложные пароли. Избегайте использования очевидных паролей, которые легко угадать. Лучше всего использовать комбинацию букв, цифр и символов. Используйте уникальные пароли для всего аккаунта. Не воспользуйтесь один и тот же пароль для разных сервисов. Используйте двухфакторную проверку (2FA). Это привносит дополнительный уровень безопасности, требуя подтверждение входа на ваш аккаунт через другое устройство или метод. Будьте осторожны с онлайн-сервисами. Не доверяйте персональную информацию ненадежным сайтам и сервисам. Обновляйте программное обеспечение. Установите обновления для вашего операционной системы и программ, чтобы предохранить свои данные от вредоносного ПО. Вывод Слив сит фраз в интернете может привести к серьезным последствиям, таким как кража личной информации и финансовых потерь. Чтобы охранить себя, следует принимать меры предосторожности и использовать надежные методы для хранения и управления своими личными данными в сети
взлом кошелька
Даркнет и сливы в Телеграме
Даркнет – это сегмент интернета, которая не индексируется регулярными поисковыми системами и требует индивидуальных программных средств для доступа. В даркнете существует изобилие скрытых сайтов, где можно найти различные товары и услуги, в том числе и нелегальные.
Одним из востребованных способов распространения информации в даркнете является использование мессенджера Телеграм. Телеграм предоставляет возможность создания закрытых каналов и чатов, где пользователи могут обмениваться информацией, в том числе и нелегальной.
Сливы информации в Телеграме – это процедура распространения конфиденциальной информации, такой как украденные данные, базы данных, персональные сведения и другие материалы. Эти сливы могут включать в себя информацию о кредитных картах, паролях, персональных сообщениях и даже фотографиях.
Сливы в Телеграме могут быть опасными, так как они могут привести к утечке конфиденциальной информации и нанести ущерб репутации и финансовым интересам людей. Поэтому важно быть осторожным при обмене информацией в интернете и не доверять сомнительным источникам.
Вот кошельки с балансом у бота
Криптокошельки с балансом: зачем их покупают и как использовать
В мире криптовалют все возрастающую популярность приобретают криптокошельки с предустановленным балансом. Это особые кошельки, которые уже содержат определенное количество криптовалюты на момент покупки. Но зачем люди приобретают такие кошельки, и как правильно использовать их?
Почему покупают криптокошельки с балансом?
Удобство: Криптокошельки с предустановленным балансом предлагаются как готовое к использованию решение для тех, кто хочет быстро начать пользоваться криптовалютой без необходимости покупки или обмена на бирже.
Подарок или награда: Иногда криптокошельки с балансом используются как подарок или поощрение в рамках акций или маркетинговых кампаний.
Анонимность: При покупке криптокошелька с балансом нет обязательства предоставлять личные данные, что может быть важно для тех, кто ценит анонимность.
Как использовать криптокошелек с балансом?
Проверьте безопасность: Убедитесь, что кошелек безопасен и не подвержен взлому. Проверьте репутацию продавца и источник приобретения кошелька.
Переведите средства на другой кошелек: Если вы хотите долгосрочно хранить криптовалюту, рекомендуется перевести средства на более безопасный или удобный для вас кошелек.
Не храните все средства на одном кошельке: Для обеспечения безопасности рекомендуется распределить средства между несколькими кошельками.
Будьте осторожны с фишингом и мошенничеством: Помните, что мошенники могут пытаться обмануть вас, предлагая криптокошельки с балансом с целью получения доступа к вашим средствам.
Заключение
Криптокошельки с балансом могут быть удобным и легким способом начать пользоваться криптовалютой, но необходимо помнить о безопасности и осторожности при их использовании.Выбор и приобретение криптокошелька с балансом – это значительный шаг, который требует внимания к деталям и осознанного подхода.”
слив сид фраз
Слив сид фраз (seed phrases) является единственным из наиболее популярных способов утечки персональной информации в мире криптовалют. В этой статье мы разберем, что такое сид фразы, зачем они важны и как можно защититься от их утечки.
Что такое сид фразы?
Сид фразы, или мнемонические фразы, представляют собой комбинацию слов, которая используется для создания или восстановления кошелька криптовалюты. Обычно сид фраза состоит из 12 или 24 слов, которые являются собой ключ к вашему кошельку. Потеря или утечка сид фразы может приводить к потере доступа к вашим криптовалютным средствам.
Почему важно защищать сид фразы?
Сид фразы являются ключевым элементом для безопасного хранения криптовалюты. Если злоумышленники получат доступ к вашей сид фразе, они сумеют получить доступ к вашему кошельку и украсть все средства.
Как защититься от утечки сид фраз?
Никогда не передавайте свою сид фразу ничьему, даже если вам происходит, что это привилегированное лицо или сервис.
Храните свою сид фразу в безопасном и секурном месте. Рекомендуется использовать аппаратные кошельки или специальные программы для хранения сид фразы.
Используйте дополнительные методы защиты, такие как двусторонняя аутентификация, для усиления безопасности вашего кошелька.
Регулярно делайте резервные копии своей сид фразы и храните их в других безопасных местах.
Заключение
Слив сид фраз является серьезной угрозой для безопасности владельцев криптовалют. Понимание важности защиты сид фразы и принятие соответствующих мер безопасности помогут вам избежать потери ваших криптовалютных средств. Будьте бдительны и обеспечивайте надежную защиту своей сид фразы
Сид-фразы, или напоминающие фразы, представляют собой комбинацию слов, которая используется для составления или восстановления кошелька криптовалюты. Эти фразы обеспечивают вход к вашим криптовалютным средствам, поэтому их надежное хранение и использование очень важны для защиты вашего криптоимущества от утери и кражи.
Что такое сид-фразы кошельков криптовалют?
Сид-фразы представляют собой набор произвольно сгенерированных слов, часто от 12 до 24, которые служат для создания уникального ключа шифрования кошелька. Этот ключ используется для восстановления возможности доступа к вашему кошельку в случае его повреждения или утери. Сид-фразы обладают большой защиты и шифруются, что делает их секурными для хранения и передачи.
Зачем нужны сид-фразы?
Сид-фразы обязательны для обеспечения безопасности и доступности вашего криптоимущества. Они позволяют восстановить возможность доступа к кошельку в случае утери или повреждения физического устройства, на котором он хранится. Благодаря сид-фразам вы можете быстро создавать резервные копии своего кошелька и хранить их в безопасном месте.
Как обеспечить безопасность сид-фраз кошельков?
Никогда не передавайте сид-фразой ни с кем. Сид-фраза является вашим ключом к кошельку, и ее раскрытие может привести к утере вашего криптоимущества.
Храните сид-фразу в защищенном месте. Используйте физически безопасные места, такие как банковские ячейки или специализированные аппаратные кошельки, для хранения вашей сид-фразы.
Создавайте резервные копии сид-фразы. Регулярно создавайте резервные копии вашей сид-фразы и храните их в разных безопасных местах, чтобы обеспечить возможность доступа к вашему кошельку в случае утери или повреждения.
Используйте дополнительные меры безопасности. Включите двухфакторную верификацию и другие методы защиты для своего кошелька криптовалюты, чтобы обеспечить дополнительный уровень безопасности.
Заключение
Сид-фразы кошельков криптовалют являются ключевым элементом надежного хранения криптоимущества. Следуйте рекомендациям по безопасности, чтобы защитить свою сид-фразу и обеспечить безопасность своих криптовалютных средств.
Столбец бэклинков
После того, как множества обновлений поисковой системы G необходимо использовать разнообразные варианты сортировки.
Сегодня есть способ привлечь внимание поисковых систем к вашему сайту с помощью обратных ссылок.
Обратные линки представляют собой эффективный инструмент продвижения, но и обладают органическим трафиком, хотя прямых продаж с этих ресурсов скорее всего не будет, но переходы будут, и именно органического трафика мы также достигаем.
Что в итоге получим на выходе:
Мы показываем сайт поисковым системам через обратные ссылки.
Получают естественные переходы на сайт, а это также подтверждение поисковым системам, что ресурс активно посещается пользователями.
Как мы демонстрируем поисковым системам, что сайт ликвиден:
1 обратная ссылка делается на главную страницу, где основная информация.
Делаем обратные ссылки через редиректы трастовых сайтов.
Главное – мы добавляем сайт в специализированные инструменты для анализа сайтов, где он кэшируется, а затем полученные ссылки размещаются в виде редиректов на блогах, форумах, в комментариях.
Это нужное действие показывает поисковым системамКАРТУ САЙТА, так как анализаторы сайтов отображают всю информацию о сайтах со всеми ключевыми словами и заголовками и это очень ХОРОШО
I dugg some of you post as I cogitated they were extremely helpful extremely helpful
ggg
هنا النص مع استخدام السبينتاكس:
“بناء الروابط الخلفية
بعد التحديثات العديدة لمحرك البحث G، تحتاج إلى تنفيذ خيارات ترتيب مختلفة.
هناك أسلوب لجذب انتباه محركات البحث إلى موقعك على الويب باستخدام الروابط الخلفية.
الروابط الخلفية غير فقط أداة فعالة للترويج، ولكن لديها أيضًا حركة مرور عضوية، والمبيعات المباشرة من هذه الموارد على الأرجح غالبًا ما لا تكون كذلك، ولكن التحولات ستكون، وهي حركة المرور التي نحصل عليها أيضًا.
ما سنحصل عليه في النهاية في النهاية في الإخراج:
نعرض الموقع لمحركات البحث من خلال الروابط الخلفية.
2- نحصل على تبديلات عضوية إلى الموقع، وهي أيضًا إشارة لمحركات البحث أن المورد يستخدمه الناس.
كيف نظهر لمحركات البحث أن الموقع سائل:
1 يتم عمل رابط خلفي للصفحة الرئيسية حيث المعلومات الرئيسية
نقوم بعمل لينكات خلفية من خلال عمليات إعادة توجيه المواقع الموثوقة
الأهم من ذلك أننا نضع الموقع على أداة منفصلة من أدوات تحليل المواقع، ويدخل الموقع في ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت لهذه المحللات، ثم الروابط المستلمة التي نضعها كتوجيه مرة أخرى على المدونات والمنتديات والتعليقات.
هذا العملية المهم يعرض لمحركات البحث خريطة الموقع، حيث تعرض أدوات تحليل المواقع جميع المعلومات عن المواقع مع جميع الكلمات الرئيسية والعناوين وهو عمل جيد جداً
جميع المعلومات عن خدماتنا على الموقع!
hello!,I really like your writing so a lot! proportion we be in contact more approximately your article on AOL? I need an expert in this space to resolve my problem. May be that’s you! Looking ahead to look you.
I truly appreciate this post. I’ve been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thx again
Perfect work you have done, this site is really cool with good information.
Player線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
Player如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 – Casino, Gambling、中國 – 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 – オンラインカジノ、越南 – Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。
I like this post, enjoyed this one regards for posting. “The difference between stupidity and genius is that genius has its limits.” by Albert Einstein.
娛樂城評價
Player娛樂城遊戲評測網 《娛樂城評價》分類專區,幫您整了出網路上各大線上娛樂城重點摘要,以便您快速了解各大娛樂城重點資訊。
錢盈娛樂城介紹
錢盈娛樂城於2022年成立,是一個專注於現金投注的線上遊戲平台,提供了包括體育賭博、真人百家樂、老虎機、彩票和電子遊戲等多樣化的遊戲選…
F1方程式娛樂城介紹
F1方程式娛樂城屬於小型線上娛樂城版,整體晚間非常簡陋而且含有諸多瑕疵以及不完善,首先奇怪的點在於完全沒有可以註冊的地方,我們這邊猜測…
CZ168娛樂城介紹
CZ168娛樂城在雖然在簡介中自稱有12年的經營時間,但是經過我們實際的調查以及訪問該品牌網頁後發現,並沒有任何12年前或是更近的資料…
包你發娛樂城介紹
包你發娛樂城是個很多明星都在代言的線上賭博平台,玩家在這裡是用虛擬貨幣來存款,算是那種幣商型的賭場。這個平台沒有直接的提款選項,玩家要…
富遊娛樂城介紹
隨著2024年的到來,最新的線上娛樂平台排行榜已經更新,這一次的排名綜合考慮了各種因素,包括體驗金、促銷活動、提款效率和遊戲多樣性,目…
Player線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
Player如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 – Casino, Gambling、中國 – 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 – オンラインカジノ、越南 – Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。
Как охранять свои личные данные: берегитесь утечек информации в интернете. Сегодня охрана своих данных становится более насущной важной задачей. Одним из наиболее часто встречающихся способов утечки личной информации является слив «сит фраз» в интернете. Что такое сит фразы и в каком объеме обезопаситься от их утечки? Что такое «сит фразы»? «Сит фразы» — это синтезы слов или фраз, которые регулярно используются для доступа к различным онлайн-аккаунтам. Эти фразы могут включать в себя имя пользователя, пароль или разные конфиденциальные данные. Киберпреступники могут пытаться получить доступ к вашим аккаунтам, используя этих сит фраз. Как сохранить свои личные данные? Используйте комплексные пароли. Избегайте использования простых паролей, которые легко угадать. Лучше всего использовать комбинацию букв, цифр и символов. Используйте уникальные пароли для каждого аккаунта. Не применяйте один и тот же пароль для разных сервисов. Используйте двухфакторную проверку (2FA). Это вводит дополнительный уровень безопасности, требуя подтверждение входа на ваш аккаунт посредством другое устройство или метод. Будьте осторожны с онлайн-сервисами. Не доверяйте персональную информацию ненадежным сайтам и сервисам. Обновляйте программное обеспечение. Установите обновления для вашего операционной системы и программ, чтобы защитить свои данные от вредоносного ПО. Вывод Слив сит фраз в интернете может привести к серьезным последствиям, таким подобно кража личной информации и финансовых потерь. Чтобы сохранить себя, следует принимать меры предосторожности и использовать надежные методы для хранения и управления своими личными данными в сети
сид фразы кошельков
Сид-фразы, или мемориальные фразы, представляют собой сочетание слов, которая используется для составления или восстановления кошелька криптовалюты. Эти фразы обеспечивают возможность к вашим криптовалютным средствам, поэтому их надежное хранение и использование чрезвычайно важны для защиты вашего криптоимущества от утери и кражи.
Что такое сид-фразы кошельков криптовалют?
Сид-фразы формируют набор случайно сгенерированных слов, часто от 12 до 24, которые предназначаются для создания уникального ключа шифрования кошелька. Этот ключ используется для восстановления возможности доступа к вашему кошельку в случае его повреждения или утери. Сид-фразы обладают значительной защиты и шифруются, что делает их секурными для хранения и передачи.
Зачем нужны сид-фразы?
Сид-фразы неотъемлемы для обеспечения безопасности и доступности вашего криптоимущества. Они позволяют восстановить возможность доступа к кошельку в случае утери или повреждения физического устройства, на котором он хранится. Благодаря сид-фразам вы можете быстро создавать резервные копии своего кошелька и хранить их в безопасном месте.
Как обеспечить безопасность сид-фраз кошельков?
Никогда не делитесь сид-фразой ни с кем. Сид-фраза является вашим ключом к кошельку, и ее раскрытие может влечь за собой утере вашего криптоимущества.
Храните сид-фразу в секурном месте. Используйте физически защищенные места, такие как банковские ячейки или специализированные аппаратные кошельки, для хранения вашей сид-фразы.
Создавайте резервные копии сид-фразы. Регулярно создавайте резервные копии вашей сид-фразы и храните их в разных безопасных местах, чтобы обеспечить вход к вашему кошельку в случае утери или повреждения.
Используйте дополнительные меры безопасности. Включите другие методы защиты и двухфакторную аутентификацию для своего кошелька криптовалюты, чтобы обеспечить дополнительный уровень безопасности.
Заключение
Сид-фразы кошельков криптовалют являются ключевым элементом безопасного хранения криптоимущества. Следуйте рекомендациям по безопасности, чтобы защитить свою сид-фразу и обеспечить безопасность своих криптовалютных средств.
Криптокошельки с балансом: зачем их покупают и как использовать
В мире криптовалют все расширяющуюся популярность приобретают криптокошельки с предустановленным балансом. Это индивидуальные кошельки, которые уже содержат определенное количество криптовалюты на момент покупки. Но зачем люди приобретают такие кошельки, и как правильно использовать их?
Почему покупают криптокошельки с балансом?
Удобство: Криптокошельки с предустановленным балансом предлагаются как готовое к работе решение для тех, кто хочет быстро начать пользоваться криптовалютой без необходимости покупки или обмена на бирже.
Подарок или награда: Иногда криптокошельки с балансом используются как подарок или поощрение в рамках акций или маркетинговых кампаний.
Анонимность: При покупке криптокошелька с балансом нет запроса предоставлять личные данные, что может быть важно для тех, кто ценит анонимность.
Как использовать криптокошелек с балансом?
Проверьте безопасность: Убедитесь, что кошелек безопасен и не подвержен взлому. Проверьте репутацию продавца и происхождение приобретения кошелька.
Переведите средства на другой кошелек: Если вы хотите долгосрочно хранить криптовалюту, рекомендуется перевести средства на более безопасный или практичный для вас кошелек.
Не храните все средства на одном кошельке: Для обеспечения безопасности рекомендуется распределить средства между несколькими кошельками.
Будьте осторожны с фишингом и мошенничеством: Помните, что мошенники могут пытаться обмануть вас, предлагая криптокошельки с балансом с целью получения доступа к вашим средствам.
Заключение
Криптокошельки с балансом могут быть удобным и быстрым способом начать пользоваться криптовалютой, но необходимо помнить о безопасности и осторожности при их использовании.Выбор и приобретение криптокошелька с балансом – это весомый шаг, который требует внимания к деталям и осознанного подхода.”
You should take part in a contest for one of the best blogs on the web. I will recommend this site!
I have been browsing online more than three hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It’s pretty worth enough for me. In my view, if all site owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the internet will be a lot more useful than ever before.
kantorbola
Kantorbola adalah situs slot gacor terbaik di indonesia , kunjungi situs RTP kantor bola untuk mendapatkan informasi akurat slot dengan rtp diatas 95% . Kunjungi juga link alternatif kami di kantorbola77 dan kantorbola99 .
Kantorbola adalah situs slot gacor terbaik di indonesia , kunjungi situs RTP kantor bola untuk mendapatkan informasi akurat slot dengan rtp diatas 95% . Kunjungi juga link alternatif kami di kantorbola77 dan kantorbola99 .
taurus118
I just couldn’t go away your website before suggesting that I actually loved the standard info a person provide in your visitors? Is gonna be back incessantly in order to check up on new posts
Java Burn: What is it? Java Burn is marketed as a natural weight loss product that can increase the speed and efficiency of a person’s natural metabolism, thereby supporting their weight loss efforts
What is Lottery Defeater Software? Lottery software is a specialized software designed to predict and facilitate individuals in winning lotteries.
Rikvip Club: Trung Tâm Giải Trí Trực Tuyến Hàng Đầu tại Việt Nam
Rikvip Club là một trong những nền tảng giải trí trực tuyến hàng đầu tại Việt Nam, cung cấp một loạt các trò chơi hấp dẫn và dịch vụ cho người dùng. Cho dù bạn là người dùng iPhone hay Android, Rikvip Club đều có một cái gì đó dành cho mọi người. Với sứ mạng và mục tiêu rõ ràng, Rikvip Club luôn cố gắng cung cấp những sản phẩm và dịch vụ tốt nhất cho khách hàng, tạo ra một trải nghiệm tiện lợi và thú vị cho người chơi.
Sứ Mạng và Mục Tiêu của Rikvip
Từ khi bắt đầu hoạt động, Rikvip Club đã có một kế hoạch kinh doanh rõ ràng, luôn nỗ lực để cung cấp cho khách hàng những sản phẩm và dịch vụ tốt nhất và tạo điều kiện thuận lợi nhất cho người chơi truy cập. Nhóm quản lý của Rikvip Club có những mục tiêu và ước muốn quyết liệt để biến Rikvip Club thành trung tâm giải trí hàng đầu trong lĩnh vực game đổi thưởng trực tuyến tại Việt Nam và trên toàn cầu.
Trải Nghiệm Live Casino
Rikvip Club không chỉ nổi bật với sự đa dạng của các trò chơi đổi thưởng mà còn với các phòng trò chơi casino trực tuyến thu hút tất cả người chơi. Môi trường này cam kết mang lại trải nghiệm chuyên nghiệp với tính xanh chín và sự uy tín không thể nghi ngờ. Đây là một sân chơi lý tưởng cho những người yêu thích thách thức bản thân và muốn tận hưởng niềm vui của chiến thắng. Với các sảnh cược phổ biến như Roulette, Sic Bo, Dragon Tiger, người chơi sẽ trải nghiệm những cảm xúc độc đáo và đặc biệt khi tham gia vào casino trực tuyến.
Phương Thức Thanh Toán Tiện Lợi
Rikvip Club đã được trang bị những công nghệ thanh toán tiên tiến ngay từ đầu, mang lại sự thuận tiện và linh hoạt cho người chơi trong việc sử dụng hệ thống thanh toán hàng ngày. Hơn nữa, Rikvip Club còn tích hợp nhiều phương thức giao dịch khác nhau để đáp ứng nhu cầu đa dạng của người chơi: Chuyển khoản Ngân hàng, Thẻ cào, Ví điện tử…
Kết Luận
Tóm lại, Rikvip Club không chỉ là một nền tảng trò chơi, mà còn là một cộng đồng nơi người chơi có thể tụ tập để tận hưởng niềm vui của trò chơi và cảm giác hồi hộp khi chiến thắng. Với cam kết cung cấp những sản phẩm và dịch vụ tốt nhất, Rikvip Club chắc chắn là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những người yêu thích trò chơi trực tuyến tại Việt Nam và cả thế giới.
What Is Potent Stream? Potent Stream is a male health formula that helps to maintain healthy urinary and prostate health by killing off all the toxins in the body
국외선물의 시작 골드리치증권와 동참하세요.
골드리치는 오랜기간 고객님들과 더불어 선물시장의 길을 함께 동행해왔으며, 투자자분들의 확실한 투자 및 높은 수익률을 지향하여 항상 전력을 기울이고 있습니다.
무엇때문에 20,000+명 이상이 골드리치와 동참하나요?
신속한 솔루션: 간단하며 빠른속도의 프로세스를 갖추어 어느누구라도 간편하게 사용할 수 있습니다.
안전 프로토콜: 국가기관에서 채택한 최상의 등급의 보안체계을 채택하고 있습니다.
스마트 인가절차: 전체 거래데이터은 부호화 가공되어 본인 외에는 아무도 누구도 내용을 열람할 수 없습니다.
보장된 수익률 마련: 리스크 부분을 감소시켜, 보다 더 확실한 수익률을 공개하며 그에 따른 리포트를 공유합니다.
24 / 7 상시 고객상담: 연중무휴 24시간 실시간 서비스를 통해 회원분들을 모두 뒷받침합니다.
함께하는 동반사: 골드리치증권는 공기업은 물론 금융권들 및 다양한 협력사와 함께 동행해오고.
외국선물이란?
다양한 정보를 알아보세요.
해외선물은 외국에서 거래되는 파생상품 중 하나로, 지정된 기초자산(예시: 주식, 화폐, 상품 등)을 기초로 한 옵션계약 계약을 말합니다. 본질적으로 옵션은 명시된 기초자산을 미래의 어떤 시점에 정해진 금액에 매수하거나 팔 수 있는 권리를 부여합니다. 해외선물옵션은 이러한 옵션 계약이 국외 마켓에서 거래되는 것을 뜻합니다.
해외선물은 크게 매수 옵션과 풋 옵션으로 분류됩니다. 콜 옵션은 지정된 기초자산을 미래에 정해진 가격에 사는 권리를 부여하는 반면, 매도 옵션은 명시된 기초자산을 미래에 일정 가격에 매도할 수 있는 권리를 제공합니다.
옵션 계약에서는 미래의 명시된 일자에 (만료일이라 칭하는) 일정 금액에 기초자산을 매수하거나 매도할 수 있는 권리를 가지고 있습니다. 이러한 금액을 행사 가격이라고 하며, 만기일에는 해당 권리를 실행할지 여부를 결정할 수 있습니다. 따라서 옵션 계약은 투자자에게 향후의 시세 변화에 대한 보호나 이익 창출의 기회를 부여합니다.
국외선물은 마켓 참가자들에게 다양한 투자 및 차익거래 기회를 마련, 외환, 상품, 주식 등 다양한 자산유형에 대한 옵션 계약을 포괄할 수 있습니다. 거래자는 매도 옵션을 통해 기초자산의 하향에 대한 안전장치를 받을 수 있고, 매수 옵션을 통해 상승장에서의 수익을 타깃팅할 수 있습니다.
해외선물 거래의 원리
행사 금액(Exercise Price): 국외선물에서 실행 금액은 옵션 계약에 따라 특정한 금액으로 계약됩니다. 만기일에 이 금액을 기준으로 옵션을 실행할 수 있습니다.
만료일(Expiration Date): 옵션 계약의 만기일은 옵션의 실행이 허용되지않는 최종 일자를 뜻합니다. 이 날짜 다음에는 옵션 계약이 종료되며, 더 이상 거래할 수 없습니다.
풋 옵션(Put Option)과 콜 옵션(Call Option): 매도 옵션은 기초자산을 지정된 가격에 팔 수 있는 권리를 부여하며, 매수 옵션은 기초자산을 지정된 금액에 매수하는 권리를 허락합니다.
계약료(Premium): 외국선물 거래에서는 옵션 계약에 대한 계약료을 지불해야 합니다. 이는 옵션 계약에 대한 가격으로, 마켓에서의 수요량와 공급량에 따라 변경됩니다.
행사 방식(Exercise Strategy): 투자자는 종료일에 옵션을 행사할지 여부를 선택할 수 있습니다. 이는 시장 환경 및 거래 전략에 따라 다르며, 옵션 계약의 이익을 최대화하거나 손실을 최소화하기 위해 결정됩니다.
마켓 위험요인(Market Risk): 국외선물 거래는 마켓의 변화추이에 영향을 받습니다. 시세 변화이 기대치 못한 진로으로 일어날 경우 손해이 발생할 수 있으며, 이러한 시장 위험요인를 축소하기 위해 거래자는 계획을 수립하고 투자를 설계해야 합니다.
골드리치와 함께하는 국외선물은 확실한 믿을만한 수 있는 투자를 위한 최적의 선택입니다. 투자자분들의 투자를 지지하고 가이드하기 위해 우리는 전력을 다하고 있습니다. 함께 더 나은 미래를 향해 계속해나가세요.
Euro
UEFA Euro 2024 Sân Chơi Bóng Đá Hấp Dẫn Nhất Của Châu Âu
Euro 2024 là sự kiện bóng đá lớn nhất của châu Âu, không chỉ là một giải đấu mà còn là một cơ hội để các quốc gia thể hiện tài năng, sự đoàn kết và tinh thần cạnh tranh.
Euro 2024 hứa hẹn sẽ mang lại những trận cầu đỉnh cao và kịch tính cho người hâm mộ trên khắp thế giới. Cùng tìm hiểu các thêm thông tin hấp dẫn về giải đấu này tại bài viết dưới đây, gồm:
Nước chủ nhà
Đội tuyển tham dự
Thể thức thi đấu
Thời gian diễn ra
Sân vận động
Euro 2024 sẽ được tổ chức tại Đức, một quốc gia có truyền thống vàng của bóng đá châu Âu.
Đức là một đất nước giàu có lịch sử bóng đá với nhiều thành công quốc tế và trong những năm gần đây, họ đã thể hiện sức mạnh của mình ở cả mặt trận quốc tế và câu lạc bộ.
Việc tổ chức Euro 2024 tại Đức không chỉ là một cơ hội để thể hiện năng lực tổ chức tuyệt vời mà còn là một dịp để giới thiệu văn hóa và sức mạnh thể thao của quốc gia này.
Đội tuyển tham dự giải đấu Euro 2024
Euro 2024 sẽ quy tụ 24 đội tuyển hàng đầu từ châu Âu. Các đội tuyển này sẽ là những đại diện cho sự đa dạng văn hóa và phong cách chơi bóng đá trên khắp châu lục.
Các đội tuyển hàng đầu như Đức, Pháp, Tây Ban Nha, Bỉ, Italy, Anh và Hà Lan sẽ là những ứng viên nặng ký cho chức vô địch.
Trong khi đó, các đội tuyển nhỏ hơn như Iceland, Wales hay Áo cũng sẽ mang đến những bất ngờ và thách thức cho các đối thủ.
Các đội tuyển tham dự được chia thành 6 bảng đấu, gồm:
Bảng A: Đức, Scotland, Hungary và Thuỵ Sĩ
Bảng B: Tây Ban Nha, Croatia, Ý và Albania
Bảng C: Slovenia, Đan Mạch, Serbia và Anh
Bảng D: Ba Lan, Hà Lan, Áo và Pháp
Bảng E: Bỉ, Slovakia, Romania và Ukraina
Bảng F: Thổ Nhĩ Kỳ, Gruzia, Bồ Đào Nha và Cộng hoà Séc
I do love the way you have presented this particular matter plus it does indeed supply me a lot of fodder for thought. However, because of what I have observed, I basically hope when the actual feed-back pack on that men and women remain on point and in no way embark upon a tirade involving the news of the day. All the same, thank you for this exceptional point and even though I do not necessarily concur with it in totality, I respect the viewpoint.
I like this web blog its a master peace ! Glad I observed this on google .
Just wanna remark that you have a very nice internet site, I like the layout it actually stands out.
I’d always want to be update on new content on this website , saved to favorites! .
There is apparently a bundle to realize about this. I suppose you made various nice points in features also.
Hi are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you need any html coding knowledge to make your own blog? Any help would be really appreciated!
Hi there, I found your site via Google while looking for a related topic, your site came up, it looks good. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Glad to be one of several visitors on this amazing internet site : D.
Hello! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any issues with hackers? My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing months of hard work due to no back up. Do you have any solutions to stop hackers?
The most talked about weight loss product is finally here! FitSpresso is a powerful supplement that supports healthy weight loss the natural way. Clinically studied ingredients work synergistically to support healthy fat burning, increase metabolism and maintain long lasting weight loss. https://fitspresso-try.com/
Prodentim: What is it? Some of the finest and highest quality ingredients are used to produce Prodentim, an oral health supplement
I am really impressed with your writing skills and also with the layout on your weblog. Is this a paid theme or did you customize it yourself? Either way keep up the excellent quality writing, it’s rare to see a nice blog like this one today..
certainly like your website but you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling issues and I find it very troublesome to tell the reality on the other hand I¦ll definitely come again again.
Hi! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting fed up of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform. I would be great if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
I cling on to listening to the news update speak about getting free online grant applications so I have been looking around for the best site to get one. Could you advise me please, where could i get some?
Thank you a lot for giving everyone such a wonderful opportunity to read critical reviews from this site. It’s usually very kind and jam-packed with a lot of fun for me and my office peers to visit your site the equivalent of three times a week to study the new items you will have. And definitely, I’m actually satisfied considering the amazing ideas served by you. Some 3 tips in this posting are really the most impressive we have all ever had.
Very clear web site, thankyou for this post.
Gerakl24: Профессиональная Смена Фундамента, Венцов, Полов и Передвижение Домов
Компания Gerakl24 специализируется на оказании всесторонних услуг по смене фундамента, венцов, полов и переносу строений в городе Красноярск и в окрестностях. Наша группа профессиональных мастеров обеспечивает высокое качество исполнения всех типов ремонтных работ, будь то из дерева, с каркасом, из кирпича или бетонные строения.
Достоинства услуг Gerakl24
Навыки и знания:
Каждая задача выполняются лишь высококвалифицированными специалистами, имеющими большой практику в сфере возведения и восстановления строений. Наши специалисты эксперты в своей области и осуществляют работу с безупречной точностью и вниманием к мелочам.
Всесторонний подход:
Мы предлагаем разнообразные услуги по восстановлению и восстановлению зданий:
Реставрация фундамента: укрепление и замена старого фундамента, что гарантирует долговечность вашего здания и устранить проблемы, связанные с оседанием и деформацией.
Реставрация венцов: замена нижних венцов деревянных домов, которые обычно гниют и разрушаются.
Установка новых покрытий: замена старых полов, что значительно улучшает внешний вид и функциональные характеристики.
Передвижение домов: безопасное и качественное передвижение домов на другие участки, что помогает сохранить здание и избежать дополнительных затрат на создание нового.
Работа с любыми видами зданий:
Дома из дерева: восстановление и защита деревянных строений, обработка от гниения и насекомых.
Каркасные дома: усиление каркасных конструкций и реставрация поврежденных элементов.
Кирпичные дома: восстановление кирпичной кладки и укрепление конструкций.
Дома из бетона: ремонт и укрепление бетонных конструкций, устранение трещин и повреждений.
Качество и прочность:
Мы работаем с лишь качественные материалы и передовые технологии, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность всех работ. Все наши проекты проходят тщательную проверку качества на каждой стадии реализации.
Индивидуальный подход:
Мы предлагаем каждому клиенту подходящие решения, учитывающие ваши требования и желания. Наша цель – чтобы конечный результат полностью удовлетворял вашим запросам и желаниям.
Почему стоит выбрать Геракл24?
Работая с нами, вы получаете надежного партнера, который берет на себя все заботы по ремонту и реконструкции вашего строения. Мы обеспечиваем выполнение всех проектов в установленные сроки и с соблюдением всех строительных норм и стандартов. Выбрав Геракл24, вы можете не сомневаться, что ваше здание в надежных руках.
Мы предлагаем консультацию и дать ответы на все вопросы. Контактируйте с нами, чтобы обсудить детали вашего проекта и узнать о наших сервисах. Мы сохраним и улучшим ваш дом, сделав его безопасным и комфортным для проживания на долгие годы.
Геракл24 – ваш надежный партнер в реставрации и ремонте домов в Красноярске и за его пределами.
Very interesting details you have noted, thanks for putting up. “Strength does not come from physical capacity. It comes from an indomitable will.” by Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi.
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต
Very good visual appeal on this web site, I’d rate it 10 10.
Как обезопасить свои данные: берегитесь утечек информации в интернете. Сегодня обеспечение безопасности своих данных становится все более важной задачей. Одним из наиболее распространенных способов утечки личной информации является слив «сит фраз» в интернете. Что такое сит фразы и в какой мере обезопаситься от их утечки? Что такое «сит фразы»? «Сит фразы» — это комбинации слов или фраз, которые часто используются для получения доступа к различным онлайн-аккаунтам. Эти фразы могут включать в себя имя пользователя, пароль или другие конфиденциальные данные. Киберпреступники могут пытаться получить доступ к вашим аккаунтам, с помощью этих сит фраз. Как обезопасить свои личные данные? Используйте непростые пароли. Избегайте использования простых паролей, которые легко угадать. Лучше всего использовать комбинацию букв, цифр и символов. Используйте уникальные пароли для каждого аккаунта. Не воспользуйтесь один и тот же пароль для разных сервисов. Используйте двухфакторную аутентификацию (2FA). Это прибавляет дополнительный уровень безопасности, требуя подтверждение входа на ваш аккаунт посредством другое устройство или метод. Будьте осторожны с онлайн-сервисами. Не доверяйте свою информацию ненадежным сайтам и сервисам. Обновляйте программное обеспечение. Установите обновления для вашего операционной системы и программ, чтобы уберечь свои данные от вредоносного ПО. Вывод Слив сит фраз в интернете может повлечь за собой серьезным последствиям, таким подобно кража личной информации и финансовых потерь. Чтобы защитить себя, следует принимать меры предосторожности и использовать надежные методы для хранения и управления своими личными данными в сети
Good day I am so glad I found your web site, I really found you by mistake, while I was searching on Bing for something else, Anyhow I am here now and would just like to say thank you for a remarkable post and a all round entertaining blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to go through it all at the minute but I have bookmarked it and also added in your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a great deal more, Please do keep up the great job.
טלגראס היא תוכנה רווחת בישראל לרכישת קנאביס באופן אינטרנטי. זו מעניקה ממשק נוח ומאובטח לרכישה ולקבלת שילוחים של מוצרי מריחואנה מרובים. בסקירה זו נבחן עם העיקרון שמאחורי האפליקציה, איך זו עובדת ומה היתרונות מ השימוש בזו.
מה זו הפלטפורמה?
האפליקציה הווה שיטה לקנייה של קנאביס באמצעות היישומון טלגראם. היא נשענת על ערוצי תקשורת וקהילות טלגראם ייעודיות הקרויות ״טלגראס כיוונים, שם אפשר להזמין מרחב פריטי קנאביס ולקבל אותם ישירותית למשלוח. ערוצי התקשורת אלו מסודרים על פי איזורים גיאוגרפיים, במטרה להקל את קבלתם של השילוחים.
כיצד זה עובד?
התהליך פשוט יחסית. ראשית, צריך להצטרף לערוץ טלגראס הרלוונטי לאזור המחיה. שם ניתן לעיין בתפריטים של הפריטים השונים ולהרכיב עם הפריטים המבוקשים. לאחר ביצוע ההרכבה וסגירת התשלום, השליח יגיע לכתובת שנרשמה עם החבילה שהוזמן.
מרבית ערוצי הטלגראס מציעים מגוון נרחב של מוצרים – סוגי קנאביס, ממתקים, שתייה ועוד. בנוסף, אפשר לראות ביקורות של לקוחות שעברו לגבי איכות הפריטים והשירות.
מעלות הנעשה בטלגראס
מעלה עיקרי מ הפלטפורמה הינו הנוחיות והפרטיות. ההרכבה וההכנות מתקיימים ממרחק מאיזשהו מיקום, בלי צורך בהתכנסות פנים אל פנים. כמו כן, הפלטפורמה מוגנת ביסודיות ומבטיחה חיסיון גבוהה.
מלבד אל כך, עלויות הפריטים בטלגראס נוטים לבוא זולים, והמשלוחים מגיעים במהירות ובמסירות רבה. קיים אף מרכז תמיכה פתוח לכל שאלה או בעיית.
לסיכום
טלגראס הווה שיטה חדשנית ויעילה לקנות מוצרי צמח הקנאביס בישראל. זו משלבת את הנוחות הדיגיטלית מ היישומון הפופולרית, ועם הזריזות והדיסקרטיות מ דרך השילוח הישירות. ככל שהדרישה למריחואנה גובר, פלטפורמות בדוגמת זו צפויות להמשיך ולצמוח.
Its wonderful as your other articles : D, regards for posting.
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS – Giải pháp vượt trội cho các tín đồ iOS
Trong thế giới công nghệ đầy sôi động hiện nay, trải nghiệm người dùng luôn là yếu tố then chốt. Với sự ra đời của Bản cài đặt B29 IOS, người dùng sẽ được hưởng trọn vẹn những tính năng ưu việt, mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối. Hãy cùng khám phá những ưu điểm vượt trội của bản cài đặt này!
Tính bảo mật tối đa
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được thiết kế với mục tiêu đảm bảo an toàn dữ liệu tuyệt đối cho người dùng. Nhờ hệ thống mã hóa hiện đại, thông tin cá nhân và dữ liệu nhạy cảm của bạn luôn được bảo vệ an toàn khỏi những kẻ xâm nhập trái phép.
Trải nghiệm người dùng đỉnh cao
Giao diện thân thiện, đơn giản nhưng không kém phần hiện đại, B29 IOS mang đến cho người dùng trải nghiệm duyệt web, truy cập ứng dụng và sử dụng thiết bị một cách trôi chảy, mượt mà. Các tính năng thông minh được tối ưu hóa, giúp nâng cao hiệu suất và tiết kiệm pin đáng kể.
Tính tương thích rộng rãi
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được phát triển với mục tiêu tương thích với mọi thiết bị iOS từ các dòng iPhone, iPad cho đến iPod Touch. Dù là người dùng mới hay lâu năm của hệ điều hành iOS, B29 đều mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối.
Quá trình cài đặt đơn giản
Với những hướng dẫn chi tiết, việc cài đặt B29 IOS trở nên nhanh chóng và dễ dàng. Chỉ với vài thao tác đơn giản, bạn đã có thể trải nghiệm ngay tất cả những tính năng tuyệt vời mà bản cài đặt này mang lại.
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS không chỉ là một bản cài đặt đơn thuần, mà còn là giải pháp công nghệ hiện đại, nâng tầm trải nghiệm người dùng lên một tầm cao mới. Hãy trở thành một phần của cộng đồng sử dụng B29 IOS để khám phá những tiện ích tuyệt vời mà nó có thể mang lại!
I have been surfing online greater than three hours lately, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It?¦s pretty value sufficient for me. Personally, if all site owners and bloggers made excellent content material as you did, the internet might be a lot more helpful than ever before.
With havin so much written content do you ever run into any problems of plagorism or copyright violation? My website has a lot of completely unique content I’ve either authored myself or outsourced but it seems a lot of it is popping it up all over the web without my permission. Do you know any techniques to help protect against content from being stolen? I’d really appreciate it.
טלגראס
האפליקציה הווה פלטפורמה רווחת בישראל לקנייה של קנאביס בצורה וירטואלי. היא מספקת ממשק נוח ומאובטח לקנייה וקבלת שילוחים מ מוצרי מריחואנה מרובים. בכתבה זה נבחן את העיקרון מאחורי האפליקציה, כיצד היא פועלת ומהם היתרונות של השימוש בה.
מהי האפליקציה?
טלגראס היא דרך לקנייה של קנאביס דרך היישומון טלגרם. זו נשענת על ערוצי תקשורת וקבוצות טלגרם מיוחדות הקרויות ״כיווני טלגראס״, שם ניתן להרכיב מגוון פריטי צמח הקנאביס ולקבלת אלו ישירות למשלוח. הערוצים האלה מאורגנים לפי אזורים גאוגרפיים, כדי להקל על קבלתם של השילוחים.
כיצד זאת עובד?
התהליך פשוט יחסית. קודם כל, צריך להצטרף לערוץ הטלגראס הנוגע לאזור המגורים. שם ניתן לצפות בתפריטי המוצרים השונים ולהרכיב את המוצרים הרצויים. לאחר השלמת ההזמנה וסגירת התשלום, השליח יגיע בכתובת שנרשמה עם הארגז המוזמנת.
מרבית ערוצי טלגראס מציעים טווח נרחב מ מוצרים – סוגי מריחואנה, ממתקים, משקאות ועוד. כמו כן, אפשר לראות ביקורות של לקוחות קודמים על רמת המוצרים והשירות.
מעלות הנעשה באפליקציה
מעלה מרכזי של הפלטפורמה הוא הנוחות והפרטיות. ההזמנה והתהליך מתבצעות ממרחק מאיזשהו מיקום, ללא צורך בהתכנסות פנים אל פנים. כמו כן, האפליקציה מוגנת ביסודיות ומבטיחה חיסיון גבוה.
נוסף אל זאת, מחירי המוצרים בטלגראס נוטים לבוא זולים, והמשלוחים מגיעים במהירות ובמסירות גבוהה. קיים אף מרכז תמיכה זמין לכל שאלה או בעיה.
סיכום
האפליקציה מהווה שיטה חדשנית ויעילה לקנות מוצרי צמח הקנאביס בארץ. זו משלבת את הנוחות הדיגיטלית של האפליקציה הפופולרית, לבין הזריזות והדיסקרטיות של שיטת השילוח הישירה. ככל שהביקוש למריחואנה גדלה, אפליקציות כמו זו צפויות להמשיך ולהתפתח.
Как обезопасить свои данные: страхуйтесь от утечек информации в интернете. Сегодня охрана своих данных становится более насущной важной задачей. Одним из наиболее популярных способов утечки личной информации является слив «сит фраз» в интернете. Что такое сит фразы и в каком объеме обезопаситься от их утечки? Что такое «сит фразы»? «Сит фразы» — это смеси слов или фраз, которые часто используются для доступа к различным онлайн-аккаунтам. Эти фразы могут включать в себя имя пользователя, пароль или другие конфиденциальные данные. Киберпреступники могут пытаться получить доступ к вашим аккаунтам, с помощью этих сит фраз. Как защитить свои личные данные? Используйте непростые пароли. Избегайте использования легких паролей, которые просто угадать. Лучше всего использовать комбинацию букв, цифр и символов. Используйте уникальные пароли для всего аккаунта. Не применяйте один и тот же пароль для разных сервисов. Используйте двухфакторную аутентификацию (2FA). Это добавляет дополнительный уровень безопасности, требуя подтверждение входа на ваш аккаунт посредством другое устройство или метод. Будьте осторожны с онлайн-сервисами. Не доверяйте свою информацию ненадежным сайтам и сервисам. Обновляйте программное обеспечение. Установите обновления для вашего операционной системы и программ, чтобы уберечь свои данные от вредоносного ПО. Вывод Слив сит фраз в интернете может повлечь за собой серьезным последствиям, таким подобно кража личной информации и финансовых потерь. Чтобы обезопасить себя, следует принимать меры предосторожности и использовать надежные методы для хранения и управления своими личными данными в сети
I have been reading out a few of your stories and i can claim pretty good stuff. I will definitely bookmark your blog.
Как охранять свои данные: берегитесь утечек информации в интернете. Сегодня обеспечение безопасности личных данных становится всё больше важной задачей. Одним из наиболее распространенных способов утечки личной информации является слив «сит фраз» в интернете. Что такое сит фразы и в какой мере защититься от их утечки? Что такое «сит фразы»? «Сит фразы» — это смеси слов или фраз, которые регулярно используются для доступа к различным онлайн-аккаунтам. Эти фразы могут включать в себя имя пользователя, пароль или иные конфиденциальные данные. Киберпреступники могут пытаться получить доступ к вашим аккаунтам, с помощью этих сит фраз. Как сохранить свои личные данные? Используйте комплексные пароли. Избегайте использования несложных паролей, которые легко угадать. Лучше всего использовать комбинацию букв, цифр и символов. Используйте уникальные пароли для каждого аккаунта. Не воспользуйтесь один и тот же пароль для разных сервисов. Используйте двухфакторную аутентификацию (2FA). Это привносит дополнительный уровень безопасности, требуя подтверждение входа на ваш аккаунт посредством другое устройство или метод. Будьте осторожны с онлайн-сервисами. Не доверяйте свою информацию ненадежным сайтам и сервисам. Обновляйте программное обеспечение. Установите обновления для вашего операционной системы и программ, чтобы уберечь свои данные от вредоносного ПО. Вывод Слив сит фраз в интернете может привести к серьезным последствиям, таким как кража личной информации и финансовых потерь. Чтобы сохранить себя, следует принимать меры предосторожности и использовать надежные методы для хранения и управления своими личными данными в сети
Сохраните собственные USDT: Проверьте перевод TRC20 до пересылкой
Криптовалюты, такие вроде USDT (Tether) на блокчейне TRON (TRC20), делаются все более востребованными в области области децентрализованных финансов. Но вместе со повышением востребованности увеличивается и опасность промахов либо мошенничества при отправке средств. Как раз именно поэтому важно контролировать перевод USDT TRC20 перед ее пересылкой.
Погрешность при вводе адреса получателя или отправка на некорректный адрес сможет повлечь к безвозвратной утрате ваших USDT. Мошенники тоже смогут пытаться обмануть тебя, посылая фальшивые адреса на отправки. Утрата крипто вследствие подобных погрешностей может обернуться значительными финансовыми убытками.
Впрочем, существуют профильные службы, дающие возможность удостовериться перевод USDT TRC20 до её пересылкой. Один из числа таких сервисов предоставляет возможность наблюдать а также исследовать транзакции на блокчейне TRON.
На этом сервисе вы можете ввести адрес получателя получателя и получить детальную информацию об адресе, включая в том числе историю транзакций, остаток а также статус счета. Данное поможет установить, является или нет адрес подлинным и безопасным на отправки финансов.
Другие службы тоже дают похожие возможности по контроля операций USDT TRC20. Некоторые кошельки для криптовалют по цифровых валют имеют интегрированные функции для контроля адресов получателей и переводов.
Не пропускайте контролем перевода USDT TRC20 до её пересылкой. Крохотная осмотрительность сможет сэкономить вам множество средств а также не допустить потерю ваших важных криптовалютных активов. Применяйте заслуживающие доверия службы с целью обеспечения безопасности ваших операций а также целостности ваших USDT в блокчейне TRON.
Проверить транзакцию usdt trc20
Оградите свои USDT: Проконтролируйте транзакцию TRC20 до отправкой
Виртуальные деньги, подобные как USDT (Tether) в распределенном реестре TRON (TRC20), становятся всё всё более востребованными в области области децентрализованных финансовых услуг. Но вместе со увеличением востребованности растет также опасность ошибок иль обмана во время переводе средств. Как раз по этой причине нужно контролировать транзакцию USDT TRC20 до ее отправлением.
Промах во время вводе адреса адресата иль пересылка по некорректный адрес получателя сможет повлечь к невозможности безвозвратной потере ваших USDT. Жулики тоже смогут пытаться одурачить тебя, пересылая фальшивые адреса для отправки. Утрата криптовалюты по причине таких промахов может обернуться значительными финансовыми потерями.
Впрочем, существуют специализированные сервисы, дающие возможность проверить транзакцию USDT TRC20 до ее пересылкой. Некий из подобных служб дает опцию просматривать и анализировать транзакции на распределенном реестре TRON.
На данном обслуживании вам сможете ввести адрес получателя а также получить обстоятельную данные о адресе, включая в том числе историю операций, остаток и состояние аккаунта. Это поможет установить, является ли адрес получателя подлинным а также безопасным на отправки средств.
Иные сервисы тоже дают аналогичные возможности по контроля транзакций USDT TRC20. Некоторые кошельки для цифровых валют обладают встроенные возможности по верификации адресов получателей а также транзакций.
Не пропускайте проверкой транзакции USDT TRC20 перед ее пересылкой. Небольшая бдительность сможет сэкономить вам много денег и избежать утрату твоих ценных криптовалютных активов. Задействуйте заслуживающие доверия службы с целью достижения защищенности твоих операций и неприкосновенности твоих USDT в распределенном реестре TRON.
При взаимодействии с виртуальной валютой USDT в распределенном реестре TRON (TRC20) чрезвычайно значимо не просто удостоверять адрес получателя перед переводом средств, а также тоже регулярно отслеживать остаток своего цифрового кошелька, а также источники поступающих транзакций. Данное действие даст возможность вовремя идентифицировать все нежелательные операции а также избежать вероятные потери.
Прежде всего, необходимо проверить в точности отображаемого баланса USDT TRC20 на вашем криптокошельке. Советуется сравнивать показания с сведениями публичных блокчейн-обозревателей, для того чтобы не допустить вероятность хакерской атаки или взлома самого кошелька.
Но лишь наблюдения баланса недостаточно. Чрезвычайно существенно анализировать журнал входящих транзакций а также этих источники. В случае если вы выявите транзакции USDT от неизвестных или вызывающих опасения реквизитов, сразу же приостановите данные финансы. Существует опасность, что эти криптомонеты были добыты незаконным способом и впоследствии изъяты регуляторами.
Наш приложение дает инструменты с целью углубленного исследования поступающих USDT TRC20 транзакций относительно их законности и отсутствия связи с криминальной деятельностью. Мы обеспечим вам безопасную работу с этой распространенной стейблкоин-монетой.
Дополнительно необходимо регулярно переводить USDT TRC20 на надежные некастодиальные крипто-кошельки находящиеся под вашим абсолютным присмотром. Хранение монет на сторонних площадках всегда связано с рисками хакерских атак а также утраты финансов вследствие программных ошибок либо банкротства платформы.
Следуйте базовые меры защиты, будьте бдительны а также оперативно контролируйте баланс и источники поступлений кошелька для USDT TRC20. Данные действия позволит обезопасить ваши электронные активы от незаконного присвоения и возможных правовых последствий впоследствии.
проверить адрес usdt trc20
Название: Непременно проверяйте адрес адресата во время переводе USDT TRC20
В процессе взаимодействии со крипто, в частности с USDT в распределенном реестре TRON (TRC20), крайне важно демонстрировать бдительность и тщательность. Одна из самых распространенных ошибок, которую совершают пользователи – отправка финансов по неверный адресу. Для того чтобы устранить утрату собственных USDT, нужно неизменно старательно контролировать адресе реципиента до посылкой операции.
Цифровые адреса кошельков представляют собой обширные комплексы символов а также цифр, например, TRX9QahiFUYfHffieZThuzHbkndWvvfzThB8U. Даже небольшая опечатка либо оплошность при копировании адреса кошелька имеет возможность повлечь к тому, чтобы твои крипто станут безвозвратно лишены, поскольку они окажутся в неподконтрольный тобой криптокошелек.
Имеются многообразные методы проверки адресов кошельков USDT TRC20:
1. Зрительная инспекция. Тщательно сверьте адрес кошелька во своём кошельке со адресом кошелька получателя. В случае малейшем расхождении – не производите транзакцию.
2. Задействование веб-инструментов удостоверения.
3. Двойная аутентификация со адресатом. Попросите адресату заверить правильность адреса кошелька перед отправкой операции.
4. Пробный перевод. При значительной сумме перевода, допустимо вначале отправить небольшое величину USDT для контроля адреса.
Также рекомендуется хранить криптовалюты на личных кошельках, а не в биржах иль сторонних сервисах, чтобы обладать абсолютный управление по отношению к собственными активами.
Не пренебрегайте удостоверением адресов при осуществлении работе со USDT TRC20. Эта простая мера предосторожности окажет помощь обезопасить ваши деньги от случайной потери. Помните, чтобы в мире криптовалют операции невозвратны, а переданные монеты по неверный адрес кошелька вернуть почти нереально. Будьте бдительны и тщательны, для того чтобы обезопасить свои вложения.
I like this web site its a master peace ! Glad I noticed this on google .
b29
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS – Giải pháp vượt trội cho các tín đồ iOS
Trong thế giới công nghệ đầy sôi động hiện nay, trải nghiệm người dùng luôn là yếu tố then chốt. Với sự ra đời của Bản cài đặt B29 IOS, người dùng sẽ được hưởng trọn vẹn những tính năng ưu việt, mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối. Hãy cùng khám phá những ưu điểm vượt trội của bản cài đặt này!
Tính bảo mật tối đa
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được thiết kế với mục tiêu đảm bảo an toàn dữ liệu tuyệt đối cho người dùng. Nhờ hệ thống mã hóa hiện đại, thông tin cá nhân và dữ liệu nhạy cảm của bạn luôn được bảo vệ an toàn khỏi những kẻ xâm nhập trái phép.
Trải nghiệm người dùng đỉnh cao
Giao diện thân thiện, đơn giản nhưng không kém phần hiện đại, B29 IOS mang đến cho người dùng trải nghiệm duyệt web, truy cập ứng dụng và sử dụng thiết bị một cách trôi chảy, mượt mà. Các tính năng thông minh được tối ưu hóa, giúp nâng cao hiệu suất và tiết kiệm pin đáng kể.
Tính tương thích rộng rãi
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được phát triển với mục tiêu tương thích với mọi thiết bị iOS từ các dòng iPhone, iPad cho đến iPod Touch. Dù là người dùng mới hay lâu năm của hệ điều hành iOS, B29 đều mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối.
Quá trình cài đặt đơn giản
Với những hướng dẫn chi tiết, việc cài đặt B29 IOS trở nên nhanh chóng và dễ dàng. Chỉ với vài thao tác đơn giản, bạn đã có thể trải nghiệm ngay tất cả những tính năng tuyệt vời mà bản cài đặt này mang lại.
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS không chỉ là một bản cài đặt đơn thuần, mà còn là giải pháp công nghệ hiện đại, nâng tầm trải nghiệm người dùng lên một tầm cao mới. Hãy trở thành một phần của cộng đồng sử dụng B29 IOS để khám phá những tiện ích tuyệt vời mà nó có thể mang lại!
Проверить перевод usdt trc20
Значимость проверки трансфера USDT TRC20
Операции USDT в сети TRC20 набирают все большую востребованность, однако стоит сохранять чрезвычайно осторожными в ходе данных обработке.
Данный категория транзакций регулярно привлекается в качестве обеления активов, извлеченных противоправным способом.
Главный угроз зачисления USDT по сети TRC20 – это подобные операции способны быть приобретены благодаря разнообразных схем мошенничества, таких как утраты конфиденциальной информации, поборы, кибератаки наряду с прочие незаконные операции. Получая указанные транзакции, получатель безусловно оказываетесь соучастником криминальной активности.
Таким образом повышенно необходимо тщательно исследовать природу каждого зачисляемого транзакции с использованием USDT по сети TRC20. Обязательно интересоваться у инициатора данные о чистоте финансов, в случае малейших вопросах – отклонять такие операций.
Учитывайте, в том, что в результате обнаружения нелегальных природы денежных средств, клиент с высокой вероятностью будете привлечены со взысканиям наряду с отправителем. Поэтому рекомендуется перестраховаться и тщательно изучать каждый трансфер, предпочтительнее подвергать риску своей репутацией как и быть втянутым с значительные судебные трудности.
Демонстрация аккуратности в процессе взаимодействии через USDT TRC20 – представляет собой ключ личной денежной защищенности и защита участия в нелегальные практики. Сохраняйте внимательными и постоянно проверяйте источник виртуальных валютных средств.
Excellent website. Plenty of useful info here. I’m sending it to a few friends ans also sharing in delicious. And naturally, thanks for your effort!
Маленькая девочка без двух передних зубов очень обрадовалась этому и стала внимательно рассматривать упаковку, водя по надписям маленьким пальчиком:
—Может, хватит чипсов? Пойдем чего-нибудь нормального посмотрим? Овощей там, фруктов…
Таких слов мужчина совсем не ожидал от своей жены Тани. В их семье конституция тела совсем отличалась от стандартной и общепринятой – иметь предожирение абсолютная норма. Питание далеко отличалась от «правильного», чипсы и конфеты заменяли новомодный фреш из сельдерея и рыбу на пару. Спорт семья видела только по телевизору:
—Ты что? Ты…. Ты что, худеть собралась? Где моя Танюшка – обжорка? Это тебя кто так обидел?! представитель сильного пола абсолютно не предвидел из уст собственной половины Татианы. В этой семье конституция физической оболочки совсем не соответствовала в противовес стандартной и общепризнанной – быть с предожирением безоговорочная правило.
טלגראס
טלגראס היא תוכנה מקובלת בארץ לרכישת צמח הקנאביס באופן מקוון. זו נותנת ממשק נוח ובטוח לרכישה ולקבלת משלוחים מ מוצרי מריחואנה מגוונים. בסקירה זו נבחן עם העיקרון שמאחורי הפלטפורמה, איך זו עובדת ומה המעלות מ השימוש בה.
מה זו טלגראס?
הפלטפורמה מהווה דרך לקנייה של צמח הקנאביס באמצעות היישומון טלגרם. זו מבוססת על ערוצי תקשורת וקהילות טלגראם ייעודיות הנקראות ״טלגראס כיוונים, שבהם אפשר להזמין מרחב מוצרי צמח הקנאביס ולקבל אותם ישירותית למשלוח. ערוצי התקשורת אלו מסודרים לפי אזורים גאוגרפיים, כדי להקל את קבלתם של השילוחים.
כיצד זה פועל?
התהליך קל יחסית. ראשית, יש להצטרף לערוץ הטלגראס הרלוונטי לאזור המחיה. שם ניתן לצפות בתפריטי המוצרים המגוונים ולהזמין עם הפריטים הרצויים. לאחר השלמת ההרכבה וסגירת התשלום, השליח יופיע בכתובת שנרשמה ועמו הארגז שהוזמן.
רוב ערוצי הטלגראס מציעים מגוון רחב של מוצרים – סוגי צמח הקנאביס, ממתקים, משקאות ועוד. בנוסף, אפשר לראות ביקורות מ לקוחות קודמים על איכות המוצרים והשרות.
יתרונות השימוש בטלגראס
יתרון מרכזי מ הפלטפורמה הינו הנוחות והפרטיות. ההרכבה והתהליך מתבצעות ממרחק מאיזשהו מקום, ללא נחיצות במפגש פיזי. כמו כן, האפליקציה מוגנת היטב ומבטיחה סודיות גבוהה.
נוסף אל כך, מחירי הפריטים בפלטפורמה נוטים לבוא תחרותיים, והמשלוחים מגיעים במהירות ובהשקעה רבה. יש גם מוקד תמיכה פתוח לכל שאלה או בעיה.
לסיכום
טלגראס הינה שיטה חדשנית ויעילה לרכוש מוצרי קנאביס בישראל. היא משלבת בין הנוחיות הטכנולוגית מ האפליקציה הפופולרי, ועם הזריזות והדיסקרטיות מ דרך המשלוח הישירות. ככל שהביקוש לצמח הקנאביס גדלה, אפליקציות כמו טלגראס צפויות להמשיך ולצמוח.
Геракл24: Опытная Реставрация Основания, Венцов, Настилов и Перенос Зданий
Фирма Геракл24 специализируется на предоставлении всесторонних работ по замене основания, венцов, полов и перемещению домов в населённом пункте Красноярск и в окрестностях. Наша группа квалифицированных мастеров гарантирует отличное качество исполнения всех видов восстановительных работ, будь то из дерева, каркасные, из кирпича или бетонные дома.
Преимущества работы с Геракл24
Навыки и знания:
Весь процесс осуществляются лишь высококвалифицированными мастерами, имеющими большой практику в сфере создания и ремонта зданий. Наши сотрудники профессионалы в своем деле и осуществляют работу с безупречной точностью и вниманием к деталям.
Всесторонний подход:
Мы осуществляем полный спектр услуг по реставрации и восстановлению зданий:
Смена основания: замена и укрепление фундамента, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы вашего дома и предотвратить проблемы, вызванные оседанием и деформацией.
Смена венцов: реставрация нижних венцов из дерева, которые наиболее часто подвержены гниению и разрушению.
Замена полов: замена старых полов, что кардинально улучшает внешний вид и функциональные характеристики.
Перенос строений: безопасное и надежное перемещение зданий на другие участки, что обеспечивает сохранение строения и избегает дополнительных затрат на возведение нового.
Работа с любыми типами домов:
Деревянные дома: реставрация и усиление деревянных элементов, защита от разрушения и вредителей.
Каркасные строения: реставрация каркасов и реставрация поврежденных элементов.
Кирпичные дома: ремонт кирпичных стен и укрепление конструкций.
Бетонные строения: реставрация и усиление бетонных элементов, ремонт трещин и дефектов.
Качество и прочность:
Мы применяем только высококачественные материалы и новейшее оборудование, что гарантирует долгий срок службы и прочность всех выполненных задач. Каждый наш проект подвергаются строгому контролю качества на каждом этапе выполнения.
Личный подход:
Каждому клиенту мы предлагаем индивидуальные решения, учитывающие ваши требования и желания. Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы итог нашей работы соответствовал вашим ожиданиям и требованиям.
Почему выбирают Геракл24?
Работая с нами, вы найдете надежного партнера, который берет на себя все заботы по ремонту и реконструкции вашего строения. Мы обещаем выполнение всех проектов в установленные сроки и с соблюдением всех правил и норм. Связавшись с Геракл24, вы можете быть уверены, что ваше здание в надежных руках.
Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать и дать ответы на все вопросы. Свяжитесь с нами, чтобы обсудить ваш проект и получить больше информации о наших услугах. Мы поможем вам сохранить и улучшить ваш дом, обеспечив его безопасность и комфорт на долгие годы.
Геракл24 – ваш надежный партнер в реставрации и ремонте домов в Красноярске и за его пределами.
I just couldn’t depart your site before suggesting that I actually enjoyed the standard info a person provide for your visitors? Is going to be back often to check up on new posts
How to lose weight
?Life doesn’t end after bullying from colleagues or complete disappointment in life. More and more days were filled in the calendar every day. And the trip to the sea was getting closer, as the kilograms were evaporating as much as they could!
Woah! I’m really enjoying the template/theme of this site. It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s challenging to get that “perfect balance” between usability and visual appeal. I must say you have done a superb job with this. Additionally, the blog loads very quick for me on Internet explorer. Outstanding Blog!
טלגראס כיוונים
ברוכים הנכנסים לפורטל המידע והסיוע המוכר והרשמי מאת טלגרף כיוונים! בנקודה זו תוכלו למצוא את כלל הנתונים והמידע המעודכן והאקטואלי ביותר אודות פלטפורמה טלגראס והדרכים ליישום שלה כנדרש.
מהו טלגראס מסלולים?
טלגרמות נתיבים מהווה פלטפורמה המבוססת על טלגרם המשמשת לתפוצה וקנייה סביב קנאביס וקנבי בתחום. דרך המסרים והמסגרות בטלגרם, צרכנים מורשים לקנות ולקבל אל מוצרי קנאביס בדרך נגיש וזריז.
באיזה אופן להתחיל בטלגראס כיוונים?
על מנת להשתלב בשימוש בטלגרם, אתם נדרשים להצטרף לשיחות ולפורומים המומלצים. כאן במאגר זה רשאים למצוא מדריך עבור קישורים למקומות מעורבים וימינים. במקביל לכך, תוכלו להתחיל בתהליך הרכישה וההשגה סביב מוצרי הדשא.
מדריכים ומידע
במקום הזה תמצאו אוסף מתוך מפרטים ומידע מפורטים אודות השימוש בטלגראס, בכלל:
– החברות לערוצים איכותיים
– פעילות ההזמנה
– בטיחות והגנה בשימוש בפלטפורמת טלגרם
– והרבה מידע נוסף
צירים רצויים
לגבי נושא זה קישורים לערוצים ולפורומים מומלצים בפלטפורמת טלגרם:
– מקום הנתונים והעדכונים המוסמך
– מקום הייעוץ והתמיכה ללקוחות
– קבוצה לאספקת מוצרי מריחואנה אמינים
– מבחר אתרים דשא מובטחות
צוות מעניקים אתם בשל הצטרפותכם למרכז המידע והנתונים של טלגראס מסלולים ומצפים לקהל חוויית צריכה מרוצה ובטוחה!
I got what you mean , regards for posting.Woh I am delighted to find this website through google.
Aw, this was a very nice post. In concept I want to put in writing like this additionally – taking time and precise effort to make an excellent article… but what can I say… I procrastinate alot and not at all seem to get one thing done.
Замена венцов красноярск
Gerakl24: Квалифицированная Смена Основания, Венцов, Полов и Перенос Зданий
Компания Геракл24 специализируется на оказании полных работ по смене основания, венцов, настилов и перемещению зданий в месте Красноярске и за его пределами. Наша команда квалифицированных экспертов гарантирует превосходное качество исполнения всех видов восстановительных работ, будь то деревянные, каркасного типа, из кирпича или из бетона дома.
Преимущества сотрудничества с Геракл24
Профессионализм и опыт:
Все работы проводятся лишь опытными специалистами, с многолетним долгий опыт в сфере создания и восстановления строений. Наши мастера эксперты в своей области и реализуют проекты с высочайшей точностью и вниманием к мелочам.
Комплексный подход:
Мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг по реставрации и восстановлению зданий:
Реставрация фундамента: усиление и реставрация старого основания, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы вашего здания и устранить проблемы, связанные с оседанием и деформацией.
Смена венцов: восстановление нижних венцов деревянных зданий, которые обычно гниют и разрушаются.
Установка новых покрытий: монтаж новых настилов, что существенно улучшает внешний облик и функциональность помещения.
Перемещение зданий: качественный и безопасный перенос строений на другие участки, что позволяет сохранить ваше строение и избежать дополнительных затрат на создание нового.
Работа с любыми типами домов:
Древесные строения: реставрация и усиление деревянных элементов, обработка от гниения и насекомых.
Каркасные строения: укрепление каркасов и смена поврежденных частей.
Дома из кирпича: ремонт кирпичных стен и укрепление конструкций.
Дома из бетона: ремонт и укрепление бетонных конструкций, исправление трещин и разрушений.
Надежность и долговечность:
Мы используем только высококачественные материалы и новейшее оборудование, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы и прочность всех выполненных задач. Все проекты проходят тщательную проверку качества на каждой стадии реализации.
Личный подход:
Для каждого клиента мы предлагаем индивидуальные решения, с учетом всех особенностей и пожеланий. Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы результат нашей работы полностью соответствовал ваши ожидания и требования.
Почему стоит выбрать Геракл24?
Обратившись к нам, вы получаете надежного партнера, который берет на себя все заботы по ремонту и реконструкции вашего строения. Мы обеспечиваем выполнение всех проектов в установленные сроки и с в соответствии с нормами и стандартами. Выбрав Геракл24, вы можете не сомневаться, что ваше здание в надежных руках.
Мы предлагаем консультацию и ответить на ваши вопросы. Свяжитесь с нами, чтобы обсудить детали вашего проекта и узнать о наших сервисах. Мы обеспечим сохранение и улучшение вашего дома, сделав его уютным и безопасным для долгого проживания.
Геракл24 – ваш партнер по реставрации и ремонту домов в Красноярске и окрестностях.
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
Good article and right to the point. I don’t know if this is truly the best place to ask but do you people have any ideea where to get some professional writers? Thank you :)
Психология в рассказах, истории из жизни.
Thank you for helping out, great info. “Hope is the denial of reality.” by Margaret Weis.
I’ve been surfing on-line greater than three hours these days, but I by no means discovered any attention-grabbing article like yours. It¦s beautiful price enough for me. In my opinion, if all website owners and bloggers made excellent content as you did, the web will probably be much more helpful than ever before.
I always was concerned in this subject and stock still am, thanks for putting up.
There is noticeably a bundle to learn about this. I assume you made sure nice factors in features also.
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
What Is LeanBiome? LeanBiome, a new weight loss solution, includes beneficial strains of gut bacteria that work fast for weight loss.
Licenze Office in offerta
сеть сайтов pbn
Работая в поисковой оптимизации, нужно знать, что не получится одним способом вывести веб-сайт в верхние позиции поисковиков, так как поисковики это как трек с финишной прямой, а интернет-ресурсы это автомобили для гонок, которые все хотят занять первое место.
Так вот:
Перечень – Для того чтобы сайт был приспособлен и быстр, важна
улучшение
Сайт должен иметь только уникальный контент, это текст и картинки
В ОБЯЗАТЕЛЬНОМ ПОРЯДКЕ ссылочный профиль через сайты с статьями и напрямую на главную
Укрепление обратных ссылок с помощью сайтов второго уровня
Пирамида ссылок, это ссылки Tier-1, Tier-2, третьего уровня
И самое главное это личная сеть веб-сайтов PBN, которая подключается на основной сайт
Все PBN-сайты должны быть без следов, т.е. системы поиска не должны понимать, что это один хозяин всех сайтов, поэтому крайне важно следовать все эти правила.
Gerakl24: Опытная Смена Основания, Венцов, Полов и Перенос Зданий
Компания Геракл24 профессионально занимается на предоставлении комплексных услуг по смене фундамента, венцов, покрытий и переносу строений в месте Красноярске и в окрестностях. Наша команда квалифицированных экспертов гарантирует отличное качество исполнения различных типов ремонтных работ, будь то деревянные, каркасные, кирпичные постройки или бетонные дома.
Преимущества услуг Gerakl24
Навыки и знания:
Весь процесс проводятся лишь высококвалифицированными экспертами, имеющими большой практику в направлении создания и восстановления строений. Наши сотрудники эксперты в своей области и выполняют задачи с максимальной точностью и вниманием к деталям.
Всесторонний подход:
Мы предоставляем все виды работ по реставрации и восстановлению зданий:
Замена фундамента: усиление и реставрация старого основания, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы вашего здания и предотвратить проблемы, вызванные оседанием и деформацией.
Замена венцов: восстановление нижних венцов деревянных зданий, которые наиболее часто подвержены гниению и разрушению.
Установка новых покрытий: монтаж новых настилов, что кардинально улучшает визуальное восприятие и практическую полезность.
Перенос строений: безопасное и надежное перемещение зданий на другие участки, что позволяет сохранить ваше строение и предотвращает лишние расходы на возведение нового.
Работа с различными типами строений:
Деревянные дома: восстановление и укрепление деревянных конструкций, обработка от гниения и насекомых.
Каркасные строения: реставрация каркасов и смена поврежденных частей.
Кирпичные строения: реставрация кирпичной кладки и усиление стен.
Бетонные строения: восстановление и укрепление бетонных структур, устранение трещин и повреждений.
Надежность и долговечность:
Мы применяем только проверенные материалы и передовые технологии, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы и надежность всех выполненных работ. Все наши проекты подвергаются строгому контролю качества на всех этапах выполнения.
Персонализированный подход:
Каждому клиенту мы предлагаем персонализированные решения, учитывающие все особенности и пожелания. Наша цель – чтобы итог нашей работы полностью удовлетворял вашим ожиданиям и требованиям.
Почему выбирают Геракл24?
Сотрудничая с нами, вы найдете надежного партнера, который возьмет на себя все хлопоты по ремонту и реставрации вашего дома. Мы обеспечиваем выполнение всех работ в установленные сроки и с соблюдением всех строительных норм и стандартов. Связавшись с Геракл24, вы можете быть уверены, что ваше строение в надежных руках.
Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать и ответить на ваши вопросы. Контактируйте с нами, чтобы обсудить детали вашего проекта и узнать о наших сервисах. Мы обеспечим сохранение и улучшение вашего дома, обеспечив его безопасность и комфорт на долгие годы.
Gerakl24 – ваш выбор для реставрации и ремонта домов в Красноярске и области.
Some truly nice stuff on this internet site, I enjoy it.
線上娛樂城的世界
隨著網際網路的飛速發展,網上娛樂城(線上賭場)已經成為許多人消遣的新選擇。網上娛樂城不僅提供多元化的游戲選擇,還能讓玩家在家中就能體驗到賭場的樂趣和快感。本文將研究網上娛樂城的特點、優勢以及一些常見的游戲。
什麼叫線上娛樂城?
網上娛樂城是一種通過網際網路提供賭博遊戲的平台。玩家可以透過電腦設備、手機或平板電腦進入這些網站,參與各種賭博活動,如撲克、輪盤、二十一點和吃角子老虎等。這些平台通常由專業的軟體公司開發,確保遊戲的公正和安全。
線上娛樂城的好處
便利:玩家不需要離開家,就能體驗賭錢的興奮。這對於那些住在在遠離的實體賭場地區的人來說尤其方便。
多樣化的游戲選擇:在線娛樂城通常提供比實體賭場更多的游戲選擇,並且經常改進遊戲內容,保持新鮮感。
福利和獎金:許多線上娛樂城提供多樣的獎勵計劃,包括註冊獎勵、存款獎勵和忠誠度計劃,吸引新玩家並促使老玩家持續遊戲。
安全性和隱私:正當的網上娛樂城使用高端的加密技術來保護玩家的個人資料和財務交易,確保游戲過程的公平和公平。
常有的在線娛樂城游戲
德州撲克:德州撲克是最受歡迎的博彩游戲之一。網上娛樂城提供多樣撲克牌變體,如德州撲克、奧馬哈撲克和七張牌等。
輪盤:輪盤賭是一種古老的賭場遊戲遊戲,玩家可以賭注在數字、數字組合上或顏色上上,然後看轉球落在哪個位置。
黑傑克:又稱為二十一點,這是一種競爭玩家和莊家點數的遊戲,目標是讓手牌點數盡量接近21點但不超過。
吃角子老虎:吃角子老虎是最容易且是最常見的賭博游戲之一,玩家只需轉捲軸,等待圖案排列出贏得的組合。
總結
線上娛樂城為現代的賭博愛好者提供了一個方便、興奮且多元化的娛樂方式。不論是撲克牌愛好者還是老虎機迷,大家都能在這些平台上找到適合自己的遊戲。同時,隨著科技的不斷提升,線上娛樂城的游戲體驗將變得越來越逼真和有趣。然而,玩家在享用游戲的同時,也應該保持,避免沉溺於賭錢活動,維持健康的娛樂心態。
This really answered my downside, thank you!
This really answered my problem, thank you!
An interesting discussion is worth comment. I think that you should write more on this topic, it might not be a taboo subject but generally people are not enough to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
I wanted to thank you for this great read!! I definitely enjoying every little bit of it I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you post…
Explore Exciting Offers and Bonus Spins: Your Comprehensive Guide
At our gaming platform, we are focused to providing you with the best gaming experience possible. Our range of deals and free rounds ensures that every player has the chance to enhance their gameplay and increase their chances of winning. Here’s how you can take advantage of our amazing promotions and what makes them so special.
Bountiful Free Rounds and Rebate Deals
One of our standout offers is the opportunity to earn up to 200 bonus spins and a 75% cashback with a deposit of just $20 or more. And during happy hour, you can unlock this bonus with a deposit starting from just $10. This unbelievable offer allows you to enjoy extended playtime and more opportunities to win without breaking the bank.
Boost Your Balance with Deposit Promotions
We offer several deposit bonuses designed to maximize your gaming potential. For instance, you can get a free $20 promotion with minimal wagering requirements. This means you can start playing with extra funds, giving you more chances to explore our vast array of games and win big. Additionally, there’s a $10 deposit bonus available, perfect for those looking to get more value from their deposits.
Multiply Your Deposits for Bigger Wins
Our “Play Big!” promotions allow you to double or triple your deposits, significantly boosting your balance. Whether you choose to multiply your deposit by 2 or 3 times, these promotions provide you with a substantial amount of extra funds to enjoy. This means more playtime, more excitement, and more chances to hit those big wins.
Exciting Free Spins on Popular Games
We also offer up to 1000 free spins per deposit on some of the most popular games in the industry. Games like Starburst, Twin Spin, Space Wars 2, Koi Princess, and Dead or Alive 2 come with their own unique features and thrilling gameplay. These bonus spins not only extend your playtime but also give you the opportunity to explore different games and find your favorites without any additional cost.
Why Choose Our Platform?
Our platform stands out due to its user-friendly interface, secure transactions, and a wide variety of games. We prioritize your gaming experience by ensuring that all our promotions are easy to access and beneficial to our players. Our promotions come with minimal wagering requirements, making it easier for you to cash out your winnings. Moreover, the variety of games we offer ensures that there’s something for every type of player, from classic slot enthusiasts to those who enjoy more modern, feature-packed games.
Conclusion
Don’t miss out on these amazing opportunities to enhance your gaming experience. Whether you’re looking to enjoy bonus spins, rebate, or lavish deposit bonuses, we have something for everyone. Join us today, take advantage of these amazing promotions, and start your journey to big wins and endless fun. Happy gaming!
sapporo88
sapporo88
Captivating Developments and Renowned Releases in the World of Digital Entertainment
In the ever-evolving environment of digital entertainment, there’s perpetually something groundbreaking and thrilling on the forefront. From enhancements optimizing revered timeless titles to forthcoming releases in renowned series, the videogame landscape is thriving as in current times.
Here’s a overview into the up-to-date news and specific the iconic titles mesmerizing enthusiasts worldwide.
Newest Announcements
1. New Enhancement for Skyrim Enhances NPC Look
A newly-released modification for The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim has captured the notice of players. This enhancement brings lifelike heads and flowing hair for all non-player characters, enhancing the experience’s graphics and immersiveness.
2. Total War Games Release Situated in Star Wars Universe Realm Under Development
The Creative Assembly, famous for their Total War Games franchise, is supposedly working on a forthcoming release situated in the Star Wars Universe galaxy. This thrilling combination has fans awaiting the analytical and engaging experience that Total War Games releases are known for, at last set in a realm far, far away.
3. Grand Theft Auto VI Launch Announced for Autumn 2025
Take-Two Interactive’s Chief Executive Officer has communicated that GTA VI is scheduled to launch in Q4 2025. With the overwhelming popularity of its prior release, Grand Theft Auto V, players are excited to explore what the future installment of this legendary franchise will offer.
4. Expansion Initiatives for Skull & Bones Season Two
Designers of Skull & Bones have announced enhanced initiatives for the world’s second season. This pirate-themed experience offers additional updates and improvements, sustaining fans immersed and enthralled in the universe of oceanic swashbuckling.
5. Phoenix Labs Faces Staff Cuts
Disappointingly, not every developments is uplifting. Phoenix Labs Studio, the creator developing Dauntless Experience, has revealed significant workforce reductions. Regardless of this challenge, the experience persists to be a popular choice within players, and the team stays committed to its fanbase.
Renowned Releases
1. The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt
With its engaging experience, absorbing domain, and compelling adventure, The Witcher 3 Game keeps a revered game within enthusiasts. Its intricate narrative and vast open world continue to captivate fans in.
2. Cyberpunk 2077
Regardless of a problematic arrival, Cyberpunk 2077 Game stays a much-anticipated experience. With constant updates and enhancements, the game persists in evolve, providing players a perspective into a cyberpunk environment teeming with mystery.
3. Grand Theft Auto V
Still decades after its initial arrival, GTA 5 keeps a iconic preference amidst enthusiasts. Its expansive sandbox, enthralling story, and shared mode sustain enthusiasts returning for more explorations.
4. Portal
A legendary brain-teasing game, Portal 2 Game is acclaimed for its innovative features and ingenious map design. Its demanding challenges and witty storytelling have established it as a standout game in the videogame realm.
5. Far Cry
Far Cry Game is praised as a standout installments in the universe, presenting enthusiasts an free-roaming experience rife with danger. Its captivating plot and iconic personalities have cemented its status as a fan favorite experience.
6. Dishonored Game
Dishonored Game is celebrated for its stealth features and exceptional setting. Enthusiasts adopt the role of a otherworldly executioner, traversing a metropolis filled with societal intrigue.
7. Assassin’s Creed
As part of the renowned Assassin’s Creed Series lineup, Assassin’s Creed is cherished for its compelling story, compelling systems, and era-based realms. It stays a exceptional experience in the franchise and a favorite among gamers.
In conclusion, the universe of gaming is thriving and ever-changing, with fresh advan
You really make it appear really easy along with your presentation but I find this matter to be really one thing that I think I would by no means understand. It kind of feels too complicated and very huge for me. I am taking a look ahead in your subsequent put up, I¦ll attempt to get the hold of it!
এক রোমাঞ্চকর খেলা এবং জনপ্রিয় বোনাস
বিশ্ববিদ্যালয় ক্রিকেট ফেডারেশন এর সম্মুখীন অংশগ্রহণের প্রস্তাবনা পান, আমরা আনন্দিত এবং অপেক্ষায় আছি যে সম্মুখীন খেলা এবং অনেক সুযোগ প্রদান করা হয়েছে। আমরা আপনাকে একটি অদ্ভুত স্বাগত বোনাসের সুযোগ প্রদান করতে চাই, যা আপনি প্রথম আমানতে 200% পাবেন। এছাড়াও, আমরা সাপ্তাহিক এফবি শেয়ার করে ১০০ টাকা বোনাস প্রদান করি এবং প্রতিদিন ১০০% বোনাস প্রদান করা হয়। এই সময়ে আমরা আমাদের সবচেয়ে বেশি খেলা এবং জনপ্রিয় খেলা – ব্যাকারাট, লাইভশো, ফিশিং, এবং স্লট আমাদের নিখুঁতভাবে চেষ্টা করি।
আমাদের ক্রিকেট এক্সচেঞ্জ অংশগ্রহণ করে আপনি এই সব আনন্দ এবং বোনাস থেকে উপভোগ করতে পারেন। আমাদের অনেক উচ্চমানের খেলা এবং সাথেই জনপ্রিয় খেলা সহ বিভিন্ন বোনাস প্রদান করা হয়েছে এবং সাথেই অনেক আরও আকর্ষণীয় বোনাস আপনাকে আশা করছি।
আমাদের সাথে যোগাযোগ করুন cricket affiliate প্রোগ্রামে অংশগ্রহণ করতে এবং সরাসরি crickex affiliate login এবং crickex login করুন। সাথেই আপনি 9wicket খেলার অনুভব করতে পারেন এবং এটি অপূর্ব এবং রোমাঞ্চকর হয়ে উঠবে। তাহলে, আপনি কি অপেক্ষা করছেন? এখনই যোগ দিন এবং সবচেয়ে জনপ্রিয় খেলা এবং স্বাগত বোনাস পেতে শুরু করুন!
Welcome to Cricket Affiliate | Kick off with a smashing Welcome Bonus !
First Deposit Fiesta! | Make your debut at Cricket Exchange with a 200% bonus.
Daily Doubles! | Keep the scoreboard ticking with a 100% daily bonus at 9wicket!
#cricketaffiliate
IPL 2024 Jackpot! | Stand to win ₹50,000 in the mega IPL draw at cricket world!
Social Sharer Rewards! | Post and earn 100 tk weekly through Crickex affiliate login.
https://www.cricket-affiliate.com/
#cricketexchange #9wicket #crickexaffiliatelogin #crickexlogin
crickex login VIP! | Step up as a VIP and enjoy weekly bonuses!
Join the Action! | Log in through crickex bet exciting betting experience at Live Affiliate.
Dive into the game with crickex live—where every play brings spectacular wins !
Uncover Thrilling Bonuses and Extra Spins: Your Definitive Guide
At our gaming platform, we are devoted to providing you with the best gaming experience possible. Our range of deals and free spins ensures that every player has the chance to enhance their gameplay and increase their chances of winning. Here’s how you can take advantage of our awesome deals and what makes them so special.
Generous Extra Spins and Rebate Offers
One of our standout promotions is the opportunity to earn up to 200 bonus spins and a 75% rebate with a deposit of just $20 or more. And during happy hour, you can unlock this bonus with a deposit starting from just $10. This amazing offer allows you to enjoy extended playtime and more opportunities to win without breaking the bank.
Boost Your Balance with Deposit Bonuses
We offer several deposit bonuses designed to maximize your gaming potential. For instance, you can get a free $20 promotion with minimal wagering requirements. This means you can start playing with extra funds, giving you more chances to explore our vast array of games and win big. Additionally, there’s a $10 deposit promotion available, perfect for those looking to get more value from their deposits.
Multiply Your Deposits for Bigger Wins
Our “Play Big!” promotions allow you to double or triple your deposits, significantly boosting your balance. Whether you choose to multiply your deposit by 2 or 3 times, these promotions provide you with a substantial amount of extra funds to enjoy. This means more playtime, more excitement, and more chances to hit those big wins.
Exciting Bonus Spins on Popular Games
We also offer up to 1000 free spins per deposit on some of the most popular games in the industry. Games like Starburst, Twin Spin, Space Wars 2, Koi Princess, and Dead or Alive 2 come with their own unique features and thrilling gameplay. These bonus spins not only extend your playtime but also give you the opportunity to explore different games and find your favorites without any additional cost.
Why Choose Our Platform?
Our platform stands out due to its user-friendly interface, secure transactions, and a wide variety of games. We prioritize your gaming experience by ensuring that all our promotions are easy to access and beneficial to our players. Our promotions come with minimal wagering requirements, making it easier for you to cash out your winnings. Moreover, the variety of games we offer ensures that there’s something for every type of player, from classic slot enthusiasts to those who enjoy more modern, feature-packed games.
Conclusion
Don’t miss out on these unbelievable opportunities to enhance your gaming experience. Whether you’re looking to enjoy free spins, cashback, or bountiful deposit promotions, we have something for everyone. Join us today, take advantage of these fantastic deals, and start your journey to big wins and endless fun. Happy gaming!
Daily bonuses
Uncover Thrilling Promotions and Extra Spins: Your Comprehensive Guide
At our gaming platform, we are dedicated to providing you with the best gaming experience possible. Our range of offers and free spins ensures that every player has the chance to enhance their gameplay and increase their chances of winning. Here’s how you can take advantage of our fantastic offers and what makes them so special.
Lavish Free Rounds and Rebate Deals
One of our standout offers is the opportunity to earn up to 200 bonus spins and a 75% cashback with a deposit of just $20 or more. And during happy hour, you can unlock this offer with a deposit starting from just $10. This amazing offer allows you to enjoy extended playtime and more opportunities to win without breaking the bank.
Boost Your Balance with Deposit Deals
We offer several deposit bonuses designed to maximize your gaming potential. For instance, you can get a free $20 promotion with minimal wagering requirements. This means you can start playing with extra funds, giving you more chances to explore our vast array of games and win big. Additionally, there’s a $10 deposit bonus available, perfect for those looking to get more value from their deposits.
Multiply Your Deposits for Bigger Wins
Our “Play Big!” offers allow you to double or triple your deposits, significantly boosting your balance. Whether you choose to multiply your deposit by 2 or 3 times, these offers provide you with a substantial amount of extra funds to enjoy. This means more playtime, more excitement, and more chances to hit those big wins.
Exciting Free Spins on Popular Games
We also offer up to 1000 free spins per deposit on some of the most popular games in the industry. Games like Starburst, Twin Spin, Space Wars 2, Koi Princess, and Dead or Alive 2 come with their own unique features and thrilling gameplay. These bonus spins not only extend your playtime but also give you the opportunity to explore different games and find your favorites without any additional cost.
Why Choose Our Platform?
Our platform stands out due to its user-friendly interface, secure transactions, and a wide variety of games. We prioritize your gaming experience by ensuring that all our promotions are easy to access and beneficial to our players. Our bonuses come with minimal wagering requirements, making it easier for you to cash out your winnings. Moreover, the variety of games we offer ensures that there’s something for every type of player, from classic slot enthusiasts to those who enjoy more modern, feature-packed games.
Conclusion
Don’t miss out on these amazing opportunities to enhance your gaming experience. Whether you’re looking to enjoy bonus spins, rebate, or bountiful deposit bonuses, we have something for everyone. Join us today, take advantage of these amazing deals, and start your journey to big wins and endless fun. Happy gaming!
भारत में ऑनलाइन क्रिकेट सट्टेबाजी की बढ़ती लोकप्रियता
भारत में ऑनलाइन क्रिकेट सट्टेबाजी की लोकप्रियता का तेजी से बढ़ना कई कारकों का परिणाम है। इनमें से कुछ प्रमुख कारक निम्नानुसार हैं:
इंटरनेट और स्मार्टफोन की बढ़ती पहुंच:
देश के कोने-कोने में इंटरनेट की उपलब्धता और किफायती डेटा प्लान्स ने लोगों को ऑनलाइन प्लेटफॉर्म्स पर क्रिकेट सट्टेबाजी में भाग लेने की सुविधा दी है। इसके अतिरिक्त, सस्ते और प्रभावी स्मार्टफोन्स की उपलब्धता ने यह और भी सरल बना दिया है। अब लोग अपने मोबाइल डिवाइसों के माध्यम से बेटवीसा जैसे ऑनलाइन कैसीनो और खेल प्लेटफॉर्मों पर कहीं से भी और कभी भी सट्टेबाजी कर सकते हैं।
क्रिकेट लीग और टूर्नामेंट्स की बढ़ती संख्या:
आईपीएल (Indian Premier League) ने भारतीय क्रिकेट को एक नया आयाम दिया है, और इसका ग्लैमर तथा वैश्विक अपील सट्टेबाजों के लिए अत्यधिक आकर्षक है। इसके अलावा, बीबीएल (Big Bash League), सीपीएल (Caribbean Premier League), और पीएसएल (Pakistan Super League) जैसे अंतरराष्ट्रीय लीग्स ने भी भारतीय सट्टेबाजों को लुभाया है।
कानूनी स्थिति और सुरक्षा:
भले ही भारत में सट्टेबाजी के कानून जटिल और राज्यों के हिसाब से भिन्न हैं, कई ऑनलाइन प्लेटफॉर्म्स जैसे बेटवीसा ने सुरक्षित और भरोसेमंद सेवाएं प्रदान कर खिलाड़ियों का विश्वास जीता है। इनके पास कुराकाओ गेमिंग लाइसेंस है और वे खिलाड़ियों की सुरक्षा और गोपनीयता का ध्यान रखते हैं। इसके अलावा, सुरक्षित और तेज़ डिजिटल भुगतान विकल्पों ने भी ऑनलाइन सट्टेबाजी को बढ़ावा दिया है।
आसान और यूज़र-फ्रेंडली प्लेटफॉर्म्स:
ऑनलाइन सट्टेबाजी प्लेटफॉर्म्स ने उपयोगकर्ताओं के लिए सट्टेबाजी को सरल और सहज बना दिया है। आधुनिक और यूज़र-फ्रेंडली इंटरफेस ने नए खिलाड़ियों के लिए भी सट्टेबाजी को आसान बना दिया है। साथ ही, लाइव सट्टेबाजी के विकल्पों ने रोमांच और भी बढ़ा दिया है।
सामाजिक और मनोरंजक तत्व:
क्रिकेट सट्टेबाजी सिर्फ पैसे कमाने का साधन नहीं है, बल्कि यह मनोरंजन और सामाजिक गतिविधि का भी हिस्सा बन गया है। खिलाड़ी अपने दोस्तों और परिवार के सदस्यों के साथ मिलकर सट्टेबाजी करते हैं और मैचों का आनंद लेते हैं। इसके अलावा, सट्टेबाजी ने क्रिकेट मैच देखने के रोमांच को कई गुना बढ़ा दिया है।
विशेषज्ञता और जानकारी की उपलब्धता:
क्रिकेट सट्टेबाजी में सफलता के लिए विशेषज्ञता और जानकारी की महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका है। कई वेबसाइट्स और ऐप्स सट्टेबाजों को मैचों का विश्लेषण, भविष्यवाणियां और सट्टेबाजी टिप्स प्रदान करते हैं। साथ ही, लाइव स्ट्रीमिंग और अपडेट्स की सुविधा ने सट्टेबाजों को मैच की हर बारीकी पर नजर रखने में मदद की है।
इन सभी कारकों के साथ-साथ, प्रमुख ऑनलाइन प्लेटफॉर्म्स जैसे बेटवीसा की भूमिका भी महत्वपूर्ण है। बेटवीसा ने भारत में ऑनलाइन क्रिकेट सट्टेबाजी को बढ़ावा देने में महत्वपूर्ण योगदान दिया है। इसके उपयोग में आसानी, सुरक्षा उपाय, और विश्वसनीय सेवाएं भारतीय खिलाड़ियों को आकर्षित करती हैं।
निष्कर्ष के रूप में, यह कहा जा सकता है कि भारत में ऑनलाइन क्रिकेट सट्टेबाजी की लोकप्रियता का तेजी से बढ़ना कई कारकों का परिणाम है, और आने वाले समय में यह रुझान जारी रहेगा।
Betvisa Bet
Betvisa Bet | Catch the BPL Excitement with Betvisa!
Hunt for ₹10million! | Enter the BPL at Betvisa and chase a staggering Bounty.
Valentine’s Boost at Visa Bet! | Feel the rush of a 143% Love Mania Bonus .
predict BPL T20 outcomes | score big rewards through Betvisa login!
#betvisa
Betvisa bonus Win! | Leverage your 10 free spins to possibly win $8,888.
Share and Earn! | win ₹500 via the Betvisa app download!
https://www.betvisa-bet.com/hi
#visabet #betvisalogin #betvisaapp #betvisaIndia
Sign-Up Jackpot! | Register at Betvisa India and win ₹8,888.
Double your play! | with a ₹1,000 deposit and get ₹2,000 free at Betvisa online!
Download the Betvisa download today and don’t miss out on the action!
I like what you guys are usually up too. This type of clever work and reporting! Keep up the wonderful works guys I’ve included you guys to my blogroll.
Hi! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I really enjoy reading through your blog posts. Can you suggest any other blogs/websites/forums that cover the same subjects? Many thanks!
borju89
game reviews
Engaging Innovations and Iconic Franchises in the Domain of Gaming
In the ever-evolving realm of videogames, there’s continuously something fresh and exciting on the cusp. From modifications elevating iconic classics to anticipated launches in iconic universes, the interactive entertainment realm is prospering as in recent memory.
Here’s a snapshot into the most recent news and some of the iconic experiences mesmerizing players across the globe.
Latest News
1. Cutting-Edge Mod for Skyrim Elevates NPC Visuals
A recent customization for Skyrim has attracted the attention of fans. This enhancement implements lifelike heads and hair physics for each non-player characters, enhancing the title’s graphics and engagement.
2. Total War Games Experience Located in Star Wars Universe in Development
Creative Assembly, acclaimed for their Total War Series lineup, is allegedly developing a anticipated experience situated in the Star Wars Setting galaxy. This thrilling crossover has fans eagerly anticipating the tactical and engaging experience that Total War Games titles are celebrated for, finally situated in a realm far, far away.
3. Grand Theft Auto VI Debut Announced for Fall 2025
Take-Two’s Head has announced that Grand Theft Auto VI is planned to debut in Autumn 2025. With the colossal popularity of its prior release, Grand Theft Auto V, gamers are excited to explore what the upcoming sequel of this renowned series will provide.
4. Growth Plans for Skull & Bones Sophomore Season
Studios of Skull and Bones have communicated amplified developments for the game’s second season. This swashbuckling journey promises fresh features and enhancements, maintaining players invested and immersed in the universe of maritime swashbuckling.
5. Phoenix Labs Developer Faces Staff Cuts
Unfortunately, not everything updates is uplifting. Phoenix Labs, the studio responsible for Dauntless Experience, has announced large-scale staff cuts. Regardless of this setback, the game remains to be a renowned option across fans, and the studio stays attentive to its community.
Renowned Games
1. The Witcher 3
With its engaging story, captivating domain, and enthralling experience, The Witcher 3 remains a beloved release across players. Its rich story and wide-ranging free-roaming environment keep to draw enthusiasts in.
2. Cyberpunk
In spite of a rocky arrival, Cyberpunk 2077 continues to be a highly anticipated title. With ongoing improvements and enhancements, the game persists in improve, providing enthusiasts a glimpse into a cyberpunk setting filled with peril.
3. Grand Theft Auto 5
Yet eras subsequent to its initial arrival, GTA 5 keeps a beloved option among fans. Its expansive nonlinear world, engaging story, and shared components maintain fans coming back for further explorations.
4. Portal 2
A legendary brain-teasing title, Portal 2 Game is celebrated for its revolutionary systems and ingenious environmental design. Its demanding conundrums and clever narrative have made it a remarkable release in the digital entertainment landscape.
5. Far Cry Game
Far Cry Game is celebrated as a standout titles in the brand, presenting players an open-world journey abundant with danger. Its compelling experience and iconic entities have solidified its standing as a iconic game.
6. Dishonored
Dishonored Game is hailed for its covert gameplay and exceptional world. Fans embrace the persona of a otherworldly executioner, exploring a metropolitan area teeming with political intrigue.
7. Assassin’s Creed II
As part of the acclaimed Assassin’s Creed Universe lineup, Assassin’s Creed 2 is adored for its engrossing plot, engaging systems, and period realms. It keeps a standout game in the universe and a favorite across fans.
In summary, the realm of gaming is vibrant and ever-changing, with fresh developments
video games guide
Exciting Advancements and Iconic Titles in the Realm of Videogames
In the fluid realm of gaming, there’s continuously something new and captivating on the horizon. From modifications improving iconic staples to new releases in renowned franchises, the videogame industry is flourishing as in current times.
We’ll take a glimpse into the latest developments and certain the iconic experiences mesmerizing players worldwide.
Latest Updates
1. Innovative Mod for The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim Improves Non-Player Character Look
A newly-released enhancement for Skyrim has caught the notice of players. This customization introduces lifelike faces and flowing hair for each non-player entities, elevating the world’s visual appeal and engagement.
2. Total War Games Game Set in Star Wars Universe World Under Development
The Creative Assembly, famous for their Total War series, is said to be creating a forthcoming title placed in the Star Wars Setting world. This thrilling combination has players looking forward to the strategic and compelling experience that Total War Games titles are known for, now placed in a world remote.
3. GTA VI Release Communicated for Late 2025
Take-Two’s CEO has revealed that GTA VI is expected to arrive in Autumn 2025. With the overwhelming popularity of its previous installment, Grand Theft Auto V, players are anticipating to witness what the forthcoming iteration of this legendary series will deliver.
4. Extension Developments for Skull and Bones Season Two
Creators of Skull and Bones have disclosed enhanced plans for the game’s sophomore season. This high-seas experience offers additional content and changes, sustaining enthusiasts invested and immersed in the world of high-seas swashbuckling.
5. Phoenix Labs Faces Staff Cuts
Regrettably, not every announcements is favorable. Phoenix Labs Studio, the team responsible for Dauntless Game, has announced substantial workforce reductions. Despite this setback, the game keeps to be a iconic choice within players, and the studio keeps committed to its community.
Iconic Releases
1. The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt
With its engaging narrative, immersive universe, and compelling adventure, The Witcher 3 continues to be a revered experience across enthusiasts. Its expansive story and wide-ranging free-roaming environment continue to attract gamers in.
2. Cyberpunk 2077 Game
Notwithstanding a rocky arrival, Cyberpunk remains a much-anticipated experience. With persistent patches and adjustments, the title continues to advance, providing fans a view into a cyberpunk environment filled with mystery.
3. GTA 5
Still years subsequent to its first launch, Grand Theft Auto 5 remains a beloved choice within players. Its vast open world, enthralling story, and shared features sustain gamers coming back for further journeys.
4. Portal
A classic brain-teasing game, Portal 2 Game is acclaimed for its innovative systems and ingenious map design. Its challenging puzzles and witty dialogue have solidified it as a remarkable title in the videogame industry.
5. Far Cry 3 Game
Far Cry is hailed as one of the best titles in the series, offering enthusiasts an open-world journey rife with danger. Its compelling experience and memorable entities have established its status as a fan favorite title.
6. Dishonored Universe
Dishonored Universe is acclaimed for its sneaky gameplay and distinctive environment. Players embrace the role of a extraordinary executioner, traversing a metropolitan area filled with institutional peril.
7. Assassin’s Creed Game
As part of the iconic Assassin’s Creed Franchise series, Assassin’s Creed Game is adored for its immersive story, captivating mechanics, and period realms. It stays a remarkable title in the collection and a iconic within enthusiasts.
In conclusion, the world of gaming is flourishing and dynamic, with groundbreaking advan
Some truly nice stuff on this internet site, I love it.
I truly appreciate this post. I have been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thank you again
supermoney88
sunmory33
BetVisa: Asia’s Premier Online Gambling Destination
BetVisa, an online gambling platform that has been making waves in the Asian market since its inception in 2017, has established itself as a leading and trusted name in the industry. With a Curacao gaming license and over 2 million users, BetVisa offers a comprehensive suite of gaming options that cater to a diverse range of player preferences.
One of the standout features of BetVisa is its extensive selection of slot games, live casinos, lotteries, sportsbooks, sports exchanges, and e-sports. This diverse portfolio ensures that players can enjoy a wide variety of gaming experiences, from the thrill of spinning the reels to the adrenaline-fueled action of sports betting.
In addition to its impressive game selection, BetVisa also prides itself on providing a seamless and secure user experience. The platform offers a variety of convenient and reliable payment methods, making it easy for players to deposit and withdraw funds. Furthermore, BetVisa’s 24-hour friendly live customer support ensures that any queries or concerns are addressed promptly and efficiently.
For those seeking to explore the world of online gambling, BetVisa presents an enticing opportunity. With its user-friendly interface, diverse game selection, and commitment to security and customer satisfaction, BetVisa has quickly become a go-to destination for players across Asia.
Whether you’re a seasoned gambler or a newcomer to the world of online gaming, BetVisa offers a safe and exciting platform to indulge in your favorite games. From the thrill of sports betting on the Visa Bet platform to the immersive experience of the BetVisa casino, the possibilities are endless.
So, why not join the millions of players who have already discovered the unparalleled excitement and convenience of BetVisa? Log in to the platform, explore its vast array of gaming options, and embark on a journey that promises endless entertainment and the chance to win big.
Betvisa Bet | Step into the Arena with Betvisa!
Spin to Win Daily at Betvisa PH! | Take a whirl and bag ?8,888 in big rewards.
Valentine’s 143% Love Boost at Visa Bet! | Celebrate romance and rewards !
Deposit Bonus Magic! | Deposit 50 and get an 88 bonus instantly at Betvisa Casino.
#betvisa
Free Cash & More Spins! | Sign up betvisa login,grab 500 free cash plus 5 free spins.
Sign-Up Fortune | Join through betvisa app for a free ?500 and fabulous ?8,888.
https://www.betvisa-bet.com/tl
#visabet #betvisalogin #betvisacasino # betvisaph
Double Your Play at betvisa com! | Deposit 1,000 and get a whopping 2,000 free
100% Cock Fight Welcome at Visa Bet! | Plunge into the exciting world .Bet and win!
Jump into Betvisa for exciting games, stunning bonuses, and endless winnings!
ANGKOT88: Situs Game Deposit Pulsa Terbaik di Indonesia
ANGKOT88 adalah situs game deposit pulsa terbaik tahun 2020 di Indonesia. Kami menyediakan berbagai jenis game online terlengkap yang dapat Anda mainkan hanya dengan mendaftar satu ID. Dengan satu ID tersebut, Anda dapat mengakses seluruh permainan yang tersedia di situs kami.
Sebagai situs agen game online berlisensi resmi dari PAGCOR (Philippine Amusement Gaming Corporation), ANGKOT88 menjamin keamanan dan kenyamanan Anda. Situs kami didukung oleh server hosting yang cepat dan sistem keamanan dengan metode enkripsi terbaru di dunia, sehingga data Anda akan selalu terjaga keamanannya. Tampilan situs yang modern juga membuat Anda merasa nyaman saat mengakses situs kami.
Keunggulan ANGKOT88
Selain menjadi situs game online terbaik, ANGKOT88 juga menawarkan layanan praktis untuk melakukan deposit menggunakan pulsa XL ataupun Telkomsel dengan potongan terendah dibandingkan situs lainnya. Ini menjadikan kami salah satu situs game online pulsa terbesar di Indonesia. Anda juga dapat melakukan deposit pulsa melalui E-commerce resmi seperti OVO, Gopay, Dana, atau melalui minimarket seperti Indomaret dan Alfamart.
Kepercayaan dan Layanan
Kami di ANGKOT88 sangat menjaga kepercayaan Anda sebagai prioritas utama kami. Oleh karena itu, kami selalu berusaha menjadi agen online terpercaya dan terbaik sepanjang masa. Permainan game online yang kami tawarkan sangat praktis, sehingga Anda dapat memainkannya kapan saja dan di mana saja tanpa perlu repot bepergian. Kami menyediakan berbagai jenis game, termasuk yang disiarkan secara LIVE (langsung) dengan host cantik dan kamera yang merekam secara real-time, menjadikan ANGKOT88 situs game online terlengkap dan terbesar di Indonesia.
Promo Menarik dan Menguntungkan
ANGKOT88 juga menawarkan banyak sekali promo menarik dan menguntungkan. Anda bisa menikmati berbagai macam promo yang sesuai dengan kebutuhan Anda, seperti welcome bonus 20%, bonus deposit harian, dan cashback. Semua promo ini tersedia di situs ANGKOT88. Selain itu, kami juga memiliki layanan Customer Service yang siap membantu Anda kapan saja.
Jadi, tunggu apa lagi? Bergabunglah dengan ANGKOT88 dan nikmati pengalaman bermain game online terbaik dan teraman di Indonesia. Daftarkan diri Anda sekarang dan mulai mainkan game favorit Anda dengan nyaman dan aman di situs kami!
supermoney88
SUPERMONEY88: Situs Game Online Deposit Pulsa Terbaik di Indonesia
SUPERMONEY88 adalah situs game online deposit pulsa terbaik tahun 2020 di Indonesia. Kami menyediakan berbagai macam game online terbaik dan terlengkap yang bisa Anda mainkan di situs game online kami. Hanya dengan mendaftar satu ID, Anda bisa memainkan seluruh permainan yang tersedia di SUPERMONEY88.
Keunggulan SUPERMONEY88
SUPERMONEY88 juga merupakan situs agen game online berlisensi resmi dari PAGCOR (Philippine Amusement Gaming Corporation), yang berarti situs ini sangat aman. Kami didukung dengan server hosting yang cepat dan sistem keamanan dengan metode enkripsi termutakhir di dunia untuk menjaga keamanan database Anda. Selain itu, tampilan situs kami yang sangat modern membuat Anda nyaman mengakses situs kami.
Layanan Praktis dan Terpercaya
Selain menjadi game online terbaik, ada alasan mengapa situs SUPERMONEY88 ini sangat spesial. Kami memberikan layanan praktis untuk melakukan deposit yaitu dengan melakukan deposit pulsa XL ataupun Telkomsel dengan potongan terendah dari situs game online lainnya. Ini membuat situs kami menjadi salah satu situs game online pulsa terbesar di Indonesia. Anda bisa melakukan deposit pulsa menggunakan E-commerce resmi seperti OVO, Gopay, Dana, atau melalui minimarket seperti Indomaret dan Alfamart.
Kami juga terkenal sebagai agen game online terpercaya. Kepercayaan Anda adalah prioritas kami, dan itulah yang membuat kami menjadi agen game online terbaik sepanjang masa.
Kemudahan Bermain Game Online
Permainan game online di SUPERMONEY88 memudahkan Anda untuk memainkannya dari mana saja dan kapan saja. Anda tidak perlu repot bepergian lagi, karena SUPERMONEY88 menyediakan beragam jenis game online. Kami juga memiliki jenis game online yang dipandu oleh host cantik, sehingga Anda tidak akan merasa bosan.
Nice post. I was checking constantly this blog and I am impressed! Extremely useful information specially the last part :) I care for such information a lot. I was seeking this particular information for a long time. Thank you and best of luck.
sapporo88
SUPERMONEY88: Situs Game Online Deposit Pulsa Terbaik di Indonesia
SUPERMONEY88 adalah situs game online deposit pulsa terbaik tahun 2020 di Indonesia. Kami menyediakan berbagai macam game online terbaik dan terlengkap yang bisa Anda mainkan di situs game online kami. Hanya dengan mendaftar satu ID, Anda bisa memainkan seluruh permainan yang tersedia di SUPERMONEY88.
Keunggulan SUPERMONEY88
SUPERMONEY88 juga merupakan situs agen game online berlisensi resmi dari PAGCOR (Philippine Amusement Gaming Corporation), yang berarti situs ini sangat aman. Kami didukung dengan server hosting yang cepat dan sistem keamanan dengan metode enkripsi termutakhir di dunia untuk menjaga keamanan database Anda. Selain itu, tampilan situs kami yang sangat modern membuat Anda nyaman mengakses situs kami.
Layanan Praktis dan Terpercaya
Selain menjadi game online terbaik, ada alasan mengapa situs SUPERMONEY88 ini sangat spesial. Kami memberikan layanan praktis untuk melakukan deposit yaitu dengan melakukan deposit pulsa XL ataupun Telkomsel dengan potongan terendah dari situs game online lainnya. Ini membuat situs kami menjadi salah satu situs game online pulsa terbesar di Indonesia. Anda bisa melakukan deposit pulsa menggunakan E-commerce resmi seperti OVO, Gopay, Dana, atau melalui minimarket seperti Indomaret dan Alfamart.
Kami juga terkenal sebagai agen game online terpercaya. Kepercayaan Anda adalah prioritas kami, dan itulah yang membuat kami menjadi agen game online terbaik sepanjang masa.
Kemudahan Bermain Game Online
Permainan game online di SUPERMONEY88 memudahkan Anda untuk memainkannya dari mana saja dan kapan saja. Anda tidak perlu repot bepergian lagi, karena SUPERMONEY88 menyediakan beragam jenis game online. Kami juga memiliki jenis game online yang dipandu oleh host cantik, sehingga Anda tidak akan merasa bosan.
sunmory33
pro88
PRO88: Situs Game Online Deposit Pulsa Terbaik di Indonesia
PRO88 adalah situs game online deposit pulsa terbaik tahun 2020 di Indonesia. Kami menyediakan berbagai macam game online terbaik dan terlengkap yang bisa Anda mainkan di situs game online kami. Hanya dengan mendaftar satu ID, Anda bisa memainkan seluruh permainan yang tersedia di PRO88.
Keunggulan PRO88
PRO88 juga merupakan situs agen game online berlisensi resmi dari PAGCOR (Philippine Amusement Gaming Corporation), yang berarti situs ini sangat aman. Kami didukung dengan server hosting yang cepat dan sistem keamanan dengan metode enkripsi termutakhir di dunia untuk menjaga keamanan database Anda. Selain itu, tampilan situs kami yang sangat modern membuat Anda nyaman mengakses situs kami.
Berbagai Macam Game Online
Kami menyediakan berbagai macam game online terbaik yang bisa Anda mainkan kapan saja dan di mana saja. Dengan satu ID, Anda bisa menikmati semua permainan yang tersedia, mulai dari permainan kartu, slot, hingga taruhan olahraga. PRO88 memastikan semua game yang kami sediakan adalah yang terbaik dan terlengkap di Indonesia.
Keamanan dan Kenyamanan
Kami memahami betapa pentingnya keamanan dan kenyamanan bagi para pemain. Oleh karena itu, PRO88 menggunakan server hosting yang cepat dan sistem keamanan dengan metode enkripsi termutakhir di dunia. Ini memastikan bahwa data pribadi dan transaksi Anda selalu aman bersama kami. Tampilan situs yang modern juga dirancang untuk memberikan pengalaman bermain yang nyaman dan menyenangkan.
Kesimpulan
PRO88 adalah pilihan terbaik untuk Anda yang mencari situs game online deposit pulsa yang aman dan terpercaya. Dengan berbagai macam game online terbaik dan terlengkap, serta dukungan keamanan yang canggih, PRO88 siap memberikan pengalaman bermain game yang tak terlupakan. Daftar sekarang juga di PRO88 dan nikmati semua permainan yang tersedia hanya dengan satu ID.
Kunjungi kami di PRO88 dan mulailah petualangan game online Anda bersama kami!
supermoney88
Greetings! I know this is kinda off topic however I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest authoring a blog post or vice-versa? My site goes over a lot of the same subjects as yours and I feel we could greatly benefit from each other. If you might be interested feel free to shoot me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Awesome blog by the way!
как продвинуть сайт
Советы по SEO продвижению.
Информация о том как работать с низкочастотными запросами ключевыми словами и как их выбирать
Стратегия по деятельности в соперничающей нише.
Имею постоянных взаимодействую с несколькими компаниями, есть что поделиться.
Ознакомьтесь мой аккаунт, на 31 мая 2024г
число завершённых задач 2181 только здесь.
Консультация проходит устно, без снимков с экрана и отчетов.
Время консультации указано 2 часа, но по сути всегда на контакте без строгой привязки ко времени.
Как работать с софтом это уже отдельная история, консультация по работе с софтом договариваемся отдельно в специальном кворке, выясняем что нужно при коммуникации.
Всё спокойно на расслабоне не в спешке
To get started, the seller needs:
Мне нужны сведения от Telegram канала для контакта.
коммуникация только в устной форме, переписываться нету времени.
субботы и воскресенья выходные
sunmory33
angkot88
ANGKOT88: Situs Game Deposit Pulsa Terbaik di Indonesia
ANGKOT88 adalah situs game deposit pulsa terbaik tahun 2020 di Indonesia. Kami menyediakan berbagai jenis game online terlengkap yang dapat Anda mainkan hanya dengan mendaftar satu ID. Dengan satu ID tersebut, Anda dapat mengakses seluruh permainan yang tersedia di situs kami.
Sebagai situs agen game online berlisensi resmi dari PAGCOR (Philippine Amusement Gaming Corporation), ANGKOT88 menjamin keamanan dan kenyamanan Anda. Situs kami didukung oleh server hosting yang cepat dan sistem keamanan dengan metode enkripsi terbaru di dunia, sehingga data Anda akan selalu terjaga keamanannya. Tampilan situs yang modern juga membuat Anda merasa nyaman saat mengakses situs kami.
Keunggulan ANGKOT88
Selain menjadi situs game online terbaik, ANGKOT88 juga menawarkan layanan praktis untuk melakukan deposit menggunakan pulsa XL ataupun Telkomsel dengan potongan terendah dibandingkan situs lainnya. Ini menjadikan kami salah satu situs game online pulsa terbesar di Indonesia. Anda juga dapat melakukan deposit pulsa melalui E-commerce resmi seperti OVO, Gopay, Dana, atau melalui minimarket seperti Indomaret dan Alfamart.
Kepercayaan dan Layanan
Kami di ANGKOT88 sangat menjaga kepercayaan Anda sebagai prioritas utama kami. Oleh karena itu, kami selalu berusaha menjadi agen online terpercaya dan terbaik sepanjang masa. Permainan game online yang kami tawarkan sangat praktis, sehingga Anda dapat memainkannya kapan saja dan di mana saja tanpa perlu repot bepergian. Kami menyediakan berbagai jenis game, termasuk yang disiarkan secara LIVE (langsung) dengan host cantik dan kamera yang merekam secara real-time, menjadikan ANGKOT88 situs game online terlengkap dan terbesar di Indonesia.
Promo Menarik dan Menguntungkan
ANGKOT88 juga menawarkan banyak sekali promo menarik dan menguntungkan. Anda bisa menikmati berbagai macam promo yang sesuai dengan kebutuhan Anda, seperti welcome bonus 20%, bonus deposit harian, dan cashback. Semua promo ini tersedia di situs ANGKOT88. Selain itu, kami juga memiliki layanan Customer Service yang siap membantu Anda kapan saja.
Jadi, tunggu apa lagi? Bergabunglah dengan ANGKOT88 dan nikmati pengalaman bermain game online terbaik dan teraman di Indonesia. Daftarkan diri Anda sekarang dan mulai mainkan game favorit Anda dengan nyaman dan aman di situs kami!
bocor88
Hi! I’ve been following your website for some time now and finally got the courage to go ahead and give you a shout out from Porter Texas! Just wanted to say keep up the excellent job!
Excellent items from you, man. I’ve take note your stuff previous to and you are just extremely magnificent. I really like what you’ve obtained here, certainly like what you are saying and the way in which wherein you say it. You are making it enjoyable and you still take care of to keep it sensible. I can not wait to read far more from you. That is actually a terrific web site.
娛樂城
在線娛樂城的天地
隨著網際網路的快速發展,線上娛樂城(在線賭場)已經成為許多人娛樂的新選擇。線上娛樂城不僅提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,還能讓玩家在家中就能體驗到賭場的刺激和樂趣。本文將研究在線娛樂城的特色、優勢以及一些常見的的遊戲。
什麼是網上娛樂城?
在線娛樂城是一種透過網際網路提供賭博遊戲的平台。玩家可以經由電腦、智能手機或平板電腦進入這些網站,參與各種賭博活動,如德州撲克、賭盤、黑傑克和老虎机等。這些平台通常由專業的程序公司開發,確保遊戲的公正和安全性。
網上娛樂城的好處
便利性:玩家不用離開家,就能體驗賭錢的快感。這對於那些生活在偏遠實體賭場區域的人來說特別方便。
多元化的游戲選擇:在線娛樂城通常提供比實體賭場更多樣化的遊戲選擇,並且經常改進遊戲內容,保持新鮮。
福利和獎勵計劃:許多在線娛樂城提供多樣的獎勵計劃,包括註冊獎勵、存款獎金和忠誠計劃,引誘新玩家並鼓勵老玩家繼續遊戲。
安全性和隱私:正規的線上娛樂城使用先進的加密技術來保護玩家的個人資料和金融交易,確保游戲過程的安全和公平。
常有的線上娛樂城遊戲
撲克牌:德州撲克是最受歡迎的賭博游戲之一。網上娛樂城提供多樣撲克變體,如德州撲克、奧馬哈撲克和七張撲克等。
賭盤:輪盤是一種古老的賭場遊戲,玩家可以下注在單個數字、數字組合或顏色上,然後看球落在哪個區域。
21點:又稱為二十一點,這是一種比拼玩家和莊家點數的游戲,目標是讓手牌點數盡量接近21點但不超過。
老虎机:老虎機是最受歡迎也是最流行的博彩遊戲之一,玩家只需旋轉捲軸,等待圖案圖案排列出獲勝的組合。
結尾
在線娛樂城為現代的賭博愛好者提供了一個便捷、興奮且豐富的娛樂選擇。不論是撲克牌愛好者還是老虎機迷,大家都能在這些平台上找到適合自己的游戲。同時,隨著技術的不斷發展,在線娛樂城的游戲體驗將變化越來越真實和吸引人。然而,玩家在享受游戲的同時,也應該保持,避免沉溺於博彩活動,保持健康健康的心態。
娛樂城
網上娛樂城的天地
隨著互聯網的迅速發展,在線娛樂城(在線賭場)已經成為許多人娛樂的新選擇。在線娛樂城不僅提供多元化的遊戲選擇,還能讓玩家在家中就能體驗到賭場的樂趣和快感。本文將探討網上娛樂城的特徵、利益以及一些常有的遊戲。
什麼叫線上娛樂城?
在線娛樂城是一種通過網際網路提供賭博游戲的平台。玩家可以透過計算機、手機或平板設備進入這些網站,參與各種賭博活動,如撲克、輪盤賭、二十一點和老虎機等。這些平台通常由專業的的軟件公司開發,確保遊戲的公正性和安全。
線上娛樂城的好處
方便性:玩家不用離開家,就能享用賭博的快感。這對於那些居住在偏遠實體賭場地區的人來說尤為方便。
多種的游戲選擇:在線娛樂城通常提供比實體賭場更多樣化的遊戲選擇,並且經常更新游戲內容,保持新鮮感。
福利和獎金:許多在線娛樂城提供多樣的獎勵計劃,包括註冊紅利、存款獎勵和忠誠度計劃,吸引新玩家並鼓勵老玩家持續遊戲。
穩定性和隱私性:正當的在線娛樂城使用先進的的加密來保護玩家的個人資料和金融交易,確保游戲過程的公平和公正性。
常見的的在線娛樂城游戲
撲克:德州撲克是最受歡迎的賭錢遊戲之一。在線娛樂城提供多種德州撲克變體,如德州撲克、奧馬哈撲克和七張牌撲克等。
輪盤賭:輪盤賭是一種經典的賭博遊戲,玩家可以投注在單個數字、數字組合上或顏色上,然後看小球落在哪個地方。
21點:又稱為21點,這是一種競爭玩家和莊家點數的游戲,目標是讓手牌點數點數儘量接近21點但不超過。
吃角子老虎:老虎机是最簡單也是最受歡迎的博彩遊戲之一,玩家只需轉捲軸,等待圖案圖案排列出贏得的組合。
總結
線上娛樂城為現代賭博愛好者提供了一個便捷、刺激的且多樣化的娛樂活動。不論是撲克迷還是吃角子老虎迷,大家都能在這些平台上找到適合自己的遊戲。同時,隨著科技的不斷進步,網上娛樂城的游戲體驗將變化越來越逼真和吸引人。然而,玩家在體驗遊戲的同時,也應該自律,避免沉溺於賭錢活動,保持健康的心態。
Советы по сео стратегии продвижению.
Информация о том как работать с низкочастотными запросами ключевыми словами и как их подбирать
Тактика по деятельности в конкурентоспособной нише.
Обладаю постоянных клиентов сотрудничаю с тремя фирмами, есть что рассказать.
Посмотрите мой профиль, на 31 мая 2024г
общий объём успешных проектов 2181 только здесь.
Консультация проходит устно, никаких скриншотов и отчетов.
Длительность консультации указано 2 часа, и реально всегда на доступен без жёсткой фиксации времени.
Как управлять с программным обеспечением это уже отдельная история, консультация по использованию ПО обсуждаем отдельно в другом кворке, выясняем что необходимо при разговоре.
Всё спокойно на расслабленно не в спешке
To get started, the seller needs:
Мне нужны данные от Telegram канала для связи.
общение только вербально, вести переписку нету времени.
Суббота и Вс выходной
Hi there very nice website!! Guy .. Beautiful .. Amazing .. I will bookmark your blog and take the feeds additionally?KI am glad to find so many helpful info here in the post, we’d like develop more strategies on this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
I have not checked in here for a while since I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are great quality so I guess I will add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend :)
이광수 마약
빠릿한 입출금 서비스와 메이저업체의 안전성
토토사이트 접속 시 가장 중요한 요소 중 하나는 신속한 충환전 프로세스입니다. 보통 세 분 내에 입금, 십 분 이내에 환전이 완수되어야 합니다. 대형 주요업체들은 넉넉한 스태프 고용을 통해 이러한 빠릿한 입출금 처리를 보장하며, 이로써 고객들에게 안전한 느낌을 드립니다. 주요사이트를 접속하면서 빠른 경험을 해보세요. 우리는 여러분이 안전하게 웹사이트를 접속할 수 있도록 돕는 먹튀 해결 팀입니다.
보증금 걸고 배너를 운영
먹튀 해결 전문가는 적어도 3000만 원에서 1억 원의 보증 자금을 예치한 사이트들의 배너를 운영합니다. 만약 먹튀 문제가 발생할 시, 배팅 규정에 반하지 않은 배팅 기록을 캡처해서 먹튀 해결 팀에 문의 주시면, 사실 확인 후 보증 금액으로 신속하게 피해 보상을 처리해드립니다. 피해가 생기면 즉시 캡처해서 피해 내용을 기록해두시고 제출해 주세요.
장기 운영 안전업체 확인
먹튀해결사는 적어도 4년간 먹튀 사고 없이 무사히 운영하고 있는 사이트들을 검증하여 광고 배너 입점을 허용합니다. 이 때문에 어느 누구나 알고 있는 주요사이트를 안전하게 이용할 수 있는 기회를 제공하고 있습니다. 철저한 검증 절차를 통해 인증된 사이트를 놓치지 말고, 안심하고 베팅을 즐겨보세요.
투명성과 공정성을 가진 먹튀 검증
먹튀 해결 전문가의 먹튀 확인은 투명함과 공평성을 기반으로 실시합니다. 항상 고객들의 의견을 최우선으로 생각하며, 기업의 회유나 이득에 흔들리지 않으며 하나의 삭제 없이 사실만을 기반으로 검증해오고 있습니다. 먹튀 문제를 당한 후 후회하지 않도록, 지금 바로 시작하세요.
먹튀 검증 사이트 목록
먹튀 해결 팀이 골라낸 안전한 토토사이트 검증된 업체 목록 입니다. 현재 등록되어 있는 검증된 업체들은 먹튀 사고 발생 시 100% 보장을 해드립니다. 하지만, 제휴 기간이 만료된 업체에서 발생한 문제에 대해서는 책임지지 않습니다.
독보적인 먹튀 검증 알고리즘
먹튀 해결 팀은 공정한 도박 문화를 만들기 위해 계속해서 애쓰고 있습니다. 저희가 추천하는 스포츠토토사이트에서 안전하게 베팅하시기 바랍니다. 회원님의 먹튀 신고 내용은 먹튀 목록에 등록 노출되어 해당되는 토토사이트에 심각한 영향을 끼칩니다. 먹튀 목록 작성 시 먹튀블러드 만의 검증 지식을 충분히 활용하여 정확한 검증을 하도록 하겠습니다.
안전한 베팅 환경을 조성하기 위해 항상 애쓰는 먹튀 해결 전문가와 같이 안전하게 경험해보세요.
Lottery Defeater: What Is It? A software tool called Lottery Defeater was created to raise the odds of winning lottery tickets.
What is Aizen Power? Aizen Power is an all-natural supplement to improve overall male health.
сео консультация
Советы по оптимизации продвижению.
Информация о том как взаимодействовать с низкочастотными запросами и как их подбирать
Стратегия по деятельности в конкурентоспособной нише.
У меня есть регулярных работаю с 3 фирмами, есть что рассказать.
Ознакомьтесь мой профиль, на 31 мая 2024г
количество завершённых задач 2181 только на этом сайте.
Консультация проходит в устной форме, никаких скринов и документов.
Длительность консультации указано 2 ч, но по реально всегда на доступен без жёсткой привязки ко времени.
Как работать с ПО это уже отдельная история, консультация по использованию ПО обсуждаем отдельно в другом услуге, определяем что необходимо при общении.
Всё без суеты на расслабленно не в спешке
To get started, the seller needs:
Мне нужны контакты от телеграмм чата для связи.
коммуникация только устно, переписываться нету времени.
Сб и воскресенья нерабочие дни
https://centennialspecialtytours.com/
I am often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has really peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information.
timnas4d
Inspirasi dari Kutipan Taylor Swift: Harapan dan Cinta dalam Lagu-Lagunya
Taylor Swift, seorang musisi dan penulis lagu terkenal, tidak hanya terkenal berkat melodi yang elok dan nyanyian yang merdu, tetapi juga karena lirik-lirik lagunya yang bermakna. Pada syair-syairnya, Swift sering menggambarkan beraneka ragam unsur kehidupan, mulai dari cinta hingga rintangan hidup. Berikut adalah beberapa ucapan motivatif dari lagu-lagu, beserta maknanya.
“Mungkin yang paling baik belum tiba.” – “All Too Well”
Arti: Meskipun dalam masa-masa sulit, selalu ada secercah asa dan kemungkinan untuk hari yang lebih baik.
Lirik ini dari lagu “All Too Well” mengingatkan kita jika walaupun kita bisa jadi menghadapi masa-masa sulit sekarang, selalu ada potensi kalau waktu yang akan datang akan memberikan perubahan yang lebih baik. Hal ini adalah amanat harapan yang memperkuat, memotivasi kita untuk tetap bertahan dan tidak mengalah, lantaran yang terbaik mungkin belum datang.
“Aku akan bertahan karena aku tidak bisa menjalankan apa pun tanpa kamu.” – “You Belong with Me”
Arti: Menemukan cinta dan dukungan dari orang lain dapat menghadirkan kita kekuatan dan kemauan keras untuk melanjutkan melalui kesulitan.
wajik777
Ashley JKT48: Bintang yang Bercahaya Terang di Langit Idol
Siapa Ashley JKT48?
Siapa figur muda berkemampuan yang mencuri perhatian sejumlah besar penggemar lagu di Indonesia dan Asia Tenggara? Itulah Ashley Courtney Shintia, atau yang terkenal dengan nama panggungnya, Ashley JKT48. Bergabung dengan grup idola JKT48 pada tahun 2018, Ashley dengan cepat berubah menjadi salah satu anggota paling populer.
Riwayat Hidup
Dilahirkan di Jakarta pada tgl 13 Maret 2000, Ashley berdarah darah Tionghoa-Indonesia. Beliau memulai karier di bidang entertainment sebagai model dan aktris, sebelum kemudian bergabung dengan JKT48. Kepribadiannya yang ceria, nyanyiannya yang mantap, dan keterampilan menari yang mengagumkan membuatnya idol yang sangat dikasihi.
Penghargaan dan Apresiasi
Popularitas Ashley telah diakui melalui aneka award dan nominasi. Pada masa 2021, beliau meraih penghargaan “Member Terpopuler JKT48” di ajang Penghargaan Musik JKT48. Ia juga diberi gelar sebagai “Idol Terindah di Asia” oleh sebuah majalah daring pada tahun 2020.
Peran dalam JKT48
Ashley memainkan fungsi penting dalam kelompok JKT48. Ia adalah anggota Tim KIII dan berperan sebagai dancer utama dan vokalis. Ashley juga merupakan bagian dari sub-unit “J3K” dengan Jessica Veranda dan Jennifer Rachel Natasya.
Karir Solo
Selain aktivitasnya di JKT48, Ashley juga merintis karier solo. Beliau telah meluncurkan beberapa lagu single, termasuk “Myself” (2021) dan “Falling Down” (2022). Ashley juga telah berkolaborasi bareng artis lain, seperti Afgan dan Rossa.
Hidup Pribadi
Di luar dunia pertunjukan, Ashley dikenal sebagai orang yang rendah hati dan ramah. Beliau menggemari menghabiskan waktu dengan keluarga dan kawan-kawannya. Ashley juga memiliki kegemaran melukis dan fotografi.
txid транзакции проверить usdt 5
Контроль аккаунта USDT
Проверка токенов на платформе TRC20 и других виртуальных операций
На этом веб-сайте вы детальные оценки различных сервисов для анализа транзакций и счетов, охватывая антиотмывочные контроли для криптовалюты и прочих криптовалют. Вот важные функции, доступные в наших обзорах:
Контроль криптовалюты на платформе TRC20
Известные ресурсы предлагают полную верификацию платежей USDT на платформе TRC20 блокчейна. Это гарантирует выявлять подозрительную действия и выполнять правовым положениям.
Анализ операций криптовалюты
В представленных обзорах описаны инструменты для комплексного мониторинга и наблюдения транзакций монет, что гарантирует обеспечивать ясность и защиту операций.
антиотмывочного закона проверка токенов
Многие сервисы предоставляют антиотмывочного закона анализ криптовалюты, давая возможность идентифицировать и исключать примеры финансовых преступлений и экономических нарушений.
Проверка счета монет
Наши ревью охватывают ресурсы, предназначенные для дают возможность проверять счета криптовалюты на выявление подозрительных действий и подозреваемых действий, обеспечивая повышенную уровень безопасности защищенности.
Контроль транзакции токенов на блокчейне TRC20
Вы сможете найти описаны ресурсы, обеспечивающие анализ платежей криптовалюты на блокчейне TRC20 блокчейна, что соответствие соответствие всем необходимым требованиям правилам.
Анализ кошелька адреса криптовалюты
В описаниях представлены платформы для проверки аккаунтов счетов монет на потенциальных рисков рисков.
Проверка адреса токенов на платформе TRC20
Наши описания представляют сервисы, поддерживающие анализ кошельков токенов в блокчейн-сети TRC20 платформы, что помогает исключение незаконных операций и денежных нарушений.
Проверка токенов на отсутствие подозрительных действий
Обозреваемые инструменты дают возможность проверять транзакции и счета на прозрачность, фиксируя необычную активность.
антиотмывочного закона проверка монет TRC20
В описаниях вы найдете ресурсы, поддерживающие антиотмывочную проверку для токенов в блокчейн-сети TRC20 платформы, что позволяет вашему делу соблюдать мировым положениям.
Контроль монет на сети ERC20
Наши ревью охватывают платформы, предоставляющие проверку монет на платформе ERC20 сети, что обеспечивает гарантирует комплексный анализ переводов и счетов.
Анализ цифрового кошелька
Мы описываем сервисы, обеспечивающие опции по проверке криптовалютных кошельков, содержащие отслеживание транзакций и фиксирование подозреваемой операций.
Верификация адреса цифрового кошелька
Наши ревью включают платформы, предназначенные для контролировать кошельки криптовалютных кошельков для поддержания дополнительного уровня защищенности.
Проверка криптокошелька на платежи
В наших описаниях представлены ресурсы для верификации цифровых кошельков на операции, что обеспечивает поддерживать обеспечивать прозрачность операций.
Верификация цифрового кошелька на отсутствие подозрительных действий
Наши оценки охватывают решения, позволяющие проверять цифровые кошельки на отсутствие подозрительных действий, фиксируя возможные подозрительные платежи.
Ознакомившись с данные оценки, вам удастся выберете надежные платформы для контроля и контроля цифровых транзакций, чтобы поддерживать надежный степень безопасности защищенности и соответствовать необходимым правовым стандартам.
I got what you intend, regards for putting up.Woh I am happy to find this website through google. “You must pray that the way be long, full of adventures and experiences.” by Constantine Peter Cavafy.
internet casinos
Online Gambling Sites: Advancement and Advantages for Modern Community
Overview
Online gambling platforms are virtual platforms that provide users the opportunity to participate in gambling games such as card games, spin games, 21, and slot machines. Over the last several years, they have turned into an integral part of digital leisure, offering various benefits and possibilities for players around the world.
Availability and Ease
One of the primary advantages of digital casinos is their availability. Players can play their favorite games from any location in the world using a computer, tablet, or smartphone. This conserves hours and money that would otherwise be used traveling to traditional casinos. Furthermore, 24/7 access to games makes online gambling sites a easy option for people with busy schedules.
Variety of Activities and Experience
Online gambling sites provide a wide range of games, enabling all users to find an option they enjoy. From traditional table activities and table activities to slot machines with various themes and progressive prizes, the diversity of games ensures there is an option for every taste. The option to engage at different proficiencies also makes digital gambling sites an ideal location for both beginners and experienced gamblers.
Financial Advantages
The online gambling sector adds greatly to the economic system by creating employment and generating income. It backs a diverse variety of careers, including software developers, customer support agents, and marketing specialists. The revenue produced by digital casinos also adds to government funds, which can be used to support community services and development projects.
Advancements in Technology
Digital casinos are at the cutting edge of tech innovation, continuously adopting new innovations to improve the playing experience. Superior visuals, live dealer games, and VR gambling sites provide engaging and authentic gaming entertainment. These innovations not only enhance player satisfaction but also push the limits of what is achievable in online leisure.
Safe Betting and Assistance
Many online casinos promote responsible gambling by providing resources and assistance to help users manage their betting habits. Features such as deposit limits, self-ban options, and availability to assistance programs ensure that players can engage in betting in a safe and monitored setting. These steps demonstrate the sector’s commitment to promoting healthy betting habits.
Community Engagement and Community
Online casinos often provide social features that allow players to interact with each other, creating a feeling of belonging. Group activities, communication tools, and social media links allow players to network, exchange stories, and build relationships. This social aspect improves the overall gaming entertainment and can be particularly helpful for those seeking social interaction.
Conclusion
Digital casinos provide a diverse variety of advantages, from availability and ease to economic contributions and innovations. They offer diverse betting choices, support safe betting, and promote community engagement. As the industry continues to grow, digital casinos will probably remain a major and beneficial force in the world of online leisure.
No-Cost Slot Games: Amusement and Advantages for All
Gratis slot games have become a in-demand form of internet-based entertainment, granting players the thrill of slot machines absent any cash investment.
The main objective of complimentary slot games is to grant a fun and engaging way for individuals to savor the thrill of slot machines devoid of any cash jeopardy. They are crafted to simulate the sensation of real-money slots, enabling players to spin the reels, savor various themes, and win digital winnings.
Pleasure: Gratis slot games are an excellent option of entertainment, providing durations of pleasure. They display colorful graphics, compelling audio, and varied ideas that suit a wide selection of preferences.
Proficiency Improvement: For beginners, free slot games present a risk-free setting to learn the operations of slot machines. Players can get accustomed with different game features, winning combinations, and extras without the apprehension of forfeiting money.
Unwinding: Playing free slot games can be a excellent way to decompress. The straightforward gameplay and the opportunity for digital payouts make it an fulfilling hobby.
Interpersonal Connections: Many no-cost slot games feature group-oriented features such as challenges and the opportunity to network with fellow players. These elements inject a collective layer to the gaming experience, empowering players to measure up against one another.
Advantages of Free Slot Games
1. Accessibility and Convenience
Gratis slot games are readily accessible to anyone with an internet connection. They can be accessed on multiple apparatuses including computers, mobile devices, and handsets. This comfort allows players to enjoy their favorite pursuits whenever and irrespective of location.
2. Monetary Innocuousness
One of the most significant benefits of free slot games is that they exclude the financial hazards linked to gambling. Players can enjoy the thrill of rotating the reels and hitting big rewards devoid of spending any funds.
3. Variety of Games
No-Cost slot games are available in a wide collection of concepts and formats, from classic fruit-themed slots to current video slots with intricate storylines and graphics. This range ensures that there is an option for everyone, independent of their inclinations.
4. Improving Mental Capabilities
Playing complimentary slot games can contribute to enhance thinking abilities such as pattern recognition. The task to consider winning combinations, learn game mechanics, and estimate consequences can offer a cerebral workout that is equally rewarding and advantageous.
5. Risk-Free Trial Phase for Real-Money Play
For those considering progressing to for-profit slots, gratis slot games present a valuable preparation phase. Players can experience multiple games, hone strategies, and gain self-belief in advance of opting to invest actual money. This preparation can lead to a more educated and enjoyable real-money gaming interaction.
Summary
Gratis slot games provide a wealth of perks, from absolute fun to skill development and shared experiences. They offer a worry-free and non-monetary way to experience the rush of slot machines, constituting them a beneficial complement to the world of electronic leisure. Whether you’re looking to destress, hone your intellectual faculties, or merely derive entertainment, gratis slot games are a fantastic possibility that steadfastly enchant players worldwide.
slots machines
Complimentary Slot Machines: Entertainment and Advantages for Users
Overview
Slot-based activities have traditionally been a fixture of the casino experience, granting participants the chance to secure major payouts with merely the pull of a switch or the press of a interface. In recent years, slot-based activities have as well grown to be popular in digital wagering environments, making them approachable to an even more more expansive group.
Fun Element
Slot-based activities are crafted to be pleasurable and engaging. They showcase vibrant visuals, exciting auditory elements, and various themes that suit a wide variety of inclinations. Whether players experience traditional fruit symbols, adventure-themed slots, or slot-based activities inspired by well-known TV shows, there is a choice for everyone. This variety provides that users can persistently find a activity that aligns with their tastes, delivering hours of pleasure.
Uncomplicated to Interact With
One of the greatest benefits of slot-based activities is their uncomplicated nature. Differently from certain casino offerings that demand skill, slot-based games are simple to comprehend. This constitutes them available to a extensive group, including newcomers who may encounter daunted by further sophisticated experiences. The uncomplicated essence of slot-related offerings permits users to decompress and relish the experience devoid of fretting about intricate protocols.
Stress Relief and Relaxation
Engaging with slot-related offerings can be a fantastic way to decompress. The monotonous character of activating the reels can be calming, granting a cognitive break from the stresses of regular activities. The possibility for winning, even it’s simply minor sums, brings an aspect of anticipation that can enhance users’ moods. Many players find that partaking in slot-based games enables them decompress and divert their attention from their concerns.
Communal Engagement
Slot-related offerings likewise present avenues for communal interaction. In physical casinos, users frequently congregate near slot-based games, cheering their fellow players on and rejoicing in triumphs collectively. Internet-based slots have in addition featured communal elements, such as competitions, permitting users to interact with others and exchange their sensations. This environment of togetherness elevates the holistic interactive encounter and can be specifically enjoyable for people aiming for group-based participation.
Monetary Upsides
The broad acceptance of slot-related offerings has substantial economic benefits. The sector generates positions for offering designers, gambling staff, and user services specialists. Additionally, the revenue generated by slot-based activities provides to the financial system, providing budgetary proceeds that support societal projects and systems. This monetary consequence expands to both physical and digital gambling establishments, establishing slot-based activities a valuable element of the gaming industry.
Mental Upsides
Engaging with slot machines can also result in cognitive advantages. The experience necessitates participants to arrive at quick decisions, identify trends, and supervise their betting approaches. These cognitive activities can facilitate sustain the intellect focused and enhance cerebral functions. In the case of mature players, involving themselves in intellectually engaging pursuits like engaging with slot-based games can be helpful for maintaining mental capacity.
Reachability and User-Friendliness
The advent of digital casinos has established slot-based activities more accessible than ever. Customers can relish their cherished slot-based activities from the ease of their own dwellings, employing desktops, pads, or smartphones. This user-friendliness allows users to engage with at any time and no matter the location they prefer, free from the obligation to travel to a land-based gaming venue. The accessibility of complimentary slot-related offerings as well allows participants to relish the game devoid of any economic outlay, constituting it an inclusive type of entertainment.
Conclusion
Slot-based games deliver a multitude of upsides to users, from absolute amusement to cognitive benefits and collaborative interaction. They grant a risk-free and zero-cost way to experience the rush of slot-related offerings, rendering them a beneficial addition to the world of online entertainment.
Whether you’re aiming to decompress, improve your cerebral skills, or merely enjoy yourself, slot machines are a wonderful option that persistently entertain participants around.
Key Takeaways:
– Slot-based games grant amusement through vibrant graphics, engaging sounds, and wide-ranging concepts
– Ease of play constitutes slot-related offerings available to a comprehensive audience
– Playing slot-based games can offer unwinding and cerebral rewards
– Group-based elements bolster the holistic interactive encounter
– Online accessibility and no-cost possibilities establish slot-related offerings open-to-all forms of entertainment
In conclusion, slot-based activities persistently grant a diverse assortment of upsides that suit users around. Whether aiming for sheer amusement, intellectual activation, or group-based involvement, slot machines stay a fantastic option in the constantly-changing world of digital leisure.
Online Casino Actual Currency: Benefits for Customers
Preface
Virtual gaming sites providing actual currency offerings have acquired immense broad acceptance, delivering users with the prospect to earn economic rewards while experiencing their most liked wagering offerings from residence. This article analyzes the rewards of virtual wagering environment real money experiences, accentuating their favorable impact on the entertainment sector.
Convenience and Accessibility
Virtual wagering environment paid activities provide user-friendliness by giving participants to utilize a broad array of activities from any setting with an internet access. This excludes the necessity to journey to a brick-and-mortar wagering facility, protecting resources. Online casinos are in addition accessible continuously, enabling users to play at their user-friendliness.
Breadth of Offerings
Online casinos provide a wider breadth of experiences than land-based wagering facilities, involving slots, pontoon, roulette, and table games. This variety enables players to experiment with new activities and uncover novel most cherished, improving their overall entertainment sensation.
Perks and Advantages
Digital gaming sites offer significant perks and discounts to lure and maintain players. These rewards can feature sign-up incentives, complimentary rounds, and cashback promotions, delivering extra significance for users. Dedication schemes also recognize users for their continued support.
Capability Building
Playing actual currency games on the internet can facilitate participants acquire abilities such as decision-making. Games like vingt-et-un and casino-style games call for participants to render selections that can impact the conclusion of the offering, enabling them acquire decision-making aptitudes.
Interpersonal Connections
ChatGPT l Валли, [06.06.2024 4:08]
Virtual wagering environments provide prospects for group-based interaction through discussion forums, forums, and video-streamed activities. Players can interact with their peers, discuss tips and methods, and sometimes establish friendships.
Financial Advantages
The internet-based gambling sector yields jobs and provides for the fiscal landscape through government proceeds and licensing charges. This fiscal effect rewards a comprehensive array of vocations, from experience developers to customer assistance specialists.
Key Takeaways
Virtual wagering environment real money experiences present multiple advantages for customers, encompassing ease, diversity, perks, capability building, social interaction, and monetary advantages. As the field persistently transform, the broad acceptance of digital gaming sites is projected to rise.
Luck Wagering Environment: In a Place Where Enjoyment Intersects With Prosperity
Luck Casino is a popular digital place recognized for its broad variety of offerings and captivating benefits. Let’s analyze why so numerous people enjoy playing at Wealth Wagering Environment and the extent to which it rewards them.
Pleasure-Providing Aspect
Prosperity Gaming Site presents a breadth of activities, including classic wagering games like vingt-et-un and spinning wheel, as together with novel slot-related offerings. This variety secures that there is an option for anyone, rendering every trip to Prosperity Wagering Environment rewarding and amusing.
Significant Rewards
One of the main attractions of Wealth Gaming Site is the opportunity to earn significant rewards. With considerable major payouts and bonuses, players have the possibility to achieve unexpected success with a one-time play or hand. Many participants have acquired major prizes, augmenting the suspense of engaging with Wealth Gaming Site.
Ease of Access and Reachability
Wealth Casino’s online system makes it convenient for users to experience their most liked games from any location. Regardless of whether at residence or while mobile, users can utilize Prosperity Wagering Environment from their laptop or handheld. This reachability secures that participants can enjoy the thrill of the gambling at any time they choose, without the need to journey.
Diversity of Options
Fortune Gambling Platform presents a wide assortment of games, ensuring that there is something for every single form of player. From time-honored table games to story-based slot-based games, the range retains players captivated and delighted. This assortment as well permits users to experiment with different offerings and find novel favorites.
Promotional Benefits
Fortune Gaming Site rewards its players with bonuses and special offers, featuring new player promotional benefits and membership systems. These special offers not merely bolster the interactive interaction but also augment the prospects of securing major payouts. Participants are persistently driven to maintain participation, constituting Luck Casino increasingly desirable.
Community and Social Interaction
ChatGPT l Валли, [06.06.2024 4:30]
Fortune Wagering Environment offers a environment of shared experience and social interaction for users. Via chat rooms and interactive platforms, users can interact with one another, share tips and strategies, and in certain cases form personal connections. This social aspect adds a supplemental dimension of enjoyment to the interactive interaction.
Key Takeaways
Prosperity Gaming Site presents a wide range of rewards for users, incorporating entertainment, the opportunity to achieve substantial winnings, simplicity, range, incentives, and shared experiences. Regardless of whether aiming for suspense or aiming to experience a reversal of fortune, Luck Casino provides an captivating encounter for everyone who partake in.
free poker machine games
Gratis Virtual Wagering Activities: A Entertaining and Profitable Sensation
Free virtual wagering games have become increasingly sought-after among players aiming for a enthralling and secure leisure experience. These experiences provide a extensive array of advantages, constituting them as a preferred possibility for a significant number of. Let’s investigate how free poker machine experiences can benefit customers and the motivations behind they are so extensively savored.
Amusement Factor
One of the principal motivations individuals savor playing complimentary slot-based experiences is for the entertainment value they offer. These activities are created to be engaging and captivating, with animated graphics and immersing audio that enhance the comprehensive gaming experience. Regardless of whether you’re a occasional player aiming to occupy your time or a dedicated gamer aiming for excitement, gratis electronic gaming games grant pleasure for all.
Capability Building
Partaking in no-cost virtual wagering experiences can in addition help refine beneficial faculties such as decision-making. These activities call for users to render immediate decisions based on the gameplay elements they are received, facilitating them sharpen their problem-solving skills and mental agility. Moreover, users can try out multiple strategies, refining their abilities free from the chance of negative outcome of losing actual currency.
Ease of Access and Reachability
An additional upside of no-cost virtual wagering offerings is their user-friendliness and reachability. These activities can be played in the digital realm from the ease of your own abode, eliminating the obligation to make trips to a land-based gambling establishment. They are in addition present around the clock, permitting customers to savor them at whatever moment that suits them. This simplicity establishes complimentary slot-based games a well-liked alternative for players with packed routines or those looking for a quick leisure fix.
Interpersonal Connections
Many no-cost virtual wagering experiences also offer collaborative features that enable participants to interact with each other. This can include communication channels, online communities, and collaborative settings where players can challenge one another. These shared experiences contribute an further aspect of enjoyment to the entertainment interaction, allowing players to engage with others who have in common their preferences.
Worry Mitigation and Emotional Refreshment
Interacting with free poker machine games can also be a excellent approach to unwind and de-stress after a extended stretch of time. The effortless activity and calming audio can help lower worry and apprehension, granting a refreshing escape from the demands of normal existence. Also, the thrill of earning virtual coins can elevate your disposition and render you revitalized.
Recap
Gratis electronic gaming games provide a extensive selection of upsides for players, incorporating amusement, proficiency improvement, convenience, social interaction, and stress relief and mental rejuvenation. Regardless of whether you’re aiming to enhance your interactive abilities or merely enjoy yourself, complimentary slot-based activities deliver a profitable and fulfilling interaction for players of every degrees.
online poker
Digital Table Games: A Provider of Entertainment and Proficiency Improvement
Online card games has materialized as a widely-accepted form of entertainment and a platform for competency enhancement for players internationally. This write-up explores the favorable aspects of online poker and how it upsides people, accentuating its widespread appeal and impact.
Fun Element
Internet-based card games grants a enthralling and engaging entertainment sensation, spellbinding customers with its calculated activity and unpredictable outcomes. The experience’s engrossing nature, together with its group-based components, grants a unique style of entertainment that numerous consider enjoyable.
Proficiency Improvement
Aside from fun, digital table games likewise acts as a medium for skill development. The offering demands problem-solving, decision-making under pressure, and the ability to read competitors, each of which add to mental growth. Customers can enhance their analytical faculties, emotional intelligence, and calculated approach abilities through frequent gameplay.
User-Friendliness and Availability
One of the main upsides of digital table games is its user-friendliness and approachability. Players can relish the experience from the ease of their abodes, at any desired moment that accommodates them. This reachability eliminates the requirement for trips to a land-based gambling establishment, making it a convenient choice for users with hectic routines.
Variety of Games and Stakes
Internet-based card games interfaces offer a broad diversity of games and bet sizes to cater to players of every skill levels and tastes. Whether you’re a learner looking to grasp the fundamentals or a veteran master aspiring to a challenge, there is a game for your skill level. This range provides that customers can persistently uncover a experience that aligns with their skill level and bankroll.
Shared Experiences
Online poker in addition grants opportunities for communal engagement. A significant number of platforms provide communication tools and group-based formats that give customers to interact with like-minded players, exchange sensations, and develop social relationships. This collaborative element adds depth to the interactive experience, rendering it even more rewarding.
Monetary Gains
For certain individuals, online poker can also be a provider of monetary gains. Adept customers can receive considerable earnings through regular interactivity, establishing it as a lucrative endeavor for those who master the game. Moreover, several virtual casino-style games tournaments provide considerable prize pools, delivering participants with the prospect to secure major payouts.
Recap
Digital table games offers a range of upsides for customers, encompassing entertainment, skill development, simplicity, social interaction, and profit potential. Its popularity continues to expand, with numerous people turning to digital table games as a wellspring of pleasure and self-improvement. Whether you’re wanting to enhance your aptitudes or just experience pleasure, virtual casino-style games is a versatile and beneficial pursuit for players of all origins.
성현아 마약
빠른 환충 서비스와 더불어 주요업체의 안전성
베팅사이트 접속 시 매우 중요한 요소 중 하나는 신속한 환충 절차입니다. 일반적으로 3분 안에 입금, 10분 안에 환충이 처리되어야 합니다. 대형 대형업체들은 필요한 인력 채용으로 이와 같은 빠른 충환전 프로세스를 보증하며, 이로써 사용자들에게 안전감을 제공합니다. 주요사이트를 접속하면서 스피드 있는 경험을 즐겨보세요. 저희는 고객님이 안심하고 사이트를 접속할 수 있도록 지원하는 먹튀해결 전문가입니다.
보증금 걸고 배너 운영
먹튀 해결 팀은 최소 3000만 원에서 억대의 보증 금액을 예치한 사이트들의 배너를 운영하고 있습니다. 혹시 먹튀 사고가 발생할 시, 베팅 규정에 어긋나지 않은 배팅 기록을 캡처하여 먹튀 해결 팀에 문의하시면, 사실 확인 후 보증 자금으로 즉시 손해 보상을 처리합니다. 피해 발생 시 빠르게 스크린샷을 찍어 피해 상황을 저장해두시고 보내주시기 바랍니다.
장기간 안전 운영 업체 확인
먹튀 해결 팀은 최대한 4년 이상 먹튀 이력 없이 안전하게 운영된 업체만을 확인하여 배너 입점을 받고 있습니다. 이 때문에 모두가 알고 있는 주요사이트를 안전하게 접속할 수 있는 기회를 제공합니다. 엄격한 검증 작업을 통해 검증된 사이트를 놓치지 마시고, 안심하고 배팅을 경험해보세요.
투명성과 공정성을 가진 먹튀 검증
먹튀해결사의 먹튀 검증은 공정성과 공평성을 근거로 실시합니다. 늘 이용자들의 관점을 우선시하며, 사이트의 유혹이나 이익에 흔들리지 않고 하나의 삭제 없이 사실만을 바탕으로 검증해왔습니다. 먹튀 문제를 당한 후 후회하지 않도록, 지금 바로 시작해보세요.
먹튀검증사이트 목록
먹튀 해결 전문가가 엄선한 안전한 베팅사이트 검증된 업체 목록 입니다. 현재 등록되어 있는 검증된 업체들은 먹튀 피해 발생 시 100% 보장을 해드립니다. 하지만, 제휴 기간이 끝난 업체에서 발생한 피해에 대해서는 책임지지 않습니다.
유일무이한 먹튀 검증 알고리즘
먹튀 해결 전문가는 깨끗한 베팅 문화를 형성하기 위해 계속해서 노력하고 있습니다. 저희가 추천하는 스포츠토토사이트에서 안심하고 베팅하세요. 회원님의 먹튀 신고는 먹튀 리스트에 기재되어 해당되는 베팅 사이트에 치명적인 영향을 끼칩니다. 먹튀 리스트를 작성할 때 먹튀블러드 만의 검증 노하우를 충분히 활용하여 공평한 심사를 할 수 있게 약속드립니다.
안전한 도박 환경을 조성하기 위해 끊임없이 애쓰는 먹튀 해결 전문가와 함께 안전하게 즐기시기 바랍니다.
I like what you guys are up too. Such clever work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my website :)
Absolutely written subject matter, Really enjoyed studying.
okestream
Instal App 888 dan Peroleh Bonus: Petunjuk Pendek
**Aplikasi 888 adalah alternatif terbaik untuk Pengguna yang membutuhkan keseruan berjudi online yang mengasyikkan dan menguntungkan. Dengan imbalan harian dan fitur menggiurkan, app ini sedia menyediakan permainan berjudi unggulan. Disini petunjuk singkat untuk memanfaatkan pelayanan Aplikasi 888.
Pasang dan Awali Dapatkan
Sistem Tersedia:
App 888 bisa di-download di Sistem Android, Sistem iOS, dan Komputer. Mulai berjudi dengan cepat di gadget apa saja.
Imbalan Sehari-hari dan Bonus
Keuntungan Masuk Setiap Hari:
Login pada hari untuk mendapatkan hadiah mencapai 100K pada masa ketujuh.
Selesaikan Misi:
Ambil kesempatan undi dengan menyelesaikan misi terkait. Tiap aktivitas menghadirkan Kamu satu kesempatan undian untuk meraih keuntungan mencapai 888K.
Penerimaan Langsung:
Keuntungan harus diterima mandiri di dalam aplikasi. Jangan lupa untuk meraih hadiah pada hari agar tidak kadaluwarsa.
Sistem Undi
Kesempatan Undi:
Satu hari, Anda bisa mengambil satu kesempatan undi dengan mengerjakan tugas.
Jika kesempatan undian berakhir, tuntaskan lebih banyak tugas untuk meraih extra kesempatan.
Tingkat Keuntungan:
Dapatkan keuntungan jika keseluruhan undian Anda melampaui 100K dalam sehari.
Kebijakan Esensial
Pengambilan Hadiah:
Bonus harus diambil mandiri dari program. Jika tidak, imbalan akan otomatis diambil ke akun pribadi Para Pengguna setelah sebuah periode.
Persyaratan Pertaruhan:
Keuntungan membutuhkan minimal satu taruhan aktif untuk diklaim.
Kesimpulan
Aplikasi 888 memberikan pengalaman berjudi yang mengasyikkan dengan imbalan besar. Unduh aplikasi sekarang juga dan nikmati kemenangan besar-besaran setiap waktu!
Untuk data lebih lanjut tentang penawaran, top up, dan skema referensi, kunjungi halaman beranda aplikasi.
yowestogel
Inspirasi dari Ucapan Taylor Swift
Penyanyi Terkenal, seorang penyanyi dan komposer populer, tidak hanya diakui berkat lagu yang menawan dan suara yang merdu, tetapi juga sebab lirik-lirik karyanya yang penuh makna. Pada lirik-liriknya, Swift sering menyajikan berbagai aspek kehidupan, dimulai dari cinta hingga tantangan hidup. Berikut ini adalah beberapa kutipan inspiratif dari karya-karya, beserta artinya.
“Mungkin yang terbaik belum datang.” – “All Too Well”
Makna: Bahkan di masa-masa sulit, senantiasa ada secercah harapan dan potensi akan hari yang lebih baik.
Lirik ini dari lagu “All Too Well” mengingatkan kita jika walaupun kita mungkin menghadapi masa-masa sulit sekarang, selalu ada potensi jika masa depan bisa mendatangkan sesuatu yang lebih baik. Ini adalah pesan harapan yang menguatkan, mendorong kita untuk tetap bertahan dan tidak putus asa, karena yang paling baik barangkali belum datang.
“Aku akan tetap bertahan karena aku tak mampu melakukan segala sesuatu tanpa kamu.” – “You Belong with Me”
Arti: Menemukan cinta dan bantuan dari orang lain dapat memberi kita daya dan niat untuk melanjutkan melalui rintangan.
maxwin89
Ashley JKT48: Bintang yang Bercahaya Cemerlang di Langit Idol
Siapakah Ashley JKT48?
Siapakah sosok muda berbakat yang menyita perhatian banyak sekali penggemar musik di Nusantara dan Asia Tenggara? Dialah Ashley Courtney Shintia, atau yang lebih dikenal dengan nama panggungnya, Ashley JKT48. Masuk dengan grup idola JKT48 pada masa 2018, Ashley dengan cepat menjadi salah satu personel paling populer.
Biografi
Lahir di Jakarta pada tanggal 13 Maret 2000, Ashley memiliki darah Tionghoa-Indonesia. Ia mengawali kariernya di industri hiburan sebagai model dan aktris, sebelum selanjutnya bergabung dengan JKT48. Sifatnya yang periang, vokal yang kuat, dan keterampilan menari yang mengesankan membentuknya sebagai idola yang sangat dicintai.
Pengakuan dan Penghargaan
Kepopuleran Ashley telah dikenal melalui banyak penghargaan dan nominasi. Pada masa 2021, ia meraih pengakuan “Anggota Paling Populer JKT48” di ajang JKT48 Music Awards. Ia juga dinobatkan sebagai “Idol Tercantik di Asia” oleh sebuah majalah digital pada tahun 2020.
Peran dalam JKT48
Ashley mengisi fungsi penting dalam kelompok JKT48. Beliau adalah anggota Tim KIII dan berfungsi sebagai dancer utama dan penyanyi utama. Ashley juga menjadi bagian dari sub-unit “J3K” bersama Jessica Veranda dan Jennifer Rachel Natasya.
Karir Mandiri
Selain aktivitasnya di JKT48, Ashley juga merintis perjalanan mandiri. Ashley telah meluncurkan beberapa single, diantaranya “Myself” (2021) dan “Falling Down” (2022). Ashley juga telah bekerja sama dengan penyanyi lain, seperti Afgan dan Rossa.
Kehidupan Personal
Di luar bidang panggung, Ashley dikenal sebagai sebagai pribadi yang rendah hati dan friendly. Beliau menikmati menghabiskan waktu bersama family dan teman-temannya. Ashley juga memiliki hobi melukis dan memotret.
Great work! This is the type of information that should be shared around the web. Shame on the search engines for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my web site . Thanks =)
daya4d
Inspirasi dari Kutipan Taylor Swift
Taylor Swift, seorang penyanyi dan songwriter populer, tidak hanya dikenal berkat melodi yang indah dan vokal yang merdu, tetapi juga karena lirik-lirik lagunya yang bermakna. Pada syair-syairnya, Swift sering menyajikan beraneka ragam faktor hidup, dimulai dari cinta sampai rintangan hidup. Berikut adalah beberapa ucapan inspiratif dari karya-karya, beserta artinya.
“Mungkin yang paling baik belum tiba.” – “All Too Well”
Makna: Bahkan di saat-saat sulit, tetap ada sedikit harapan dan kemungkinan akan masa depan yang lebih baik.
Syair ini dari lagu “All Too Well” membuat kita ingat bahwa biarpun kita mungkin menghadapi masa sulit saat ini, senantiasa ada kemungkinan bahwa hari esok bisa mendatangkan hal yang lebih baik. Situasi ini adalah pesan harapan yang menguatkan, merangsang kita untuk terus bertahan dan tidak mengalah, karena yang terbaik mungkin belum tiba.
“Aku akan bertahan karena aku tak bisa menjalankan apapun tanpamu.” – “You Belong with Me”
Arti: Menemukan cinta dan dukungan dari pihak lain dapat menyediakan kita tenaga dan kemauan keras untuk melanjutkan lewat tantangan.
ulartoto
Ashley JKT48: Idola yang Bersinar Terang di Langit Idola
Siapakah Ashley JKT48?
Siapa sosok muda berbakat yang menarik perhatian banyak sekali fans musik di Indonesia dan Asia Tenggara? Dialah Ashley Courtney Shintia, atau yang terkenal dengan nama panggungnya, Ashley JKT48. Masuk dengan grup idol JKT48 pada tahun 2018, Ashley dengan cepat berubah menjadi salah satu anggota paling favorit.
Biografi
Lahir di Jakarta pada tanggal 13 Maret 2000, Ashley berketurunan keturunan Tionghoa-Indonesia. Ia mengawali perjalanannya di bidang entertainment sebagai peraga dan aktris, hingga akhirnya selanjutnya masuk dengan JKT48. Personanya yang ceria, vokal yang kuat, dan kemampuan menari yang mengagumkan menjadikannya idola yang sangat dicintai.
Award dan Pengakuan
Kepopuleran Ashley telah dikenal melalui aneka apresiasi dan nominasi. Pada tahun 2021, ia memenangkan penghargaan “Personel Terpopuler JKT48” di event JKT48 Music Awards. Ashley juga diberi gelar sebagai “Idol Tercantik di Asia” oleh sebuah majalah digital pada tahun 2020.
Fungsi dalam JKT48
Ashley mengisi posisi penting dalam grup JKT48. Beliau adalah anggota Tim KIII dan berperan sebagai dancer utama dan vokalis. Ashley juga terlibat sebagai bagian dari unit sub “J3K” bersama Jessica Veranda dan Jennifer Rachel Natasya.
Karier Mandiri
Di luar aktivitasnya bersama JKT48, Ashley juga merintis karir mandiri. Ia telah merilis beberapa lagu tunggal, termasuk “Myself” (2021) dan “Falling Down” (2022). Ashley juga telah berkolaborasi dengan artis lain, seperti Afgan dan Rossa.
Hidup Pribadi
Di luar dunia pertunjukan, Ashley dikenali sebagai pribadi yang rendah hati dan friendly. Beliau menikmati melewatkan waktu bersama keluarga dan teman-temannya. Ashley juga punya kesukaan mewarnai dan photography.
unoslot
Instal Perangkat Lunak 888 dan Raih Besar: Panduan Singkat
**Aplikasi 888 adalah opsi unggulan untuk Kamu yang mencari permainan bermain daring yang seru dan bernilai. Bersama hadiah tiap hari dan opsi menggoda, perangkat lunak ini siap menawarkan permainan bertaruhan paling baik. Ini panduan praktis untuk menggunakan penggunaan Aplikasi 888.
Instal dan Mulailah Menang
Perangkat Terdapat:
Perangkat Lunak 888 bisa di-download di HP Android, HP iOS, dan Laptop. Segera main dengan praktis di media apa saja.
Keuntungan Setiap Hari dan Imbalan
Keuntungan Masuk Setiap Hari:
Mendaftar setiap periode untuk meraih keuntungan sebesar 100K pada hari ketujuh.
Selesaikan Misi:
Raih kesempatan undian dengan mengerjakan aktivitas terkait. Masing-masing misi menawarkan Anda satu kesempatan undi untuk mengklaim bonus sampai 888K.
Pengambilan Manual:
Keuntungan harus diterima langsung di melalui aplikasi. Jangan lupa untuk mengklaim bonus setiap masa agar tidak batal.
Cara Lotere
Kesempatan Lotere:
Satu masa, Anda bisa mengambil sebuah kesempatan pengeretan dengan mengerjakan tugas.
Jika kesempatan lotere berakhir, kerjakan lebih banyak pekerjaan untuk mengambil extra peluang.
Tingkat Hadiah:
Dapatkan bonus jika total undian Kamu melampaui 100K dalam satu hari.
Ketentuan Utama
Pengklaiman Bonus:
Keuntungan harus diterima langsung dari perangkat lunak. Jika tidak, keuntungan akan otomatis diambil ke akun Anda Pengguna setelah satu periode.
Syarat Taruhan:
Keuntungan memerlukan setidaknya satu pertaruhan efektif untuk digunakan.
Penutup
Perangkat Lunak 888 memberikan keseruan bertaruhan yang mengasyikkan dengan bonus signifikan. Unduh app sekarang dan alamilah kemenangan besar pada hari!
Untuk detail lebih lengkap tentang promo, pengisian, dan program referensi, kunjungi halaman utama aplikasi.
Virtual casinos are steadily more popular, delivering diverse incentives to attract new users. One of the most tempting propositions is the free bonus, a promo that lets gamblers to try their luck without any financial risk. This article explores the advantages of no upfront deposit bonuses and highlights how they can increase their effectiveness.
What is a No Deposit Bonus?
A no upfront deposit bonus is a kind of casino offer where users get free money or free plays without the need to submit any of their own cash. This lets gamblers to explore the gaming site, test out diverse game options and stand a chance to win real funds, all without any initial investment.
Advantages of No Deposit Bonuses
Risk-Free Exploration
No-deposit bonuses grant a safe option to explore internet casinos. Users can evaluate different game options, get to know the user interface, and evaluate the overall playing environment without using their own money. This is particularly helpful for beginners who may not be familiar with internet casinos.
Chance to Win Real Money
One of the most enticing features of no deposit bonuses is the possibility to earn real cash. While the amounts may be modest, any gains earned from the bonus can usually be withdrawn after meeting the casino’s staking criteria. This adds an element of anticipation and delivers a possible financial return without any initial cost.
Learning Opportunity
No upfront deposit bonuses offer a fantastic way to get to know how multiple casino games operate. Users can try tactics, grasp the regulations of the casino games, and develop into more proficient without being concerned about parting with their own cash. This can be significantly helpful for advanced gaming activities like blackjack.
Conclusion
Free bonuses offer multiple advantages for users, like cost-free investigation, the possibility to earn real cash, and important educational prospects. As the field continues to grow, the prevalence of no deposit bonuses is anticipated to rise.
Gratis poker offers users a unique way to partake in the activity without any financial risk. This overview looks into the benefits of playing free poker and points out why it is in demand among a lot of players.
Risk-Free Entertainment
One of the most significant merits of free poker is that it allows gamblers to partake in the excitement of poker without being concerned with losing capital. This makes it ideal for novices who hope to get to know the sport without any monetary investment.
Skill Development
Gratis poker gives a fantastic environment for users to improve their competence. Users can test out strategies, get to know the guidelines of the pastime, and obtain certainty without any pressure of losing their own capital.
Social Interaction
Participating in free poker can also foster new friendships. Digital venues often include discussion boards where players can connect with each other, exchange strategies, and potentially build relationships.
Accessibility
No-cost poker is easy to access to anybody with an online connection. This implies that gamblers can experience the game from the luxury of their own residence, at any hour.
Conclusion
No-cost poker gives various merits for participants. It is a cost-free approach to enjoy the pastime, enhance competence, engage in social connections, and play poker without hassle. As further gamblers discover the advantages of free poker, its popularity is set to expand.
Examining Promotion Casinos: A Thrilling and Available Betting Option
Preface
Promotion gambling platforms are emerging as a favored option for users seeking an thrilling and legitimate method to experience digital gambling. As opposed to conventional digital gambling platforms, sweepstakes casinos work under alternative authorized systems, enabling them to deliver activities and prizes without adhering to the identical guidelines. This piece examines the concept of promotion casinos, their advantages, and why they are enticing a rising figure of users.
Understanding Sweepstakes Casinos
A lottery gaming hub operates by offering players with virtual currency, which can be applied to play games. Gamers can achieve more internet funds or actual rewards, including currency. The main disparity from classic gambling platforms is that gamers do not buy currency directly but receive it through promotional activities, such as get a item or taking part in a no-cost entry contest. This system allows sweepstakes gaming hubs to operate authorized in many areas where classic virtual gaming is limited.
빠릿한 환충 서비스 및 메이저업체의 안전
베팅사이트 사용 시 가장 중요한 요소 중 하나는 신속한 충환전 절차입니다. 보통 3분 안에 충전, 10분 안에 출금이 처리되어야 합니다. 주요 대형업체들은 넉넉한 스태프 채용을 통해 이 같은 빠른 입출금 프로세스를 보증하며, 이를 통해 회원들에게 안전감을 제공합니다. 대형사이트를 이용하면서 빠른 경험을 즐겨보세요. 우리 여러분들이 안심하고 웹사이트를 접속할 수 있도록 돕는 먹튀해결 전문가입니다.
보증금 걸고 배너를 운영
먹튀 해결 전문가는 최대한 3000만 원에서 1억 원의 보증금을 예치한 업체들의 배너 광고를 운영 중입니다. 혹시 먹튀 문제가 발생할 경우, 베팅 규정에 어긋나지 않은 베팅 내역을 캡처하여 먹튀해결사에 문의하시면, 사실 확인 후 보증 금액으로 즉시 피해 보전 처리해 드립니다. 피해 발생 시 빠르게 스크린샷을 찍어 손해 내용을 저장해 두시고 제출해 주세요.
오랫동안 안전하게 운영된 업체 확인
먹튀 해결 전문가는 적어도 사 년 이상 먹튀 이력 없이 안정적으로 운영한 업체만을 검증하여 배너 등록을 받고 있습니다. 이로 인해 모두가 잘 알려진 대형사이트를 안전하게 사용할 수 있는 기회를 제공하고 있습니다. 엄격한 검증 작업을 통해 검증된 사이트를 놓치지 않도록, 보안된 베팅을 경험해보세요.
투명하고 공정한 먹튀 검증
먹튀 해결 팀의 먹튀 검증은 투명함과 정확함을 근거로 합니다. 언제나 고객들의 관점을 우선으로 생각하고, 사이트의 회유나 이익에 흔들리지 않고 1건의 삭제 없이 사실만을 기반으로 검증해오고 있습니다. 먹튀 문제를 당하고 후회하지 않도록, 지금 바로 시작해보세요.
먹튀 검증 사이트 목록
먹튀 해결 전문가가 골라낸 안전한 베팅사이트 검증업체 목록 입니다. 지금 등록된 검증업체들은 먹튀 피해 발생 시 100% 보증을 제공해드립니다. 그러나, 제휴가 끝난 업체에서 발생한 피해에 대해서는 책임을 지지 않습니다.
유일무이한 먹튀 검증 알고리즘
먹튀 해결 전문가는 청결한 도박 문화를 만들기 위해 늘 노력합니다. 우리가 권장하는 토토사이트에서 안전하게 배팅하세요. 고객님의 먹튀 신고 내용은 먹튀 리스트에 기재되어 해당 토토사이트에 치명적인 영향을 끼칩니다. 먹튀 리스트를 작성할 때 먹튀블러드의 검증 노하우를 충분히 활용하여 정확한 검증을 할 수 있도록 하겠습니다.
안전한 베팅 문화를 만들기 위해 계속해서 힘쓰는 먹튀 해결 팀과 함께 안전하게 즐기시기 바랍니다.
casino online
Exploring the Universe of Internet Casinos
Beginning
Currently, online casinos have altered the manner individuals enjoy gambling. With sophisticated tech, players can reach their beloved games directly from the comfort of their residences. This article delves into the pros of casino online and for why they are drawing attention.
Perks of Virtual Casinos
Ease
One of the primary pros of online casinos is ease. Users can gamble anytime and wherever they choose, eliminating the necessity to commute to a brick-and-mortar betting place.
Large Game Library
Internet casinos provide a wide variety of casino games, including vintage slot games and table games to interactive games and contemporary video slots. This diversity assures that there is a game for every kind of gambler.
Offers and Deals
Among the key enticing characteristics of internet casinos is the array of rewards and offers given to enthusiasts. These can include sign-up bonuses, complimentary spins, money-back offers, and VIP clubs.
Security and Reliability
Reputable casino online ensure user security and protection with advanced data protection methods. This protects personal data and monetary transactions.
Motives Behind the Popularity of Internet Casinos
Reachability
Internet casinos are broadly available, enabling users from various backgrounds to play casino games.
Examining Complimentary Casino Games
Start
Today, free-of-charge casino games have grown into a favored selection for gambling enthusiasts who desire to experience gambling devoid of shelling out funds. This write-up investigates the perks of complimentary casino games and the reasons they are attracting favor.
Advantages of No-Cost Casino Games
Secure Gambling
One of the major benefits of free-of-charge casino games is the capability to engage in gaming without economic risk. Users can enjoy their beloved games without concerns about losing funds.
Learning Opportunities
Complimentary casino games give an fantastic stage for users to hone their abilities. Be it mastering methods in slots, gamblers can train devoid of financial consequences.
Extensive Game Options
Free casino games supply a vast range of betting activities, like old-school slots, board games, and live dealer games. This variety assures that there is an activity for all types of players.
Why Free-of-Charge Casino Games are Favored
Attainability
No-cost casino games are widely accessible, permitting enthusiasts from different backgrounds to engage in gambling.
No Financial Commitment
Unlike cash-based gaming, free-of-charge casino games do not require a financial outlay. This permits users to play betting devoid of fretting over wasting money.
Try Before You Invest
No-cost casino games give users the chance to sample betting activities in advance of spending actual finances. This assists users craft well-thought-out choices.
Final Thoughts
Complimentary casino games provides a enjoyable and risk-free way to experience betting. With no financial commitment, a large game library, and possibilities for learning, it is understandable that countless gamblers choose free casino games for their gambling choices.
Unveiling Real Money Slots
Commencement
Cash slots have turned into a popular alternative for casino enthusiasts desiring the thrill of earning tangible money. This text investigates the benefits of money slots and the motivations they are attracting increasing players.
Benefits of Real Money Slots
Genuine Rewards
The primary attraction of real money slots is the opportunity to gain genuine funds. Unlike free slots, money slots give enthusiasts the excitement of potential monetary payouts.
Extensive Game Variety
Real money slots offer a wide variety of themes, features, and payout structures. This makes sure that there is an activity for every kind of gambler, including traditional three-reel classic slots to contemporary animated slots with multiple paylines and special bonuses.
Enticing Deals
Many web-based casinos give attractive incentives for money slot enthusiasts. These can include sign-up rewards, complimentary spins, cashback offers, and VIP schemes. Such promotions boost the total playing journey and supply additional opportunities to earn funds.
Motivations for Opting for Money Slots
The Thrill of Winning Real Money
Money slots provide an exhilarating adventure, as users await the possibility of winning actual cash. This feature imparts an extra layer of anticipation to the gameplay adventure.
Quick Earnings
Money slots provide players the pleasure of instant earnings. Gaining funds promptly improves the betting adventure, making it more gratifying.
Numerous Game Choices
Including cash slots, enthusiasts can experience a wide variety of slots, making sure that there is constantly a game fresh to test.
Conclusion
Gambling slots offers a exhilarating and gratifying casino journey. With the potential to secure tangible funds, a broad array of slot machines, and enticing promotions, it’s obvious that numerous gamblers like money slots for their betting preferences.
I have not checked in here for some time since I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are good quality so I guess I¦ll add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend :)
Thanks for sharing superb informations. Your site is very cool. I am impressed by the details that you’ve on this website. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for extra articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found just the information I already searched all over the place and simply couldn’t come across. What a great web site.
I got what you mean , appreciate it for posting.Woh I am happy to find this website through google.
Appreciate it for helping out, great information. “Courage comes and goes. Hold on for the next supply.” by Vicki Baum.
рассчитать стоимость такси https://taxi-vyzvat.ru
Pro88
hi!,I like your writing very a lot! proportion we communicate more about your article on AOL? I require an expert in this space to unravel my problem. May be that is you! Looking forward to look you.
I like this web site very much, Its a very nice billet to read and get information. “There is no human problem which could not be solved if people would simply do as I advise.” by Gore Vidal.
Советы по оптимизации продвижению.
Информация о том как работать с низкочастотными запросами и как их выбирать
Стратегия по действиям в конкурентной нише.
У меня есть регулярных взаимодействую с тремя организациями, есть что поделиться.
Изучите мой аккаунт, на 31 мая 2024г
общий объём выполненных работ 2181 только здесь.
Консультация проходит в устной форме, никаких снимков с экрана и отчетов.
Продолжительность консультации указано 2 ч, но по сути всегда на контакте без твердой привязки к графику.
Как управлять с софтом это уже отдельная история, консультация по работе с программами оговариваем отдельно в специальном услуге, выясняем что нужно при коммуникации.
Всё спокойно на расслабленно не торопясь
To get started, the seller needs:
Мне нужны данные от телеграм канала для коммуникации.
разговор только в устной форме, переписываться нету времени.
субботы и Вс выходной
I wanted to thank you for this great read!! I definitely enjoying every little bit of it I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you post…
I am continuously searching online for posts that can facilitate me. Thx!
vong lo?i euro 2024
You completed a few good points there. I did a search on the subject and found nearly all persons will consent with your blog.
Ищете способ расслабиться и получить незабываемые впечатления? Мы https://t.me/intim_tmn72 предлагаем эксклюзивные встречи с привлекательными и профессиональными компаньонками. Конфиденциальность, комфорт и безопасность гарантированы. Позвольте себе наслаждение и отдых в приятной компании.
you are really a good webmaster. The site loading velocity is incredible. It kind of feels that you are doing any distinctive trick. Moreover, The contents are masterpiece. you have done a magnificent activity on this matter!
What Is FitSpresso? FitSpresso is a dietary supplement that is made to support healthy fat-burning in the body
https://stixandstonz.ca/polaslot138
vòng loại euro 2024
Yeah bookmaking this wasn’t a risky determination outstanding post! .
I consider something really special in this website .
娛樂城官網
娛樂城官網
где купить мебель
https://formomebel.ru/stoliki/metallicheskie
голяк смотреть онлайн бесплатно в хорошем голяк смотреть онлайн
Slotเว็บตรง – ร่วมสนุกในการเล่นได้ทุกเครื่องมือที่เชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ต
ในปัจจุบันนี้ การเล่นเกมสล็อตมีความสะดวกมากยิ่งขึ้น คุณไม่ต้องเดินทางไปยังสถานที่เล่นคาสิโนที่ไหน ๆ เพียงแค่มีอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้งานได้เชื่อมต่อกับอินเทอร์เน็ต คุณก็อาจสนุกกับการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์กับ PG Slot ได้จากทุกที่
การอัพเกรดเทคโนโลยีของ PG Slot
ที่ PG Slot เราได้สร้างสรรค์โซลูชั่นสำหรับการบริการเกมคาสิโนออนไลน์เพื่อตอบสนองความต้องการของผู้เล่นให้มากที่สุด คุณไม่จำเป็นติดตั้งซอฟต์แวร์หรือนำมาใช้งานแอปพลิเคชันใด ๆ ให้น่าเบื่อหรือเปลืองพื้นที่ในอุปกรณ์ของคุณ การให้บริการเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ของเราทำงานผ่านเว็บตรงที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี HTML 5 ที่ทันสมัย
เล่นสล็อตได้ทุกเครื่องมือ
คุณอาจเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์กับ PG Slot ได้อย่างไม่ยุ่งยากเพียงเข้าสู่ในเว็บไซต์ของเรา เว็บตรงสล็อตออนไลน์ของเรารองรับทุกซอฟต์แวร์และทุกประเภททั้ง Android และ iOS ไม่ว่าคุณจะใช้สมาร์ทโฟน แล็ปท็อป หรืออุปกรณ์พกพารุ่นไหน ก็สามารถมั่นใจได้ว่าคุณจะเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ได้อย่างรื่นไหล ไม่มีการขัดข้องหรือติดขัดใด ๆ
ทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี
เว็บตรงของเรามีบริการเพียงแค่คุณเข้าสู่ในเว็บไซต์ของ PG Slot ก็อาจทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรีได้ทันที ไม่ต้องเสียค่าธรรมเนียมใด ๆ นี่เป็นโอกาสที่ดีในการเรียนรู้และศึกษาวิธีการเล่นเกี่ยวกับเกมก่อนที่จะวางเดิมพันด้วยเงินจริง
การเล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์กับ PG Slot ช่วยให้คุณสามารถเพลิดเพลินกับการเล่นเกมคาสิโนได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา ไม่ว่าคุณจะอยู่ที่ไหน เพียงแค่มีอุปกรณ์เชื่อมต่อที่เข้าถึงอินเทอร์เน็ต คุณก็อาจสนุกกับการเล่นเกมสล็อตได้อย่างไม่มีข้อจำกัดใด ๆ!
It is appropriate time to make some plans for the future and it’s time to be happy. I have read this post and if I could I want to suggest you some interesting things or tips. Perhaps you can write next articles referring to this article. I want to read even more things about it!
https://tarjomehsho.com/?keyword=data-macau-2023
https://friendscappuccinobar.ca/idcash88
I think other website proprietors should take this website as an example , very clean and great user pleasant style.
富遊娛樂城評價:2024年最新評價
推薦指數 : ★★★★★ ( 5.0/5 )
富遊娛樂城作為目前最受歡迎的博弈網站之一,在台灣擁有最高的註冊人數。
RG富遊以安全、公正、真實和順暢的品牌保證,贏得了廣大玩家的信賴。富遊線上賭場不僅提供了豐富多樣的遊戲種類,還有眾多吸引人的優惠活動。在出金速度方面,獲得無數網紅和網友的高度評價,確保玩家能享有無憂的博弈體驗。
推薦要點
新手首選: 富遊娛樂城,2024年評選首選,提供專為新手打造的豐富教學和獨家優惠。
一存雙收: 首存1000元,立獲1000元獎金,僅需1倍流水,新手友好。
免費體驗: 新玩家享免費體驗金,暢遊各式遊戲,開啟無限可能。
優惠多元: 活動豐富,流水要求低,適合各類型玩家。
玩家首選: 遊戲多樣,服務優質,是新手與老手的最佳賭場選擇。
富遊娛樂城詳情資訊
賭場名稱 : RG富遊
創立時間 : 2019年
賭場類型 : 現金版娛樂城
博弈執照 : 馬爾他牌照(MGA)認證、英屬維爾京群島(BVI)認證、菲律賓(PAGCOR)監督競猜牌照
遊戲類型 : 真人百家樂、運彩投注、電子老虎機、彩票遊戲、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲
存取速度 : 存款5秒 / 提款3-5分
軟體下載 : 支援APP,IOS、安卓(Android)
線上客服 : 需透過官方LINE
富遊娛樂城優缺點
優點
台灣註冊人數NO.1線上賭場
首儲1000贈1000只需一倍流水
擁有體驗金免費體驗賭場
網紅部落客推薦保證出金線上娛樂城
缺點
需透過客服申請體驗金
富遊娛樂城存取款方式
存款方式
提供四大超商(全家、7-11、萊爾富、ok超商)
虛擬貨幣ustd存款
銀行轉帳(各大銀行皆可)
取款方式
網站內申請提款及可匯款至綁定帳戶
現金1:1出金
富遊娛樂城平台系統
真人百家 — RG真人、DG真人、歐博真人、DB真人(原亞博/PM)、SA真人、OG真人、WM真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、熊貓體育(原亞博/PM)
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —RG電子、ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、GR電子(好路)
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌
電競遊戲 — 熊貓體育
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、DB捕魚
在现代,在线赌场提供了多种便捷的存款和取款方式。对于较大金额的存款,您可以选择中国信托、台中银行、合作金库、台新银行、国泰银行或中华邮政。这些银行提供的服务覆盖金额范围从$1000到$10万,确保您的资金可以安全高效地转入赌场账户。
如果您需要进行较小金额的存款,可以选择通过便利店充值。7-11、全家、莱尔富和OK超商都提供这种服务,适用于金额范围在$1000到$2万之间的充值。通过这些便利店,您可以轻松快捷地完成资金转账,无需担心银行的营业时间或复杂的操作流程。
在进行娱乐场提款时,您可以选择通过各大银行转账或ATM转账。这些方法不仅安全可靠,而且非常方便,适合各种提款需求。最低提款金额为$1000,而上限则没有限制,确保您可以灵活地管理您的资金。
在选择在线赌场时,玩家评价和推荐也是非常重要的。许多IG网红和部落客,如丽莎、穎柔、猫少女日记-Kitty等,都对一些知名的娱乐场给予了高度评价。这些推荐不仅帮助您找到可靠的娱乐场所,还能确保您在游戏中享受到最佳的用户体验。
总体来说,在线赌场通过提供多样化的存款和取款方式,以及得到广泛认可的服务质量,正在不断吸引更多的玩家。无论您选择通过银行还是便利店进行充值,都能体验到快速便捷的操作。同时,通过查看玩家的真实评价和推荐,您也能更有信心地选择合适的娱乐场,享受安全、公正的游戏环境。
Player台灣線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
layer如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
安全與公平性
安全永遠是我們評測的首要標準。我們審查每家娛樂城的執照資訊、監管機構以及使用的隨機數生成器,以確保其遊戲結果的公平性和隨機性。
02.
遊戲品質與多樣性
遊戲的品質和多樣性對於玩家體驗至關重要。我們評估遊戲的圖形、音效、用戶介面和創新性。同時,我們也考量娛樂城提供的遊戲種類,包括老虎機、桌遊、即時遊戲等。
03.
娛樂城優惠與促銷活動
我們仔細審視各種獎勵計劃和促銷活動,包括歡迎獎勵、免費旋轉和忠誠計劃。重要的是,我們也檢查這些優惠的賭注要求和條款條件,以確保它們公平且實用。
04.
客戶支持
優質的客戶支持是娛樂城質量的重要指標。我們評估支持團隊的可用性、響應速度和專業程度。一個好的娛樂城應該提供多種聯繫方式,包括即時聊天、電子郵件和電話支持。
05.
銀行與支付選項
我們檢查娛樂城提供的存款和提款選項,以及相關的處理時間和手續費。多樣化且安全的支付方式對於玩家來說非常重要。
06.
網站易用性、娛樂城APP體驗
一個直觀且易於導航的網站可以顯著提升玩家體驗。我們評估網站的設計、可訪問性和移動兼容性。
07.
玩家評價與反饋
我們考慮真實玩家的評價和反饋。這些資料幫助我們了解娛樂城在實際玩家中的表現。
娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 – Casino, Gambling、中國 – 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 – オンラインカジノ、越南 – Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。
Great post. I am facing a couple of these problems.
But wanna comment on few general things, The website pattern is perfect, the content is very superb : D.
As I web site possessor I believe the content matter here is rattling great , appreciate it for your hard work. You should keep it up forever! Good Luck.
https://emmerechts.com/?keyword=sultan33
娛樂城評價
2024娛樂城推薦,經過玩家實測結果出爐Top5!
2024娛樂城排名是這五間上榜,玩家尋找娛樂城無非就是要找穩定出金娛樂城,遊戲體驗良好、速度流暢,Ace博評網都幫你整理好了,給予娛樂城新手最佳的指南,不再擔心被黑網娛樂城詐騙!
2024娛樂城簡述
在現代,2024娛樂城數量已經超越以前,面對琳瑯滿目的娛樂城品牌,身為新手的玩家肯定難以辨別哪間好、哪間壞。
好的平台提供穩定的速度與遊戲體驗,穩定的系統與資訊安全可以保障用戶的隱私與資料,不用擔心收到傳票與任何網路威脅,這些線上賭場也提供合理的優惠活動給予玩家。
壞的娛樂城除了會騙取你的金錢之外,也會打著不實的廣告、優惠滿滿,想領卻是一場空!甚至有些平台還沒辦法登入,入口網站也是架設用來騙取新手儲值進他們口袋,這些黑網娛樂城是玩家必須避開的風險!
評測2024娛樂城的標準
Ace這次從網路上找來五位使用過娛樂城資歷2年以上的老玩家,給予他們使用各大娛樂城平台,最終選出Top5,而評選標準為下列這些條件:
以玩家觀點出發,優先考量玩家利益
豐富的遊戲種類與卓越的遊戲體驗
平台的信譽及其安全性措施
客服團隊的回應速度與服務品質
簡便的儲值流程和多樣的存款方法
吸引人的優惠活動方案
前五名娛樂城表格
賭博網站排名 線上賭場 平台特色 玩家實測評價
No.1 富遊娛樂城 遊戲選擇豐富,老玩家優惠多 正面好評
No.2 bet365娛樂城 知名大廠牌,運彩盤口選擇多 介面流暢
No.3 亞博娛樂城 多語言支持,介面簡潔順暢 賽事豐富
No.4 PM娛樂城 撲克牌遊戲豐富,選擇多元 直播順暢
No.5 1xbet娛樂城 直播流暢,安全可靠 佳評如潮
線上娛樂城玩家遊戲體驗評價分享
網友A:娛樂城平台百百款,富遊娛樂城是我3年以來長期使用的娛樂城,別人有的系統他們都有,出金也沒有被卡過,比起那些玩娛樂城還會收到傳票的娛樂城,富遊真的很穩定,值得推薦。
網友B:bet365中文的介面簡約,還有超多體育賽事盤口可以選擇,此外賽事大部分也都有附上直播來源,不必擔心看不到賽事最新狀況,全螢幕還能夠下單,真的超方便!
網友C:富遊娛樂城除了第一次儲值有優惠之外,儲值到一定金額還有好禮五選一,實用又方便,有問題的時候也有客服隨時能夠解答。
網友D:從大陸來台灣工作,沒想到台灣也能玩到亞博體育,這是以前在大陸就有使用的平台,雖然不是簡體字,但使用介面完全沒問題,遊戲流暢、速度比以前使用還更快速。
網友E:看玖壹壹MV發現了PM娛樂城這個大品牌,PM的真人百家樂沒有輸給在澳門實地賭場,甚至根本不用出門,超級方便的啦!
mamibet
I am often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has really peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information.
We absolutely love your blog and find almost all of your post’s to be exactly I’m looking for. Would you offer guest writers to write content to suit your needs? I wouldn’t mind composing a post or elaborating on a number of the subjects you write regarding here. Again, awesome blog!
2024娛樂城介紹
台灣2024娛樂城越開越多間,新開的線上賭場層出不窮,每間都以獨家的娛樂城優惠和體驗金來吸引玩家,致力於提供一流的賭博遊戲體驗。以下來介紹這幾間娛樂城網友對他們的真實評價,看看哪些娛樂城上榜了吧!
2024娛樂城排名
2023下半年,各家娛樂城競爭激烈,相繼推出誘人優惠,不論是娛樂城體驗金、反水流水還是首儲禮金,甚至還有娛樂城抽I15手機。以下就是2024年網友推薦的娛樂城排名:
NO.1 富遊娛樂城
NO.2 Bet365台灣
NO.3 DG娛樂城
NO.4 九州娛樂城
NO.5 亞博娛樂城
2024娛樂城推薦
根據2024娛樂城排名,以下將富遊娛樂城、BET365、亞博娛樂城、九州娛樂城、王者娛樂城推薦給大家,包含首儲贈點、免費體驗金、存提款速度、流水等等…
娛樂城遊戲種類
線上娛樂城憑藉其廣泛的遊戲種類,成功滿足了各式各樣玩家的喜好和需求。這些娛樂城遊戲不僅多元化且各具特色,能夠為玩家提供無與倫比的娛樂體驗。下面是一些最受歡迎的娛樂城遊戲類型:
電子老虎機
魔龍傳奇、雷神之鎚、戰神呂布、聚寶財神、鼠來寶、皇家777
真人百家樂
真人視訊百家樂、牛牛、龍虎、炸金花、骰寶、輪盤
電子棋牌
德州撲克、兩人麻將、21點、十三支、妞妞、三公、鬥地主、大老二、牌九
體育下注
世界盃足球賽、NBA、WBC世棒賽、英超、英雄聯盟LOL、特戰英豪
線上彩票
大樂透、539、美國天天樂、香港六合彩、北京賽車
捕魚機遊戲
三仙捕魚、福娃捕魚、招財貓釣魚、西遊降魔、吃我一砲、賓果捕魚
2024娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城/線上賭場(現金網)是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,而且是現金網,大家也許會好奇為什麼不直接叫做線上賭場或是線上博弈就好了。
其實這是有原因的,線上賭場這種東西,架站在台灣是違法的,在早期經營線上博弈被抓的風險非常高所以換了一個打模糊仗的代稱「娛樂城」來規避警方的耳目,畢竟以前沒有Google這種東西,這樣的代稱還是多少有些作用的。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種賭博平台,允許玩家在沒有預先充值的情況下參與遊戲。這種模式類似於信用卡,通常以周結或月結的方式結算遊戲費用。因此,如果玩家無法有效管理自己的投注額,可能會在月底面臨巨大的支付壓力。
娛樂城不出金怎麼辦?
釐清原因,如未違反娛樂城機制,可能是遇上黑網娛樂城,請盡快通報165反詐騙。
As a Newbie, I am constantly browsing online for articles that can aid me. Thank you
Портал о Ярославле – ваш гид по культурной жизни города. Здесь вы найдёте информацию о театрах, музеях, галереях и исторических достопримечательностях. Откройте для себя яркие события, фестивали и выставки, которые делают Ярославль культурной жемчужиной России.
Player台灣線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
layer如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
安全與公平性
安全永遠是我們評測的首要標準。我們審查每家娛樂城的執照資訊、監管機構以及使用的隨機數生成器,以確保其遊戲結果的公平性和隨機性。
02.
遊戲品質與多樣性
遊戲的品質和多樣性對於玩家體驗至關重要。我們評估遊戲的圖形、音效、用戶介面和創新性。同時,我們也考量娛樂城提供的遊戲種類,包括老虎機、桌遊、即時遊戲等。
03.
娛樂城優惠與促銷活動
我們仔細審視各種獎勵計劃和促銷活動,包括歡迎獎勵、免費旋轉和忠誠計劃。重要的是,我們也檢查這些優惠的賭注要求和條款條件,以確保它們公平且實用。
04.
客戶支持
優質的客戶支持是娛樂城質量的重要指標。我們評估支持團隊的可用性、響應速度和專業程度。一個好的娛樂城應該提供多種聯繫方式,包括即時聊天、電子郵件和電話支持。
05.
銀行與支付選項
我們檢查娛樂城提供的存款和提款選項,以及相關的處理時間和手續費。多樣化且安全的支付方式對於玩家來說非常重要。
06.
網站易用性、娛樂城APP體驗
一個直觀且易於導航的網站可以顯著提升玩家體驗。我們評估網站的設計、可訪問性和移動兼容性。
07.
玩家評價與反饋
我們考慮真實玩家的評價和反饋。這些資料幫助我們了解娛樂城在實際玩家中的表現。
娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 – Casino, Gambling、中國 – 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 – オンラインカジノ、越南 – Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。
在现代,在线赌场提供了多种便捷的存款和取款方式。对于较大金额的存款,您可以选择中国信托、台中银行、合作金库、台新银行、国泰银行或中华邮政。这些银行提供的服务覆盖金额范围从$1000到$10万,确保您的资金可以安全高效地转入赌场账户。
如果您需要进行较小金额的存款,可以选择通过便利店充值。7-11、全家、莱尔富和OK超商都提供这种服务,适用于金额范围在$1000到$2万之间的充值。通过这些便利店,您可以轻松快捷地完成资金转账,无需担心银行的营业时间或复杂的操作流程。
在进行娱乐场提款时,您可以选择通过各大银行转账或ATM转账。这些方法不仅安全可靠,而且非常方便,适合各种提款需求。最低提款金额为$1000,而上限则没有限制,确保您可以灵活地管理您的资金。
在选择在线赌场时,玩家评价和推荐也是非常重要的。许多IG网红和部落客,如丽莎、穎柔、猫少女日记-Kitty等,都对一些知名的娱乐场给予了高度评价。这些推荐不仅帮助您找到可靠的娱乐场所,还能确保您在游戏中享受到最佳的用户体验。
总体来说,在线赌场通过提供多样化的存款和取款方式,以及得到广泛认可的服务质量,正在不断吸引更多的玩家。无论您选择通过银行还是便利店进行充值,都能体验到快速便捷的操作。同时,通过查看玩家的真实评价和推荐,您也能更有信心地选择合适的娱乐场,享受安全、公正的游戏环境。
I got what you intend,saved to bookmarks, very decent site.
koitoto
Well I definitely liked reading it. This post procured by you is very helpful for good planning.
Perfectly written subject matter, appreciate it for selective information. “The earth was made round so we would not see too far down the road.” by Karen Blixen.
Some genuinely nice and utilitarian info on this site, as well I conceive the design and style has wonderful features.
I like this blog so much, saved to fav. “Respect for the fragility and importance of an individual life is still the mark of an educated man.” by Norman Cousins.
I like this weblog very much so much wonderful info .
Thanks so much for providing individuals with an exceptionally spectacular possiblity to read articles and blog posts from this blog. It really is very sweet and packed with a good time for me personally and my office mates to search your web site at the very least 3 times in a week to find out the new stuff you have got. And definitely, we’re usually fascinated concerning the brilliant methods you serve. Some 4 tips on this page are clearly the most suitable I’ve ever had.
I am not sure where you’re getting your info, but good topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more. Thanks for magnificent info I was looking for this information for my mission.
I don’t even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was great. I don’t know who you are but certainly you’re going to a famous blogger if you are not already ;) Cheers!
Does your site have a contact page? I’m having problems locating it but, I’d like to shoot you an e-mail. I’ve got some creative ideas for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great website and I look forward to seeing it grow over time.
pg slot
??????????????? — ????????? ?????????????? ??????? ?????????????????? ??? ?????????????
???????????????? ??? PG ????????????????????????? ???????? ???????????? ???????????????????????????? ??????? ???????????????? ?????? ???????? ???? ???? ??????
??? ????????? ????????????????????????????????? ????????? ???????? ????????????? ??? ???????????????????????????????? ?????? ??? HTML 5 ???????? ??????????????? ???????? ?????????????????? ????????????? ?????????? ??????????????????????????? ????? ??????????????????? ???????????? ????????? ??????????? ??????????? ????????? ????????????????????
????????????????????????
?????????????? ????????? ???? Android ???? ??????? ???????? ????????????????????????????? ?????????? ??????????????????? ????????????????? ?????????????? ??? ???????? ???????????????????? ???? ?????????????????????????? ???????????????? ??????????? ?????????? ????????????????????
????????????????????
??????????????????????????????????????? PG Slot ????? ????????? ??????????????? ???????? ??????????? ???????? ?????????? ???????????? ??????????????????? ???????????????????????? ????????? ???????????????? ????????????? ???????????????????? ????????????????????? ????????????????????
?????????????????
???????? ?????????????? ????????????????????????????? PG Slot ????????????????????????????????? ????????? ??????????????????????????????????????????????? ??? ?????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????
????????????????????????????
PG Slot ??????????????????????????????????? ????? ??????????????????????????????????????????????? 24 ??????? ????????????????? ?????????????????????????????? ??????????? ?????????????????? ???????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????
??????????????????????????
?????????????????????????????????????? PG Slot ??????? ?? ?????????????????????? ??????????????? ???????????????????????? ????????? ?????????????????????????????????????????? ????????? ?????????????????????????????
??????????????????????? PG Slot ????????????????????????? ???????????????????????????????????????????????????????? ?????????????????????????????????????????????????? ?????????????????????????????? ???????? ????????????????????? ?????????????????????????????????? ????????? ????????????????????????????? PG Slot ??????!
สล็อตเว็บตรง: ความสนุกสนานที่คุณไม่ควรพลาด
การเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ในปัจจุบันได้รับความนิยมเพิ่มมากขึ้น เนื่องจากความสะดวกสบายที่ผู้ใช้สามารถใช้งานได้ได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา โดยไม่ต้องเสียเวลาเดินทางถึงคาสิโน ในเนื้อหานี้ เราจะกล่าวถึง “สล็อต” และความเพลิดเพลินที่ท่านสามารถพบได้ในเกมสล็อตเว็บตรง
ความสะดวกสบายในการเล่นเกมสล็อต
หนึ่งในสล็อตที่เว็บตรงเป็นที่ยอดนิยมอย่างยิ่ง คือความสะดวกที่ผู้เล่นมี คุณสามารถเล่นสล็อตได้ทุกที่ตลอดเวลา ไม่ว่าจะเป็นที่บ้านของคุณ ที่ทำงาน หรือแม้แต่ขณะเดินทางอยู่ สิ่งที่จำเป็นต้องมีคืออุปกรณ์ที่เชื่อมต่อที่ต่ออินเทอร์เน็ตได้ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นโทรศัพท์มือถือ แทปเล็ต หรือโน้ตบุ๊ก
เทคโนโลยีกับสล็อตเว็บตรง
การเล่นสล็อตในปัจจุบันนี้ไม่เพียงแต่สะดวก แต่ยังประกอบด้วยเทคโนโลยีที่ทันสมัยล้ำสมัยอีกด้วย สล็อตออนไลน์เว็บตรงใช้เทคโนโลยี HTML5 ซึ่งทำให้ผู้เล่นไม่ต้องกังวลใจเกี่ยวกับการลงซอฟต์แวร์หรือแอพพลิเคชั่น แค่เปิดเบราว์เซอร์บนอุปกรณ์ที่คุณมีและเข้าไปที่เว็บของเรา คุณก็สามารถสนุกกับเกมได้ทันที
ความหลากหลายของเกมของเกมของสล็อต
สล็อตออนไลน์เว็บตรงมาพร้อมกับความหลากหลายของเกมของเกมที่ท่านสามารถเลือกเล่นได้ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นสล็อตคลาสสิกหรือเกมสล็อตที่มาพร้อมกับฟีเจอร์เด็ดและโบนัสเพียบ ท่านจะพบว่ามีเกมให้เลือกเล่นมากมาย ซึ่งทำให้ไม่เคยเบื่อกับการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์
รองรับทุกอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้
ไม่ว่าท่านจะใช้สมาร์ทโฟนแอนดรอยด์หรือ iOS คุณก็สามารถเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ได้ได้อย่างลื่นไหล เว็บไซต์ของเรารองรับทุกระบบปฏิบัติการและทุกอุปกรณ์ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นโทรศัพท์มือถือรุ่นล่าสุดหรือรุ่นเก่าแก่ หรือถึงแม้จะเป็นแทปเล็ตและแล็ปท็อป ท่านก็สามารถเพลิดเพลินกับเกมสล็อตได้อย่างเต็มที่
สล็อตทดลองฟรี
สำหรับมือใหม่กับการเล่นสล็อต หรือยังไม่แน่ใจเกี่ยวกับเกมที่ต้องการเล่น PG Slot ยังมีบริการสล็อตทดลองฟรี คุณเริ่มเล่นได้ทันทีทันทีโดยไม่ต้องสมัครสมาชิกหรือฝากเงิน การทดลองเล่นสล็อตนี้จะช่วยให้ผู้เล่นเรียนรู้วิธีการเล่นและเข้าใจเกมได้โดยไม่ต้องเสียค่าใช้จ่ายใด ๆ
โปรโมชันและโบนัส
ข้อดีอีกอย่างหนึ่งของการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์กับ PG Slot คือมีโปรโมชันและโบนัสมากมายสำหรับนักเดิมพัน ไม่ว่าคุณจะเป็นผู้เล่นใหม่หรือสมาชิกเก่า ท่านสามารถรับโบนัสและโปรโมชันต่าง ๆ ได้ตลอดเวลา ซึ่งจะเพิ่มโอกาสชนะและเพิ่มความสนุกสนานในเกม
โดยสรุป
การเล่นสล็อตที่ PG Slot เป็นการการลงทุนทางเกมที่คุ้มค่า ผู้เล่นจะได้รับความเพลิดเพลินและความง่ายดายจากการเล่นสล็อต นอกจากนี้ยังมีโอกาสชนะรางวัลและโบนัสมากมาย ไม่ว่าคุณจะใช้สมาร์ทโฟน แท็บเล็ทหรือคอมพิวเตอร์ยี่ห้อไหน ก็สามารถเล่นได้ทันที อย่ารอช้า สมัครสมาชิกและเริ่มเล่น PG Slot ทันที
https://lkr88.com/?keyword=syair-hk-asiktoto
pg slot
สล็อตเว็บตรง — ใช้ได้กับ มือถือ แท็บเล็ต คอมพิวเตอร์ ฯลฯ เพื่อเล่น
ระบบสล็อตเว็บตรง ของ PG ได้รับการพัฒนาและปรับแต่ง เพื่อให้ สามารถใช้งาน บนอุปกรณ์ที่หลากหลายได้อย่าง สมบูรณ์ ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้ โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเล็ต หรือ คอมฯ รุ่นใด
ที่ พีจีสล็อต เราเข้าใจว่าผู้เล่นต้องการ ของลูกค้า ในเรื่อง ความสะดวกสบาย และ การเข้าถึงเกมคาสิโนที่รวดเร็ว เราจึง ใช้ HTML 5 ซึ่งเป็น เทคโนโลยีล่าสุด ปัจจุบันนี้ พัฒนาเว็บของเรา คุณจึงไม่ต้อง โหลดแอป หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมเพิ่มเติม เพียง เปิดบราวเซอร์ บนอุปกรณ์ที่ คุณมีอยู่ และเยี่ยมชม เว็บของเรา คุณสามารถ สนุกกับสล็อตได้ทันที
การใช้งานกับอุปกรณ์หลากหลาย
ไม่ว่าคุณจะใช้ สมาร์ทโฟน ระบบ แอนดรอยด์ หรือ iOS ก็สามารถ เล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ได้ไม่มีสะดุด ระบบของเรา ออกแบบมาเพื่อรองรับ ทุกระบบปฏิบัติการ ไม่สำคัญว่าคุณ กำลังใช้ สมาร์ทโฟน รุ่นใหม่หรือรุ่นเก่า หรือ แม้แต่แท็บเล็ตหรือแล็ปท็อป ทุกอย่างก็สามารถ ใช้งานได้ ไม่มีปัญหา ความเข้ากันได้
เล่นได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา
หนึ่งในข้อดีของการเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot ก็คือ คุณสามารถ เล่นได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา ไม่ว่าจะ เป็นที่บ้าน ที่ออฟฟิศ หรือแม้แต่ สถานที่สาธารณะ สิ่งที่คุณต้องมีคือ การเชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ต คุณสามารถ เริ่มเกมได้ทันที และคุณไม่ต้อง กังวลเรื่องการโหลด หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมที่ ใช้พื้นที่ในอุปกรณ์
เล่นสล็อตฟรี
เพื่อให้ ผู้เล่นที่ใหม่ ได้ลองและรู้จักเกมสล็อตของเรา PG Slot ยังมีสล็อตทดลองฟรี คุณสามารถ เล่นได้ทันทีโดยไม่ต้องสมัครสมาชิกหรือฝากเงิน การ ทดลองเล่นสล็อตนี้จะช่วยให้คุณรู้จักวิธีการเล่นและเข้าใจเกมก่อนเดิมพันด้วยเงินจริง
การให้บริการและความปลอดภัย
PG Slot มุ่งมั่นในการบริการลูกค้าที่ดีที่สุด เรามี ทีมบริการที่พร้อมช่วยเหลือตลอด 24 ชั่วโมง นอกจากนี้เรายังมี ระบบความปลอดภัยที่ทันสมัย ด้วยวิธีนี้ คุณจึงมั่นใจได้ว่า ข้อมูลและการเงินของคุณจะปลอดภัย
โปรโมชั่นและโบนัสพิเศษ
ข้อดีอีกประการของการเล่นสล็อตแมชชีนกับ PG Slot คือ มี โปรโมชั่นและโบนัสพิเศษมากมายสำหรับผู้เข้าร่วม ไม่ว่าคุณจะเป็น ผู้เล่นใหม่หรือเก่า คุณสามารถ รับโปรโมชันและโบนัสได้ สิ่งนี้จะ เพิ่มโอกาสชนะและความสนุกในเกม
สรุปการเล่นสล็อตเว็บที่ PG Slot ถือเป็นการลงทุนที่คุ้มค่า คุณจะไม่เพียงได้รับความสุขและความสะดวกสบายจากเกมเท่านั้น แต่คุณยังมีโอกาสลุ้นรับรางวัลและโบนัสมากมายอีกด้วย ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเล็ต หรือคอมพิวเตอร์รุ่นใด สามารถมาร่วมสนุกกับเราได้เลยตอนนี้ อย่ารอช้า ลงทะเบียนและเริ่มเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot วันนี้!
pg สล็อต
สำหรับ ไซต์ PG Slots มีความ มี ความได้เปรียบ หลายประการ ในเปรียบเทียบกับ คาสิโนแบบ ดั้งเดิม, โดยเฉพาะ ใน ปัจจุบัน. ประโยชน์สำคัญ เหล่านี้ ได้แก่:
ความสะดวกสบาย: คุณ สามารถเข้าถึง สล็อตออนไลน์ได้ ตลอดเวลา จาก ทุกสถานที่, ช่วย ผู้เล่นสามารถ เข้าร่วม ได้ ทุกสถานที่ โดยไม่จำเป็นต้อง เสียเวลา ไปคาสิโนแบบ ปกติ ๆ
เกมหลากหลายรูปแบบ: สล็อตออนไลน์ มีการนำเสนอ ประเภทเกม ที่ มากมาย, เช่น สล็อตแบบดั้งเดิม หรือ ประเภทเกม ที่มี ความสามารถ และโบนัส พิเศษ, ไม่ก่อให้เกิด ความเบื่อหน่าย ในเกม
ส่วนลด และรางวัล: สล็อตออนไลน์ ส่วนใหญ่ เสนอ ข้อเสนอส่งเสริมการขาย และค่าตอบแทน เพื่อปรับปรุง โอกาสในการ ในการ ชนะ และ ปรับปรุง ความผ่อนคลาย ให้กับเกม
ความปลอดภัย และ ความเชื่อถือได้: สล็อตออนไลน์ โดยทั่วไป มีการ การป้องกัน ที่ มีประสิทธิภาพ, และ ทำให้มั่นใจ ว่า ข้อมูลส่วนตัว และ การเงิน จะมี คุ้มครอง
การสนับสนุนลูกค้า: PG Slots มีทีม ทีมงาน ที่มีคุณภาพ ที่มุ่งมั่น สนับสนุน ตลอด 24 ชั่วโมง
การเล่นบนโทรศัพท์: สล็อต PG ให้บริการ การเล่นบนมือถือ, ให้ ผู้เล่นสามารถทดลอง ตลอด 24 ชั่วโมง
เล่นฟรี: เกี่ยวกับ ผู้เล่นใหม่, PG ยังเสนอ ทดลองใช้ฟรี เพิ่มเติมด้วย, เพื่อให้ คุณ ทดลอง วิธีใช้ และเข้าใจ เกมก่อน เล่นด้วยเงินจริง
สล็อต PG มีลักษณะ คุณสมบัติที่ดี หลายอย่าง ที่ ก่อให้เกิด ให้ได้รับความสำคัญ ในวันนี้, ทำให้ การ ความสนุกสนาน ให้กับเกมด้วย.
ทดลองปฏิบัติเล่นสล็อต และค้นพบประสบการณ์การเล่นเกมที่ไม่เหมือนใคร!
สำหรับนักพนันที่กำลังพิจารณาความบันเทิงและโอกาสในการชนะรางวัลมหาศาล สล็อตออนไลน์เป็นอีกหนึ่งทางเลือกที่คุ้มค่าพิจารณา.ด้วยความหลากหลายของเกมสล็อตที่น่าตื่นเต้น ผู้เล่นสามารถทดลองเล่นและค้นหาเกมที่ถูกใจได้อย่างง่ายดาย.
ไม่ว่าคุณจะชอบเกมสล็อตคลาสสิกหรือต้องการความท้าทาย, ทางเลือกรอล้ำหน้าให้คุณสัมผัส. จากสล็อตที่มีหัวข้อมากมาย ไปจนถึงเกมที่มีฟีเจอร์พิเศษและรางวัล, ผู้เล่นจะได้พบกับประสบการณ์ใหม่ที่น่าตื่นเต้นและน่าติดตาม.
ด้วยการทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี, คุณสามารถปฏิบัติวิธีการเล่นและค้นตัดสินใจกลยุทธ์ที่ถูกใจก่อนเริ่มลงเดิมพันด้วยเงินจริง. นี่คือโอกาสที่จะปฏิบัติกับเกมและประยุกต์โอกาสในการคว้ารางวัลใหญ่.
อย่าเลื่อนเวลา, ลงมือกับการทดลองเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์วันนี้ และค้นพบประสบการณ์การเล่นเกมที่ไม่เหมือนใคร! เพลิดเพลินความสนใจ, ความยินดี และโอกาสในการชนะรางวัลใหญ่. กล้าก้าวไปเดินทางสู่ความสมหวังของคุณในวงการสล็อตออนไลน์แล้ววันนี้!
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg
ทดสอบ เล่น สล็อต PG พร้อม เข้าไปสู่ สู่ โลก แห่ง ความเพลิดเพลิน ที่ ไร้ขอบเขต
ต่อ คอพนัน ที่ คิดค้น กำลังมองหา อารมณ์ เกมใหม่, สล็อต PG ถือเป็น ตัวเลือก ที่ น่าสนใจ เป็นอย่างมาก. เพราะ ความแตกต่าง ของ ตัวเกมสล็อต ที่ น่าสนใจ และ น่าสนใจ, นักเล่นเกม จะสามารถ ลองเล่น และ ทดลอง ประเภทเกม ที่ ตรงกับ สไตล์การเล่น ของตนเอง.
ไม่ว่า ผู้เล่น จะต้องการ ความสนุกสนาน แบบเดิม หรือ การท้าทาย ที่แตกต่าง, สล็อต PG มี ที่หลากหลาย. ตั้งแต่ สล็อตรูปแบบคลาสสิค ที่ คุ้นชิน ไปจนถึง ตัวเกม ที่ ให้ คุณสมบัติพิเศษ และ โบนัสล้นหลาม, ผู้เล่น จะได้ พบเจอ ประสบการณ์การเล่น ที่ น่าตื่นเต้น และ เพลิดเพลิน
ด้วย การทดสอบเล่น สล็อต PG ฟรี, ผู้เล่น จะ ทดลอง เทคนิควิธีการเล่น และ ทดลอง กลยุทธ์ ต่างๆ ก่อนหน้า เริ่มเล่น ด้วยเงินจริง. เช่นนั้น คือ ทางเลือก ที่ดี ที่จะ ปรับตัว และ ปรับปรุง โอกาส ในการ ได้รับรางวัล รางวัลมากมาย.
อย่ารอช้า, เข้าร่วม ใน การทดสอบเล่น สล็อต PG เดี๋ยวนี้ และ ทดสอบ การเล่น ที่ ไม่มีขอบเขต! ทดลอง ความตื่นเต้นระคนตื่นเต้น, ความสนุกสนาน และ ความเป็นไปได้ ในการ คว้ารางวัล มหายิ่ง. เริ่มกระทำ ทำ สู่ ความก้าวหน้า ของคุณในวงการ สล็อตออนไลน์ ตั้งแต่วันนี้!
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg ซื้อฟรีสปิน
สำรวจเล่นสล็อต PG ซื้อรอบหมุนฟรี
ในยุคนี้ การเล่นเกมสล็อตบนอินเทอร์เน็ตได้รับความนิยมอย่างมาก อย่างเฉพาะเจาะจงเกมสล็อตจากผู้ผลิต PG Slot ที่มีคุณลักษณะพิเศษพิเศษมากมายให้ผู้เล่นได้บันเทิง หนึ่งในลักษณะพิเศษที่น่าสนใจและทำให้การเล่นสนุกยิ่งขึ้นคือ “การซื้อฟรีสปิน” ซึ่งเป็นการเพิ่มโอกาสสำเร็จในการชนะและเพิ่มความตื่นเต้นในการเล่น
ฟรีสปินคืออะไร?
การซื้อฟรีสปินคือการที่นักพนันสามารถซื้อช่องทางในการหมุนวงล้อสล็อตโดยไม่ต้องรอให้เกิดไอคอนฟรีสปินบนวงล้อ ซึ่งเป็นการเพิ่มช่องทางในการได้รับรางวัลพิเศษต่างๆ ภายในเกม เช่น โบนัสพิเศษ แจ็คพอต และอื่นๆ ยิ่งไปกว่านั้น การซื้อฟรีสปินยังช่วยให้นักเล่นสามารถเพิ่มจำนวนเงินรางวัลได้อย่างรวดเร็วและมีมีผลดี
ข้อดีของการทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG ซื้อการหมุนฟรี
เพิ่มโอกาสได้รับชัยชนะ: การซื้อฟรีสปินช่วยให้นักพนันมีโอกาสสำเร็จในการได้รับรางวัลมากขึ้น เนื่องด้วยมีการหมุนวงล้อฟรีเพิ่มเติม ซึ่งอาจนำไปให้การได้รับแจ็คพอตหรือรางวัลโบนัสที่สูงขึ้นอื่นๆ
ประหยัดเวลา: การซื้อตัวเลือกฟรีสปินช่วยประหยัดเวลาในการเล่น เนื่องด้วยไม่ต้องรอให้เกิดสัญญาณฟรีสปินบนวงล้อ นักเล่นสามารถเข้าสู่รอบฟรีสปินได้ทันที
ลองเล่นฟรี: สำหรับนักเล่นที่ยังไม่แน่ใจเกี่ยวกับเกม PG Slot ยังมีการเล่นฟรีให้ผู้เล่นได้ทดสอบเล่นและศึกษาเทคนิคการเล่นก่อนที่จะตัดสินใจซื้อฟรีสปินด้วยเงินจริง
เพิ่มความรื่นรมย์: การซื้อตัวเลือกการหมุนฟรีช่วยเพิ่มความบันเทิงในการเล่น เนื่องจากผู้เล่นสามารถเข้ารอบโบนัสและคุณลักษณะพิเศษพิเศษอื่นๆ ได้อย่างไม่ยาก
วิธีการทำการซื้อฟรีสปินในสล็อต PG
เลือกเกมที่ต้องการปั่นจากบริษัท PG Slot
คลิกที่ปุ่ม “ซื้อฟรีสปิน” ที่แสดงบนหน้าจอเกม
กำหนดจำนวนฟรีสปินที่ต้องการซื้อและยืนยันการซื้อ
เริ่มต้นการหมุนวงล้อและสนุกไปกับการเล่น
บทสรุป
การลองเล่นสล็อต PGและการซื้อตัวเลือกการหมุนฟรีเป็นวิธีที่น่าสนใจในการเพิ่มโอกาสสำเร็จในการชนะและเพิ่มความสนุกสนานในการเล่น ด้วยลักษณะพิเศษพิเศษนี้ ผู้ใช้งานสามารถเข้ารอบโบนัสและลักษณะพิเศษพิเศษต่างๆ ได้อย่างเร็วและมีมีผลดี ไม่ว่าคุณจะเป็นผู้เล่นไม่เคยเล่นหรือผู้เล่นที่มีชั่วโมงบิน การทดลองเล่นสล็อต PGและการซื้อตัวเลือกการหมุนฟรีจะช่วยให้คุณมีประสบการณ์การเล่นที่น่าสนใจและสนุกมากยิ่งขึ้น
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG ซื้อฟรีสปิน แล้วคุณจะพบกับความสนุกสนานและโอกาสในการชนะที่ไม่มีที่สิ้นสุด
I’d perpetually want to be update on new posts on this web site, saved to my bookmarks! .
Thanks for sharing superb informations. Your web-site is so cool. I’m impressed by the details that you have on this website. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for more articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found simply the info I already searched everywhere and simply could not come across. What an ideal web-site.
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg ฟรี
สล็อตเว็บตรง — สามารถใช้ โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเลต คอมพิวเตอร์ ฯลฯ สำหรับการเล่น
ระบบสล็อตตรงจากเว็บ ของ PG ได้รับการพัฒนาและปรับปรุง เพื่อให้ สามารถใช้งาน บนอุปกรณ์ที่หลากหลายได้อย่าง ครบถ้วน ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้ โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเลต หรือ คอมพิวเตอร์ส่วนตัว แบบไหน
ที่ PG เราเข้าใจว่าผู้เล่นต้องการ ของลูกค้า ในเรื่อง ความสะดวก และ การเข้าถึงเกมคาสิโนที่รวดเร็ว เราจึง ใช้ HTML 5 ซึ่งเป็น เทคโนโลยีล่าสุด ในตอนนี้ พัฒนาเว็บของเรา คุณจึงไม่ต้อง ติดตั้งแอป หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมเพิ่มเติม เพียง เปิดเบราว์เซอร์ บนอุปกรณ์ที่ คุณมีอยู่ และเยี่ยมชม เว็บไซต์ของเรา คุณสามารถ เล่นเกมสล็อตได้ทันที
การรองรับอุปกรณ์หลายชนิด
ไม่ว่าคุณจะใช้ โทรศัพท์มือถือ ระบบ Android หรือ iOS ก็สามารถ เล่นสล็อตได้อย่างราบรื่น ระบบของเรา ออกแบบมาให้รองรับ ระบบต่าง ๆ ไม่สำคัญว่าคุณ มี โทรศัพท์ ใหม่หรือเก่า หรือ แท็บเล็ตหรือแล็ปท็อป ทุกอย่างก็สามารถ ใช้งานได้ ไม่มีปัญหา ในเรื่องความเข้ากันได้
เล่นได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา
ข้อดีของการเล่น PG Slot ก็คือ คุณสามารถ เล่นได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา ไม่ว่าจะ เป็นที่บ้าน ออฟฟิศ หรือแม้แต่ ในที่สาธารณะ สิ่งที่คุณต้องมีคือ การเชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ต คุณสามารถ เริ่มเกมได้ทันที และคุณไม่ต้อง กังวลกับการดาวน์โหลด หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมที่ เปลืองพื้นที่อุปกรณ์
ทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี
เพื่อให้ ผู้เล่นใหม่ มีโอกาสลองและสัมผัสประสบการณ์สล็อตแมชชีนของเรา PG Slot ยังมีสล็อตทดลองฟรี คุณสามารถ เริ่มเล่นได้ทันทีโดยไม่ต้องลงทะเบียนหรือฝากเงิน การ ทดลองเล่นสล็อตนี้จะช่วยให้คุณรู้จักวิธีการเล่นและเข้าใจเกมก่อนเดิมพันด้วยเงินจริง
การบริการและความปลอดภัย
PG Slot ตั้งใจให้บริการที่ดีที่สุดกับลูกค้า เรามี ทีมบริการที่พร้อมช่วยเหลือตลอด 24 ชั่วโมง นอกจากนี้เรายังมี ระบบรักษาความปลอดภัยที่ทันสมัย ด้วยวิธีนี้ คุณจึงมั่นใจได้ว่า ข้อมูลส่วนตัวและการเงินของคุณจะปลอดภัย
โปรโมชั่นและของรางวัลพิเศษ
การเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot ยังมีข้อดี คือ มี โปรโมชันและโบนัสมากมาย ไม่ว่าคุณจะเป็น สมาชิกใหม่หรือสมาชิกเก่า คุณสามารถ รับโปรโมชันและโบนัสได้เรื่อย ๆ สิ่งนี้จะ เพิ่มโอกาสชนะและความสนุกในเกม
สรุปการเล่นสล็อตเว็บที่ PG Slot ถือเป็นการลงทุนที่คุ้มค่า คุณจะไม่เพียงได้รับความสุขและความสะดวกสบายจากเกมเท่านั้น แต่คุณยังมีโอกาสลุ้นรับรางวัลและโบนัสมากมายอีกด้วย ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเล็ต หรือคอมพิวเตอร์รุ่นใด สามารถมาร่วมสนุกกับเราได้เลยตอนนี้ อย่ารอช้า ลงทะเบียนและเริ่มเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot วันนี้!
ความรู้สึกการลองเล่นสล็อตแมชชีน PG บนพอร์ทัลเสี่ยงโชคไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์: เริ่มการเดินทางแห่งความสุขที่ไร้ขีดจำกัด
สำหรับนักเสี่ยงโชคที่ตามหาการเผชิญหน้าเกมแปลกใหม่ และคาดหวังเจอแหล่งพนันที่มั่นคง, การลองเกมสล็อต PG บนแพลตฟอร์มตรงนับว่าเป็นตัวเลือกที่น่าดึงดูดอย่างมาก. เนื่องจากมีความแตกต่างของเกมสล็อตแมชชีนที่มีให้เลือกสรรมากมาย, ผู้เล่นจะได้เผชิญกับโลกแห่งความรื่นเริงและความสนุกสนานที่ไร้ขีดจำกัด.
เว็บไซต์เสี่ยงโชคตรงนี้ นำเสนอการเล่นเกมการเล่นเดิมพันที่ปลอดภัย น่าเชื่อถือ และตรงตามความต้องการของนักเดิมพันได้เป็นอย่างดี. ไม่ว่าผู้เล่นจะติดใจสล็อตแมชชีนที่คุ้นเคยที่รู้จักดี หรือต้องการทดลองเกมใหม่ที่มีฟังก์ชันพิเศษเฉพาะและโบนัสล้นหลาม, พอร์ทัลโดยตรงนี้ก็มีให้คัดสรรอย่างหลากหลาย.
อันเนื่องมาจากระบบการทดลองเกมสล็อต PG ไม่มีค่าใช้จ่าย, ผู้เล่นจะได้จังหวะศึกษาวิธีการเล่นเกมและทดลองเทคนิคต่างๆ ก่อนที่เริ่มลงทุนโดยใช้เงินจริง. การกระทำนี้ถือเป็นโอกาสอันดีที่จะสร้างเสริมความพร้อมสมบูรณ์และเพิ่มโอกาสในการได้รางวัลมหาศาลใหญ่.
ไม่ว่าผู้เล่นจะผู้เล่นจะอยากได้ความสุขสนานแบบคลาสสิก หรือการท้าทายแปลกใหม่, เกมสล็อตแมชชีน PG บนเว็บไซต์พนันโดยตรงก็มีให้เลือกสรรอย่างมากมาย. คุณจะได้พบเจอกับการทดลองเล่นการเล่นเกมที่น่าตื่นเต้น น่ารื่นเริง และเพลิดเพลินไปกับโอกาสในการชนะรางวัลใหญ่มหาศาล.
อย่ารอ, เข้าร่วมสำรวจสล็อตแมชชีน PG บนเว็บเดิมพันไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์ขณะนี้ และค้นเจอจักรวาลแห่งความสนุกสนานที่น่าเชื่อถือ น่าค้นหา และพร้อมด้วยความสนุกเพลิดเพลินรอคอยคุณ. พบเจอความตื่นเต้นเร้าใจ, ความเพลิดเพลิน และจังหวะในการคว้ารางวัลใหญ่มหาศาล. เริ่มต้นเดินไปสู่การประสบความสำเร็จในวงการเกมออนไลน์วันนี้!
You are my intake, I have few blogs and sometimes run out from to post .
הימורי ספורט – הימור באינטרנט
הימורי ספורט נהיו לאחד התחומים המתפתחים ביותר בהימור ברשת. משתתפים יכולים להתערב על תוצאת של אירועי ספורט נפוצים לדוגמה כדורגל, כדורסל, משחק הטניס ועוד. האפשרויות להימור הן מרובות, כולל תוצאתו המאבק, כמות הגולים, כמות הנקודות ועוד. הבא דוגמאות למשחקי נפוצים עליהם ניתן להמר:
כדור רגל: ליגת אלופות, מונדיאל, ליגות אזוריות
כדורסל: NBA, ליגת יורוליג, תחרויות בינלאומיות
משחק הטניס: טורניר ווימבלדון, אליפות ארה”ב הפתוחה, אליפות צרפת הפתוחה
פוקר ברשת באינטרנט – הימורים באינטרנט
פוקר ברשת הוא אחד מהמשחקים ההימור הנפוצים ביותר כיום. משתתפים יכולים להתמודד נגד יריבים מרחבי תבל בסוגי סוגי משחק , לדוגמה טקסס הולדם, Omaha, Stud ועוד. ניתן לגלות טורנירים ומשחקי קש במבחר דרגות ואפשרויות הימור מגוונות. אתרי פוקר הטובים מציעים:
מבחר רב של וריאציות פוקר
טורנירים שבועיים וחודשיים עם פרסים כספיים גבוהים
שולחנות המשחק למשחקים מהירים ולטווח ארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ללקוחות ומועדוני VIP עם הטבות בלעדיות
בטיחות והגינות
בעת בוחרים פלטפורמה להימורים, חשוב לבחור גם אתרי הימורים מורשים ומפוקחים המציעים סביבה למשחק מאובטחת והוגנת. אתרים אלה משתמשים בטכנולוגיות אבטחה מתקדמות להגנה על מידע אישי ופיננסיים, וכן בתוכנות גנרטור מספרים רנדומליים (RNG) כדי להבטיח הגינות במשחקים במשחקי ההימורים.
בנוסף, הכרחי לשחק באופן אחראי תוך הגדרת מגבלות הימור אישיות של השחקן. מרבית האתרים מאפשרים למשתתפים לקבוע מגבלות להפסדים ופעילויות, וגם להשתמש ב- כלים נגד התמכרויות. הימרו בתבונה ואל גם תרדפו אחרי הפסד.
המדריך השלם למשחקי קזינו ברשת, משחקי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט באינטרנט
ההימורים ברשת מציעים גם עולם שלם הזדמנויות מלהיבות למשתתפים, מתחיל מקזינו באינטרנט וכל בהימורי ספורט ופוקר ברשת. בעת בחירת בפלטפורמת הימורים, חשוב לבחור גם אתרי הימורים המפוקחים המציעים גם סביבה משחק בטוחה והגיונית. זכרו גם לשחק באופן אחראי תמיד – משחקי ההימורים באינטרנט נועדו להיות מבדרים ולא גם לגרום לבעיות כלכליות או גם חברתיות.
ทดลองดำเนินการเล่นสล็อต และค้นพบประสบการณ์การเล่นเกมที่ไม่เหมือนใคร!
สำหรับนักพนันที่กำลังพิจารณาความบันเทิงและโอกาสในการได้รับรางวัลมหาศาล สล็อตออนไลน์เป็นอีกหนึ่งทางเลือกที่คุ้มค่าพิจารณา.ด้วยความขนาดใหญ่ของเกมสล็อตที่น่าตื่นเต้น ผู้เล่นสามารถทดสอบและค้นหาเกมที่เหมาะกับตัวเองได้อย่างง่ายดาย.
ไม่ว่าคุณจะชื่นชอบเกมสล็อตคลาสสิกหรือต้องการความท้าทายใหม่, ตัวเลือกรอคอยให้คุณสัมผัส. จากสล็อตที่มีธีมมากมาย ไปจนถึงเกมที่มีฟีเจอร์พิเศษและโบนัส, ผู้เล่นจะได้พบกับการเล่นเกมที่น่าตื่นเต้นและน่าติดตาม.
ด้วยการปฏิบัติสล็อตฟรี, คุณสามารถทำความคุ้นเคยวิธีการเล่นและค้นค้นพบกลยุทธ์ที่เหมาะสมก่อนลงทุนด้วยเงินจริง. นี่คือโอกาสดีที่จะปฏิบัติกับเกมและยกระดับโอกาสในการชนะรางวัลใหญ่.
อย่าขยายเวลา, เข้าไปกับการลองเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์วันนี้ และค้นพบประสบการณ์การเล่นเกมที่ไม่เหมือนใคร! สัมผัสความน่าสนใจ, ความเพลิดเพลิน และโอกาสชนะรางวัลมากมาย. ทำก้าวแรกเดินทางสู่ความเฟื่องฟูของคุณในวงการสล็อตออนไลน์แล้ววันนี้!
Would you be fascinated with exchanging hyperlinks?
roma77
Its like you read my mind! You seem to grasp a lot approximately this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I believe that you just could do with a few to power the message house a little bit, however other than that, this is excellent blog. A great read. I’ll definitely be back.
הימורי ספורט
הימורי ספורטיביים – הימור באינטרנט
הימורי ספורטיביים נעשו לאחד הענפים המשגשגים ביותר בהימורים ברשת. שחקנים מסוגלים להתערב על תוצאת של אירועי ספורטיביים מוכרים למשל כדור רגל, כדור סל, טניס ועוד. האופציות להימור הן מרובות, וביניהן תוצאת ההתמודדות, כמות הגולים, מספר הפעמים ועוד. להלן דוגמאות של למשחקים נפוצים במיוחד עליהם ניתן להתערב:
כדורגל: ליגת האלופות, גביע העולם, ליגות אזוריות
כדור סל: NBA, ליגת יורוליג, תחרויות בינלאומיות
טניס: ווימבלדון, אליפות ארה”ב הפתוחה, רולאן גארוס
פוקר באינטרנט – הימורים באינטרנט
משחק הפוקר ברשת הוא אחד מהמשחקים ההימורים המוכרים ביותר בימינו. משתתפים מסוגלים להתחרות נגד יריבים מרחבי תבל במגוון גרסאות משחק , למשל טקסס הולדם, אומהה, Stud ועוד. ניתן למצוא טורנירים ומשחקי קש במבחר דרגות ואפשרויות הימור שונות. אתרי פוקר המובילים מציעים גם:
מבחר רב של גרסאות המשחק פוקר
טורנירים שבועיים וחודשיים עם פרסים כספיים גבוהים
שולחנות למשחק מהיר ולטווח ארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ומועדוני עם הטבות עם הטבות
בטיחות והוגנות
כאשר בוחרים בפלטפורמה להימורים באינטרנט, חשוב לבחור אתרי הימורים מורשים ומפוקחים המציעים סביבת למשחק בטוחה והוגנת. אתרים אלו משתמשים בטכנולוגיות הצפנה מתקדמות להגנה על נתונים אישיים ופיננסיים, וכן באמצעות תוכנות מחולל מספרים רנדומליים (RNG) כדי להבטיח הגינות במשחקים במשחקים.
מעבר לכך, הכרחי לשחק בצורה אחראי תוך כדי הגדרת מגבלות הימורים אישיות. רוב האתרים מאפשרים גם לשחקנים לקבוע מגבלות הפסד ופעילויות, וגם לנצל כלים נגד התמכרויות. שחקו בחכמה ואל גם תרדפו אחרי הפסד.
המדריך המלא לקזינו באינטרנט, משחקי ספורט ופוקר ברשת
הימורים ברשת מציעים גם עולם שלם הזדמנויות מלהיבות לשחקנים, מתחיל מקזינו באינטרנט וגם בהימורי ספורט ופוקר ברשת. בזמן בחירת פלטפורמת הימורים, חשוב לבחור אתרי הימורים המפוקחים המציעים סביבה למשחק מאובטחת והגיונית. זכרו לשחק באופן אחראי תמיד – ההימורים באינטרנט נועדו להיות מבדרים ולא ליצור לבעיות פיננסיות או חברתיים.
קזינו אונליין
הימורי ספורטיביים – הימורים באינטרנט
הימור ספורטיביים נהיו לאחד התחומים הצומחים ביותר בהימורים באינטרנט. משתתפים מסוגלים להתערב על תוצאותיהם של אירועי ספורטיביים פופולריים לדוגמה כדורגל, כדורסל, משחק הטניס ועוד. האפשרויות להתערבות הן רבות, כולל תוצאת המאבק, מספר הגולים, מספר הנקודות ועוד. להלן דוגמאות למשחקי נפוצים במיוחד שעליהם ניתן להתערב:
כדור רגל: ליגת האלופות, מונדיאל, ליגות מקומיות
כדורסל: ליגת NBA, יורוליג, טורנירים בינלאומיים
משחק הטניס: ווימבלדון, US Open, אליפות צרפת הפתוחה
פוקר ברשת – הימור ברשת
פוקר ברשת הוא אחד ממשחקי ההימור המוכרים ביותר בימינו. שחקנים מסוגלים להתמודד מול יריבים מרחבי העולם במגוון וריאציות משחק , כגון טקסס הולדם, אומהה, סטאד ועוד. אפשר למצוא טורנירים ומשחקי במבחר דרגות ואפשרויות הימור שונות. אתרי הפוקר הטובים מציעים:
מגוון רחב של וריאציות פוקר
תחרויות שבועיות וחודשיים עם פרסים כספיים גבוהים
שולחנות למשחקים מהירים ולטווח הארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ומועדוני VIP עם הטבות עם הטבות
בטיחות ואבטחה והוגנות
בעת הבחירה בפלטפורמה להימורים, חשוב לבחור אתרים מורשים המפוקחים המציעים סביבת למשחק בטוחה והוגנת. אתרים אלה משתמשים בטכנולוגיות הצפנה מתקדמות להבטחה על מידע אישי ופיננסי, וגם בתוכנות מחולל מספרים אקראיים (RNG) כדי להבטיח הגינות במשחקי ההימורים.
מעבר לכך, הכרחי לשחק גם באופן אחראית תוך כדי קביעת מגבלות אישיות הימור אישיות. מרבית אתרי ההימורים מאפשרים לשחקנים לקבוע מגבלות הפסד ופעילויות, כמו גם להשתמש ב- כלים נגד התמכרויות. שחק בתבונה ואל תרדפו גם אחר הפסדים.
המדריך המלא לקזינו אונליין, משחקי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט
הימורים ברשת מציעים גם עולם שלם של הזדמנויות מרתקות לשחקנים, החל מקזינו אונליין וכל משחקי ספורט ופוקר ברשת. בעת בחירת פלטפורמת הימורים, חשוב לבחור אתרי הימורים המפוקחים המציעים סביבה למשחק מאובטחת והוגנת. זכרו לשחק בצורה אחראית תמיד ואחראי – משחקי ההימורים באינטרנט אמורים להיות מבדרים ולא גם ליצור בעיות פיננסיות או חברתיות.
puncak303
We are a group of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community. Your website provided us with valuable info to work on. You’ve done an impressive job and our whole community will be grateful to you.
פוקר באינטרנט
הימורי ספורטיביים – הימור באינטרנט
הימורי ספורטיביים נעשו לאחד הענפים המשגשגים ביותר בהימורים ברשת. שחקנים מסוגלים להתערב על תוצאות של אירועים ספורטיביים מוכרים לדוגמה כדור רגל, כדורסל, טניס ועוד. האפשרויות להתערבות הן רבות, וביניהן תוצאתו ההתמודדות, כמות השערים, מספר הנקודות ועוד. להלן דוגמאות של למשחקי נפוצים במיוחד שעליהם אפשרי להתערב:
כדור רגל: ליגת אלופות, מונדיאל, ליגות מקומיות
כדורסל: NBA, יורוליג, טורנירים בינלאומיים
טניס: ווימבלדון, US Open, רולאן גארוס
פוקר באינטרנט – הימורים באינטרנט
פוקר באינטרנט הוא אחד ממשחקי ההימור הפופולריים ביותר בימינו. משתתפים יכולים להתחרות נגד מתחרים מכל רחבי העולם במגוון גרסאות של המשחק , לדוגמה Texas Hold’em, אומהה, Stud ועוד. ניתן למצוא תחרויות ומשחקי קש במגוון רמות ואפשרויות שונות. אתרי פוקר המובילים מציעים גם:
מבחר רב של גרסאות המשחק פוקר
תחרויות שבועיים וחודשיות עם פרסים כספיים גבוהים
שולחנות למשחקים מהירים ולטווח הארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ללקוחות ומועדוני VIP עם הטבות
בטיחות והוגנות
כאשר הבחירה בפלטפורמה להימורים ברשת, חשוב לבחור אתרי הימורים מורשים המפוקחים המציעים סביבה משחק בטוחה והוגנת. אתרים אלו משתמשים בטכנולוגיית אבטחה מתקדמת להגנה על נתונים אישיים ופיננסי, וכן באמצעות תוכנות מחולל מספרים רנדומליים (RNG) כדי לוודא הגינות במשחקי ההימורים.
מעבר לכך, חשוב לשחק בצורה אחראי תוך כדי קביעת מגבלות הימור אישיות. רוב האתרים מאפשרים לשחקנים לקבוע מגבלות להפסדים ופעילויות, כמו גם להשתמש ב- כלים נגד התמכרויות. שחקו בחכמה ואל תרדפו גם אחרי הפסד.
המדריך השלם למשחקי קזינו באינטרנט, משחקי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט
ההימורים באינטרנט מציעים גם עולם שלם של הזדמנויות מרתקות לשחקנים, החל מקזינו באינטרנט וכל משחקי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט. בעת בחירת בפלטפורמת הימורים, הקפידו לבחור אתרי הימורים המפוקחים המציעים גם סביבת משחק מאובטחת והגיונית. זכרו גם לשחק תמיד בצורה אחראית תמיד ואחראי – ההימורים באינטרנט נועדו להיות מבדרים ולא לגרום לבעיות כלכליות או חברתיים.
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was good. I don’t know who you are but certainly you are going to a famous blogger if you aren’t already ;) Cheers!
сглобяеми къщи
https://medium.com/@momejar21741/pg-59490dd058fd
สล็อตตรงจากเว็บ — ใช้ โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเลต คอมฯ ฯลฯ ในการเล่น
ระบบสล็อตเว็บตรง ของ พีจีสล็อต ได้รับการพัฒนาและอัปเดต เพื่อให้ รองรับการใช้งาน บนอุปกรณ์ที่หลากหลายได้อย่าง เต็มที่ ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้ สมาร์ทโฟน แท็บเล็ต หรือ คอมฯ รุ่นไหน
ที่ PG Slot เราเข้าใจว่าผู้เล่นต้องการ ของผู้เล่น ในเรื่อง ความสะดวก และ การเข้าถึงเกมออนไลน์อย่างรวดเร็ว เราจึง ใช้ HTML 5 ซึ่งเป็น เทคโนโลยีที่ทันสมัยที่สุด ปัจจุบันนี้ มาพัฒนาเว็บไซต์ของเรากันเถอะ คุณจึงไม่ต้อง โหลดแอป หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมเพิ่มเติม เพียง เปิดเบราว์เซอร์ บนอุปกรณ์ที่ คุณมีอยู่ และเยี่ยมชม เว็บของเรา คุณสามารถ สนุกกับสล็อตได้ทันที
การใช้งานกับอุปกรณ์หลากหลาย
ไม่ว่าคุณจะใช้ สมาร์ทโฟน ระบบ Android หรือ iOS ก็สามารถ เล่นเกมสล็อตได้อย่างไม่มีปัญหา ระบบของเรา ออกแบบมาให้รองรับ ระบบปฏิบัติการทั้งหมด ไม่สำคัญว่าคุณ ใช้ สมาร์ทโฟน รุ่นใหม่หรือรุ่นเก่า หรือ แท็บเล็ตหรือแล็ปท็อป ทุกอย่างก็สามารถ ใช้งานได้อย่างไม่มีปัญหา ไม่มีปัญหา ในเรื่องความเข้ากันได้
สามารถเล่นได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา
ข้อดีอย่างหนึ่งของการเล่นเว็บสล็อตอย่าง PG Slot นั่นคือ คุณสามารถ เล่นได้ตลอดเวลา ไม่ว่าจะ ที่บ้าน ที่ทำงาน หรือแม้แต่ ที่สาธารณะ สิ่งที่คุณต้องมีคือ อินเทอร์เน็ต คุณสามารถ เริ่มเกมได้ทันที และคุณไม่ต้อง กังวลกับการดาวน์โหลด หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมที่ ใช้พื้นที่บนอุปกรณ์ของคุณ
ทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี
เพื่อให้ ผู้เล่นที่ใหม่ ได้ลองและรู้จักเกมสล็อตของเรา PG Slot ยังมีบริการสล็อตฟรี คุณสามารถ เล่นได้ทันทีโดยไม่ต้องสมัครสมาชิกหรือฝากเงิน การ เล่นฟรีนี้จะช่วยให้คุณเข้าใจวิธีเล่นและรู้จักเกมก่อนลงเดิมพันจริง
บริการและการรักษาความปลอดภัย
PG Slot มุ่งมั่นที่จะให้บริการที่ดีที่สุดแก่ลูกค้า เรามี ทีมงานพร้อมบริการคุณตลอดเวลา นอกจากนี้เรายังมี การรักษาความปลอดภัยที่ทันสมัย ด้วยวิธีนี้ คุณจึงมั่นใจได้ว่า ข้อมูลและการเงินของคุณจะปลอดภัย
โปรโมชั่นและของรางวัลพิเศษ
การเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot ยังมีข้อดี ก็คือ มี โปรโมชั่นและโบนัสพิเศษมากมายสำหรับผู้เข้าร่วม ไม่ว่าคุณจะเป็น สมาชิกใหม่หรือเก่า คุณสามารถ รับโปรโมชั่นและโบนัสต่างๆได้อย่างต่อเนื่อง สิ่งนี้จะ เพิ่มโอกาสชนะและสนุกกับเกมมากขึ้น
สรุปการเล่นสล็อตเว็บที่ PG Slot ถือเป็นการลงทุนที่คุ้มค่า คุณจะไม่เพียงได้รับความสุขและความสะดวกสบายจากเกมเท่านั้น แต่คุณยังมีโอกาสลุ้นรับรางวัลและโบนัสมากมายอีกด้วย ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเล็ต หรือคอมพิวเตอร์รุ่นใด สามารถมาร่วมสนุกกับเราได้เลยตอนนี้ อย่ารอช้า ลงทะเบียนและเริ่มเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot วันนี้!
of course like your web-site however you have to test the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling issues and I find it very troublesome to tell the reality then again I¦ll definitely come again again.
I went over this web site and I believe you have a lot of great info, saved to bookmarks (:.
very good submit, i definitely love this website, carry on it
Very interesting subject , thanks for posting.
купить квартиру в казани новостройка от застройщика https://kupit-kvartiru47.ru
Well I truly enjoyed studying it. This article procured by you is very practical for good planning.
What i don’t realize is in reality how you are no longer really a lot more well-liked than you may be now. You’re very intelligent. You already know therefore significantly in the case of this matter, made me in my opinion believe it from numerous varied angles. Its like men and women don’t seem to be fascinated unless it?¦s one thing to accomplish with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs great. All the time deal with it up!
I really value your work, Great post.
Thanx for the effort, keep up the good work Great work, I am going to start a small Blog Engine course work using your site I hope you enjoy blogging with the popular BlogEngine.net.Thethoughts you express are really awesome. Hope you will right some more posts.
I have learn some good stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how a lot attempt you set to create one of these excellent informative web site.
As soon as I discovered this site I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
сервера ла2
Сервера ла2
台灣線上娛樂城是指通過互聯網提供賭博和娛樂服務的平台。這些平台主要針對台灣用戶,但實際上可能在境外運營。以下是一些關於台灣線上娛樂城的重要信息:
1. 服務內容:
– 線上賭場遊戲(如老虎機、撲克、輪盤等)
– 體育博彩
– 彩票遊戲
– 真人荷官遊戲
2. 特點:
– 全天候24小時提供服務
– 可通過電腦或移動設備訪問
– 常提供優惠活動和獎金來吸引玩家
3. 支付方式:
– 常見支付方式包括銀行轉賬、電子錢包等
– 部分平台可能接受加密貨幣
4. 法律狀況:
– 在台灣,線上賭博通常是非法的
– 許多線上娛樂城實際上是在國外註冊運營
5. 風險:
– 由於缺乏有效監管,玩家可能面臨財務風險
– 存在詐騙和不公平遊戲的可能性
– 可能導致賭博成癮問題
6. 爭議:
– 這些平台的合法性和道德性一直存在爭議
– 監管機構試圖遏制這些平台的發展,但效果有限
重要的是,參與任何形式的線上賭博都存在風險,尤其是在法律地位不明確的情況下。建議公眾謹慎對待,並了解相關法律和潛在風險。
如果您想了解更多具體方面,例如如何識別和避免相關風險,我可以提供更多信息。
魔龍傳奇試玩
Kylian Mbappe https://kylianmbappe.prostoprosport-ar.com is a French footballer, striker for Paris Saint-Germain and captain of the French national team. He began playing football in the semi-professional club Bondi, which plays in the lower leagues of France. He was noticed by Monaco scouts, which he joined in 2015 and that same year, at the age of 16, he made his debut for the Monegasques. The youngest debutant and goal scorer in the club’s history.
pin-up oyunu https://azerbaijancuisine.com/# pin up
pin up azerbaycan yukle
Toni Kroos https://tonikroos.prostoprosport-ar.com is a German footballer who plays as a central midfielder for Real Madrid and the German national team. World champion 2014. The first German player in history to win the UEFA Champions League six times.
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know so much about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with a few pics to drive the message home a little bit, but other than that, this is fantastic blog. A great read. I will certainly be back.
Robert Lewandowski https://robertlewandowski.prostoprosport-ar.com is a Polish footballer, forward for the Spanish club Barcelona and captain of the Polish national team. Considered one of the best strikers in the world. Knight of the Commander’s Cross of the Order of the Renaissance of Poland.
смотреть сериал волчонок волчонок онлайн
tiktok likes buy buy tiktok likes
Very interesting subject , regards for posting.
Lionel Andres Messi Cuccittini https://lionelmessi.prostoprosport-ar.com is an Argentine footballer, forward and captain of the MLS club Inter Miami, captain of the Argentina national team. World champion, South American champion, Finalissima winner, Olympic champion. Considered one of the best football players of all time.
Yassine Bounou https://yassine-bounou.prostoprosport-ar.com also known as Bono, is a Moroccan footballer who plays as a goalkeeper for the Saudi Arabian club Al-Hilal and the Moroccan national team. On November 10, 2022, he was included in the official application of the Moroccan national team to participate in the matches of the 2022 World Cup in Qatar
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Your website is very useful. Thanks for sharing.
mexican drugstore online: northern doctors pharmacy – mexican mail order pharmacies
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs [url=https://northern-doctors.org/#]mexican pharmacy[/url] mexican pharmaceuticals online
https://northern-doctors.org/# medication from mexico pharmacy
mexican mail order pharmacies: mexican pharmacy northern doctors – mexican pharmacy
https://northern-doctors.org/# mexico drug stores pharmacies
buying prescription drugs in mexico online: mexican pharmacy northern doctors – buying from online mexican pharmacy
medicine in mexico pharmacies: buying from online mexican pharmacy – medicine in mexico pharmacies
http://northern-doctors.org/# best online pharmacies in mexico
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa [url=http://northern-doctors.org/#]mexican pharmacy[/url] medicine in mexico pharmacies
Luka Modric https://lukamodric.prostoprosport-ar.com is a Croatian footballer, central midfielder and captain of the Spanish club Real Madrid, captain of the Croatian national team. Recognized as one of the best midfielders of our time. Knight of the Order of Prince Branimir. Record holder of the Croatian national team for the number of matches played.
mexico drug stores pharmacies: mexican pharmacy online – medicine in mexico pharmacies
https://northern-doctors.org/# mexican pharmaceuticals online
purple pharmacy mexico price list: mexican pharmacy northern doctors – medicine in mexico pharmacies
buy 10k tiktok followers buy tiktok followers free
reputable mexican pharmacies online: mexican pharmacy online – mexico drug stores pharmacies
https://northern-doctors.org/# buying prescription drugs in mexico
mexico drug stores pharmacies [url=https://northern-doctors.org/#]mexican pharmacy[/url] mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa: mexican pharmacy online – purple pharmacy mexico price list
https://northern-doctors.org/# purple pharmacy mexico price list
Real nice design and fantastic subject material, absolutely nothing else we require : D.
mexico pharmacy: northern doctors pharmacy – mexican drugstore online
Great amazing things here. I?¦m very glad to see your article. Thanks a lot and i’m having a look forward to touch you. Will you please drop me a mail?
mexico pharmacy: northern doctors pharmacy – п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
http://northern-doctors.org/# buying prescription drugs in mexico online
Its fantastic as your other blog posts : D, thanks for posting. “Too much sensibility creates unhappiness too much insensibility leads to crime.” by Charles Maurice de Talleyrand.
mexico drug stores pharmacies: mexican pharmacy – buying prescription drugs in mexico online
https://northern-doctors.org/# buying prescription drugs in mexico
mexico drug stores pharmacies: mexican pharmacy northern doctors – mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
This web site is really a walk-through for all of the info you wanted about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and you’ll definitely discover it.
purple pharmacy mexico price list [url=https://northern-doctors.org/#]mexican pharmacy online[/url] best online pharmacies in mexico
mexican drugstore online: mexican pharmacy online – medicine in mexico pharmacies
http://northern-doctors.org/# buying prescription drugs in mexico online
mexican mail order pharmacies: mexican pharmacy northern doctors – mexican mail order pharmacies
Проституция в Москве существует как многосложной и разнообразной вопросом. Несмотря на то, что данная деятельность запрещается правилами, этот бизнес остаётся крупным теневым сектором.
Исторический
В Советского Союза эру секс-работа была в тени. С распадом СССР, в ситуации хозяйственной неопределенности, она стала быть более видимой.
Нынешняя Ситуация
Сейчас коммерческий секс в Москве принимает разные виды, включая люксовых эскорт-услуг до самой на улице секс-работы. Высококлассные услуги зачастую организуются через сеть, а на улице интимные услуги сконцентрирована в конкретных зонах столицы.
Социальные и Экономические Аспекты
Некоторые женщины вступают в эту сферу из-за финансовых трудностей. Коммерческий секс может оказаться привлекательным из-за перспективы мгновенного заработка, но это сопряжена с угрозу здоровью и жизни.
Юридические аспекты
Интимные услуги в России запрещена, и за эту деятельность проведение существуют серьезные меры наказания. Работников интимной сферы постоянно задерживают к дисциплинарной наказанию.
Таким образом, игнорируя запреты, интимные услуги является аспектом экономики в тени столицы с существенными социально-правовыми последствиями.
Взять займ или кредит
https://dvoe69.ru/onlajn-kalkulyator-dlya-rascheta-kredita-udobnyj-instrument-finansovogo-planirovaniya/ под проценты, подав заявку на денежный микрозайм для физических лиц. Выбирайте среди 570 лучших предложений займа онлайн. Возьмите микрозайм онлайн или наличными в день обращения. Быстрый поиск и удобное сравнение условий по займам и микрокредитам в МФО.
NGolo Kante https://ngolokante.prostoprosport-ar.com is a French footballer who plays as a defensive midfielder for the Saudi Arabian club Al-Ittihad and the French national team. His debut for the first team took place on May 18, 2012 in a match against Monaco (1:2). In the 2012/13 season, Kante became the main player for Boulogne, which played in Ligue 3.
https://northern-doctors.org/# mexican rx online
medicine in mexico pharmacies: Mexico pharmacy that ship to usa – medicine in mexico pharmacies
mexican drugstore online [url=http://northern-doctors.org/#]northern doctors pharmacy[/url] purple pharmacy mexico price list
Ruben Diogo da Silva Neves https://ruben-neves.prostoprosport-ar.com is a Portuguese footballer who plays as a midfielder for the Saudi Arabian club Al-Hilal and the Portuguese national team. Currently, Ruben Neves plays for the Al-Hilal club wearing number 8. His contract with the Saudi club is valid until the end of June 2026.
purple pharmacy mexico price list: northern doctors pharmacy – mexican drugstore online
http://northern-doctors.org/# mexico drug stores pharmacies
mexican rx online: northern doctors pharmacy – mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
http://northern-doctors.org/# reputable mexican pharmacies online
Kobe Bean Bryant https://kobebryant.prostoprosport-ar.com is an American basketball player who played in the National Basketball Association for twenty seasons for one team, the Los Angeles Lakers. He played as an attacking defender. He was selected in the first round, 13th overall, by the Charlotte Hornets in the 1996 NBA Draft. He won Olympic gold twice as a member of the US national team.
medication from mexico pharmacy: northern doctors – buying prescription drugs in mexico
https://win-line.net/בט-365-365-ספורט-תוצאות-בעברית-365-sport/
להגיש, תימוכין לדבריך.
ההתמודדות באינטרנט הפכה לתחום מושך מאוד לאחרונה, המספק מגוון רחב של אפשרויות הימורים, החל מ מכונות מזל.
בניתוח זה נבדוק את תחום הקזינו המקוון ונמסור לכם פרטים חשובים שיתרום לכם לחקור בתחום מעניין זה.
קזינו אונליין – הימורים באינטרנט
קזינו אונליין מציע אופציות שונות של פעילויות מסורתיים כגון בלאק ג’ק. ההימורים באינטרנט מאפשרים למתמודדים להתנסות מחווית הימורים מקורית בכל מקום ובשעה.
סוג המשחק סיכום קצר
מכונות מזל משחקי מזל
הימורי רולטה הימור על מספרים ואפשרויות על גלגל מסתובב
בלאק ג’ק משחק קלפים בו המטרה היא 21 נקודות
משחק קלפים פוקר משחק קלפים אסטרטגי
התמודדות בבאקרה משחק קלפים מהיר וקצר
הימורים בתחום הספורט – התמודדות באינטרנט
הימורים על אירועי ספורט הם אחד התחומים המשגשגים ביותר בהימורים באינטרנט. מבקרים מסוגלים להשקיע על תוצאים של משחקי ספורט מועדפים כגון טניס.
העסקאות מתאפשרות על הביצועים בתחרות, מספר השערים ועוד.
המשחק ניתוח תחרויות ספורט מקובלות
ניחוש תוצאה ניחוש הביצועים הסופיים בתחרות כדורגל, כדורסל, קריקט
הפרש תוצאות ניחוש ההפרש בסקורים בין הקבוצות כל ענפי הספורט
כמות הסקורים ניחוש כמות הסקורים בתחרות כדורגל, כדורסל, קריקט
הקבוצה המנצחת ניחוש מי יסיים ראשון (ללא קשר לניקוד) מגוון ענפי ספורט
הימורי חי התמודדות במהלך האירוע בזמן אמת כדורגל, טניס, כדורסל
התמרמרות מגוונת שילוב של מספר פעילויות מספר ענפי ספורט
פעילות פוקר מקוונת – הימורים באינטרנט
התמודדות בפוקר מקוון מכיל אחד מסוגי הפעילות המרכזיים המשפיעים ביותר בתקופה הנוכחית. מתמודדים מורשים להשתלב מול יריבים מאזורי הגלובליזציה במגוון
best online pharmacies in mexico: mexican northern doctors – buying from online mexican pharmacy
http://northern-doctors.org/# best online pharmacies in mexico
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs: northern doctors pharmacy – mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
mexican pharmaceuticals online [url=https://northern-doctors.org/#]northern doctors[/url] best online pharmacies in mexico
https://northern-doctors.org/# mexico drug stores pharmacies
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs: mexican pharmacy northern doctors – mexican mail order pharmacies
mexican pharmacy: mexico drug stores pharmacies – mexican pharmaceuticals online
http://northern-doctors.org/# mexican drugstore online
purple pharmacy mexico price list: northern doctors pharmacy – purple pharmacy mexico price list
Продажа подземных канализационных ёмкостей https://neseptik.com по выгодным ценам. Ёмкости для канализации подземные объёмом до 200 м3. Металлические накопительные емкости для канализации заказать и купить в Екатеринбурге.
medicine in mexico pharmacies: mexican pharmacy northern doctors – mexican pharmaceuticals online
http://northern-doctors.org/# buying prescription drugs in mexico
mexican drugstore online: mexican pharmacy online – medicine in mexico pharmacies
http://northern-doctors.org/# best online pharmacies in mexico
mexico drug stores pharmacies [url=http://northern-doctors.org/#]mexican pharmacy online[/url] best online pharmacies in mexico
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa: northern doctors pharmacy – п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
Maria Sharapova https://maria-sharapova.prostoprosport-ar.com Russian tennis player. The former first racket of the world, winner of five Grand Slam singles tournaments from 2004 to 2014, one of ten women in history who has the so-called “career slam”.
medication from mexico pharmacy: mexican northern doctors – mexican mail order pharmacies
https://northern-doctors.org/# mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
mexican pharmacy: Mexico pharmacy that ship to usa – medication from mexico pharmacy
Mohammed Khalil Ibrahim Al-Owais https://mohammed-alowais.prostoprosport-ar.com is a Saudi professional footballer who plays as a goalkeeper for the national team Saudi Arabia and Al-Hilal. He is known for his quick reflexes and alertness at the gate.
https://northern-doctors.org/# mexican mail order pharmacies
п»їbest mexican online pharmacies: northern doctors pharmacy – mexican drugstore online
medication from mexico pharmacy: mexican northern doctors – buying prescription drugs in mexico
https://northern-doctors.org/# pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa
purple pharmacy mexico price list: Mexico pharmacy that ship to usa – mexican mail order pharmacies
mexican mail order pharmacies [url=https://northern-doctors.org/#]mexican pharmacy[/url] buying prescription drugs in mexico online
https://northern-doctors.org/# mexico pharmacy
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa: mexican pharmacy online – buying prescription drugs in mexico online
https://northern-doctors.org/# buying from online mexican pharmacy
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs: mexican pharmacy northern doctors – medication from mexico pharmacy
Howdy just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading correctly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different web browsers and both show the same outcome.
Larry Joe Bird https://larry-bird.prostoprosport-br.com American basketball player who spent his entire professional career in the NBA ” Boston Celtics.” Olympic champion (1992), champion of the 1977 Universiade, 3-time NBA champion (1981, 1984, 1986), three times recognized as MVP of the season in the NBA (1984, 1985, 1986), 10 times included in the symbolic teams of the season (1980-88 – first team, 1990 – second team).
Roberto Firmino Barbosa de Oliveira https://roberto-firmino.prostoprosport-br.com Brazilian footballer, attacking midfielder, forward for the Saudi club “Al-Ahli”. Firmino is a graduate of the Brazilian club KRB, from where he moved to Figueirense in 2007. In June 2015 he moved to Liverpool for 41 million euros.
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
https://cmqpharma.online/# buying prescription drugs in mexico online
medication from mexico pharmacy
Коммерческий секс в российской столице является проблемой как многосложной и сложноустроенной вопросом. Несмотря на она нелегальна правилами, данная сфера является существенным нелегальной областью.
Контекст в прошлом
В Советского Союза годы коммерческий секс существовала в тени. После Советской империи, в условиях рыночной кризиса, проституция оказалась явной.
Нынешняя положение дел
В настоящее время проституция в российской столице включает многочисленные формы, вплоть до люксовых услуг эскорта до уличного уровня интимных услуг. Люксовые предложения в большинстве случаев организуются через онлайн, а уличная коммерческий секс концентрируется в выделенных зонах города.
Социальные и Экономические Аспекты
Большинство женщин вступают в этот бизнес по причине финансовых затруднений. Проституция может являться привлекательным из-за шансом немедленного дохода, но такая работа подразумевает риски для здоровья и безопасности.
Законодательные вопросы
Коммерческий секс в Российской Федерации нелегальна, и за ее проведение состоят серьёзные наказания. Коммерческих секс-работников зачастую привлекают к ответственности к административной и правовой ответственности.
Таким образом, игнорируя запреты, интимные услуги существует как аспектом теневой экономики Москвы с существенными социальными и правовыми последствиями.
mexican pharmacy [url=https://cmqpharma.online/#]cmqpharma.com[/url] mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
Khvicha Kvaratskhelia https://khvicha-kvaratskhelia.prostoprosport-br.com Georgian footballer, winger for Napoli and captain of the Georgian national team. A graduate of Dynamo Tbilisi. He made his debut for the adult team on September 29, 2017 in the Georgian championship match against Kolkheti-1913. In total, in the 2017 season he played 4 matches and scored 1 goal in the championship.
mexico drug stores pharmacies: cmq pharma – mexico pharmacy
Damian Emiliano Martinez https://emiliano-martinez.prostoprosport-br.com Argentine footballer, goalkeeper of the Aston Villa club and national team Argentina. Champion and best goalkeeper of the 2022 World Cup.
reputable mexican pharmacies online [url=https://cmqpharma.com/#]cmq mexican pharmacy online[/url] medication from mexico pharmacy
Jack Peter Grealish https://jackgrealish.prostoprosport-br.com English footballer, midfielder of the Manchester City club and the England national team. A graduate of the English club Aston Villa from Birmingham. In the 2012/13 season he won the NextGen Series international tournament, playing for the Aston Villa under-19 team
Kyle Andrew Walker https://kylewalker.prostoprosport-br.com English footballer, captain of the Manchester City club and the England national team. In the 2013/14 season, he was on loan at the Notts County club, playing in League One (3rd division of England). Played 37 games and scored 5 goals in the championship.
medication from mexico pharmacy [url=https://cmqpharma.com/#]cmq pharma mexican pharmacy[/url] buying prescription drugs in mexico
Son Heung Min https://sonheung-min.prostoprosport-br.com South Korean footballer, striker and captain of the English Premier League club Tottenham Hotspur and the Republic of Korea national team. In 2022 he won the Premier League Golden Boot. Became the first Asian footballer in history to score 100 goals in the Premier League
medicine in mexico pharmacies [url=https://cmqpharma.online/#]online mexican pharmacy[/url] reputable mexican pharmacies online
best online pharmacies in mexico [url=https://cmqpharma.com/#]medicine in mexico pharmacies[/url] mexican pharmaceuticals online
What is CogniCare Pro? CogniCare Pro is 100 natural and safe to take a cognitive support supplement that helps boost your memory power. This supplement works greatly for anyone of any age and without side effects
mexican drugstore online [url=http://cmqpharma.com/#]mexican pharmacy online[/url] buying prescription drugs in mexico
What is CogniCare Pro? CogniCare Pro is 100 natural and safe to take a cognitive support supplement that helps boost your memory power. This supplement works greatly for anyone of any age and without side effects
Antoine Griezmann https://antoine-griezmann.prostoprosport-fr.com French footballer, striker and midfielder for Atletico Madrid. Player and vice-captain of the French national team, as part of the national team – world champion 2018. Silver medalist at the 2016 European Championship and 2022 World Championship.
Jude Victor William Bellingham https://jude-bellingham.prostoprosport-fr.com English footballer, midfielder of the Spanish club Real Madrid and the England national team. In April 2024, he won the Breakthrough of the Year award from the Laureus World Sports Awards. He became the first football player to receive it.
mexican rx online [url=http://cmqpharma.com/#]mexican online pharmacy[/url] mexico pharmacy
Karim Mostafa Benzema https://karim-benzema.prostoprosport-fr.com French footballer, striker for the Saudi club Al-Ittihad . He played for the French national team, for which he played 97 matches and scored 37 goals.
Sweet Bonanza https://sweet-bonanza.prostoprosport-fr.com is an exciting slot from Pragmatic Play that has quickly gained popularity among players thanks to its unique gameplay, colorful graphics and the opportunity to win big prizes. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at all aspects of this game, from mechanics and bonus features to strategies for successful play and answers to frequently asked questions.
Philip Walter Foden https://phil-foden.prostoprosport-fr.com better known as Phil Foden English footballer, midfielder of the Premier club -League Manchester City and the England national team. On December 19, 2023, he made his debut at the Club World Championship in a match against the Japanese club Urawa Red Diamonds, starting in the starting lineup and being replaced by Julian Alvarez in the 65th minute.
Kylian Mbappe Lotten https://kylian-mbappe.prostoprosport-fr.com Footballeur francais, attaquant du Paris Saint-Germain et capitaine de l’equipe de France. Le 1er juillet 2024, il deviendra joueur du club espagnol du Real Madrid.
Mohamed Salah Hamed Mehrez Ghali https://mohamed-salah.prostoprosport-fr.com Footballeur egyptien, attaquant du club anglais de Liverpool et l’equipe nationale egyptienne. Considere comme l’un des meilleurs footballeurs du monde
Declan Rice https://declan-rice.prostoprosport-fr.com Footballeur anglais, milieu defensif du club d’Arsenal et de l’equipe nationale equipe d’Angleterre. Originaire de Kingston upon Thames, Declan Rice s’est entraine a l’academie de football de Chelsea des l’age de sept ans. En 2014, il devient joueur de l’academie de football de West Ham United.
Declan Rice https://declan-rice.prostoprosport-fr.com Footballeur anglais, milieu defensif du club d’Arsenal et de l’equipe nationale equipe d’Angleterre. Originaire de Kingston upon Thames, Declan Rice s’est entraine a l’academie de football de Chelsea des l’age de sept ans. En 2014, il devient joueur de l’academie de football de West Ham United.
Olivier Jonathan Giroud https://olivier-giroud.prostoprosport-fr.com French footballer, striker for Milan and the French national team. Knight of the Legion of Honor. Participant in four European Championships (2012, 2016, 2020 and 2024) and three World Championships (2014, 2018 and 2022).
Thibaut Nicolas Marc Courtois https://thhibaut-courtois.prostoprosport-fr.com Footballeur belge, gardien de but du club espagnol du Real Madrid . Lors de la saison 2010/11, il a ete reconnu comme le meilleur gardien de la Pro League belge, ainsi que comme joueur de l’annee pour Genk. Triple vainqueur du Trophee Ricardo Zamora
https://win-line.net/אתרי-הימורים-אמינים/
לשלוח, אסמכתא לדבריך.
פעילות ההימורים באינטרנט הפכה לענף מושך מאוד בעת האחרונה, המכיל אפשרויות שונות של חלופות משחק, כגון מכונות מזל.
בסקירה זה נסקור את עולם הפעילות המקוונת ונספק לכם פרטים חשובים שיסייע לכם להתמצא בתופעה אטרקטיבי זה.
משחקי פוקר – הימורים באינטרנט
הימורי ספורט מאפשר אלטרנטיבות רבות של אפשרויות קלאסיים כגון חריצים. הקזינו באינטרנט מעניקים למבקרים להשתתף מאווירת משחק מקורית בכל עת ומקום.
האירוע תיאור מקוצר
מכונות שלוט הימורים עם גלגלים
הימורי רולטה הימור על תוצאות על גלגל מסתובב
משחק הקלפים בלאק ג’ק משחק קלפים בו המטרה להגיע לסכום של 21
משחק קלפים פוקר משחק קלפים מורכב
משחק הבאקרה משחק קלפים פשוט וזריז
הימורים על אירועי ספורט – הימורים באינטרנט
הימורי ספורט מהווים אחד התחומים המתפתחים המובילים ביותר בקזינו באינטרנט. שחקנים רשאים לסחור על תוצאות של אתגרי ספורט פופולריים כגון טניס.
התמודדויות יכולים להיות על תוצאת האירוע, מספר האירועים ועוד.
סוג הפעילות פירוט ענפי ספורט נפוצים
ניחוש התפוצאה ניחוש התוצאה הסופית של המשחק כדורגל, כדורסל, אמריקאי
הפרש תוצאות ניחוש ההפרש בביצועים בין הקבוצות כדורגל, כדורסל, טניס
כמות הסקורים ניחוש כמות התוצאות בתחרות כדורגל, כדורסל, טניס
הקבוצה המנצחת ניחוש מי יהיה הזוכה (ללא קשר לתוצאה) מגוון ענפי ספורט
התמודדות דינמית התמודדות במהלך התחרות בזמן אמת כדורגל, טניס, קריקט
הימורים משולבים שילוב של מספר הימורים שונים מספר ענפי ספורט
פעילות פוקר מקוונת – התמודדות באינטרנט
התמודדות בפוקר מקוון מכיל אחד מתחומי הפעילות המשגשגים ביותר בזמן האחרון. משתתפים יכולים להשתלב כנגד שחקנים אחרים מרחבי הגלובוס בסוגים ש
What is Tea Burn? Tea Burn is a new market-leading fat-burning supplement with a natural patent formula that can increase both speed and efficiency of metabolism. Combining it with Tea, water, or coffee can help burn calories quickly.
Ronaldo de Asis Moreira https://ronaldinhogaucho.prostoprosport-br.com Brazilian footballer, played as an attacking midfielder and striker. World Champion (2002). Winner of the Golden Ball (2005). The best football player in the world according to FIFA in 2004 and 2005.
Xavi or Xavi Quentin Sy Simons https://xavi-simons.prostoprosport-fr.com Dutch footballer, midfielder of the Paris Saint-Germain club -Germain” and the Dutch national team, playing on loan for the German club RB Leipzig.
Jamal Musiala https://jamal-musiala.prostoprosport-fr.com footballeur allemand, milieu offensif du club allemand du Bayern et du equipe nationale d’Allemagne. Il a joue pour les equipes anglaises des moins de 15 ans, des moins de 16 ans et des moins de 17 ans. En octobre 2018, il a dispute deux matchs avec l’equipe nationale d’Allemagne U16. En novembre 2020, il a fait ses debuts avec l’equipe d’Angleterre U21.
Erling Breut Haaland https://erling-haaland.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista noruegues, atacante do clube ingles Manchester City e Selecao da Noruega. Detentor do recorde da Premier League inglesa em gols por temporada.
What does the Lottery Defeater Software offer? The Lottery Defeater Software is a unique predictive tool crafted to empower individuals seeking to boost their chances of winning the lottery.
Philippe Coutinho Correia https://philippecoutinho.prostoprosport-br.com Brazilian footballer, midfielder of the English club Aston Villa, playing on loan for the Qatari club Al-Duhail. He is known for his vision, passing, dribbling and long-range ability.
Mohamed Salah https://mohamedsalah.prostoprosport-br.com e um futebolista egipcio que joga como atacante do clube ingles Liverpool e do Selecao egipcia. Considerado um dos melhores jogadores de futebol do mundo. Tricampeao da Chuteira de Ouro da Premier League inglesa: em 2018 (sozinho), 2019 (junto com Sadio Mane e Pierre-Emerick Aubameyang) e 2022 (junto com Son Heung-min).
Karim Mostafa Benzema https://karim-benzema.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista frances, atacante do clube saudita Al-Ittihad . Jogou pela selecao francesa, pela qual disputou 97 partidas e marcou 37 gols.
Kaka https://kaka.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista brasileiro, meio-campista. O apelido “Kaka” e um diminutivo de Ricardo. Formado em Sao Paulo. De 2002 a 2016, integrou a Selecao Brasileira, pela qual disputou 92 partidas e marcou 29 gols. Campeao mundial 2002.
Harry Kane https://harry-kane.prostoprosport-br.com recebeu um convite para a selecao sub-alterna da Inglaterra pela primeira vez tempo 17 para o torneio juvenil em Portugal. Ao mesmo tempo, o atacante, devido a doenca grave, nao compareceu ao triunfante Campeonato Europeu Sub-17 masculino de 2010 pelos britanicos.
Luis Alberto Suarez Diaz https://luis-suarez.prostoprosport-br.com Uruguayan footballer, striker for Inter Miami and Uruguay national team. The best scorer in the history of the Uruguay national team. Considered one of the world’s top strikers of the 2010s
Thibaut Nicolas Marc Courtois https://thhibaut-courtois.prostoprosport-fr.com Footballeur belge, gardien de but du club espagnol du Real Madrid . Lors de la saison 2010/11, il a ete reconnu comme le meilleur gardien de la Pro League belge, ainsi que comme joueur de l’annee pour Genk. Triple vainqueur du Trophee Ricardo Zamora
Robert Lewandowski https://robert-lewandowski.prostoprosport-br.com e um futebolista polones, atacante do clube espanhol Barcelona e capitao da selecao polonesa. Considerado um dos melhores atacantes do mundo. Cavaleiro da Cruz do Comandante da Ordem do Renascimento da Polonia.
Kevin De Bruyne https://kevin-de-bruyne.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista belga, meio-campista do Manchester club City” e a selecao belga. Formado pelos clubes de futebol “Ghent” e “Genk”. Em 2008 iniciou sua carreira adulta, fazendo sua estreia no Genk.
Ederson Santana de Moraes https://edersonmoraes.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista brasileiro, goleiro do clube Manchester City e da Selecao Brasileira . Participante do Campeonato Mundial 2018. Bicampeao de Portugal pelo Benfica e pentacampeao de Inglaterra pelo Manchester City.
Профессиональные seo https://seo-optimizaciya-kazan.ru услуги для максимизации онлайн-видимости вашего бизнеса. Наши эксперты проведут глубокий анализ сайта, оптимизируют контент и структуру, улучшат технические аспекты и разработают индивидуальные стратегии продвижения.
Virgil van Dijk https://virgilvandijk.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista holandes, zagueiro central, capitao do clube ingles Liverpool e capitao do a selecao holandesa.
Victor James Osimhen https://victor-osimhen.prostoprosport-br.com e um futebolista nigeriano que atua como atacante. O clube italiano Napoli e a selecao nigeriana.
mexico drug stores pharmacies [url=https://cmqpharma.com/#]mexican pharmacy[/url] buying prescription drugs in mexico online
Roberto Carlos da Silva Rocha https://roberto-carlos.prostoprosport-br.com Brazilian footballer, left back. He was also capable of playing as both a central defender and a defensive midfielder. World champion 2002, silver medalist at the 1998 World Championships.
Neymar da Silva Santos Junior https://neymar.prostoprosport-br.com e um futebolista brasileiro que atua como atacante, ponta e atacante. meio-campista do clube saudita Al-Hilal e da selecao brasileira. Considerado um dos melhores jogadores do mundo. O maior artilheiro da historia da Selecao Brasileira.
Thomas Mueller https://thomasmueller.prostoprosport-br.com is a German football player who plays for the German Bayern Munich. Can play in different positions – striker, attacking midfielder. The most titled German footballer in history
rgbet
Erling Breut Haaland https://erling-haaland.prostoprosport-cz.org je norsky fotbalista, ktery hraje jako utocnik za Anglicky klub Manchester City a norska reprezentace. Rekordman anglicke Premier League v poctu golu za sezonu.
Edson Arantes do Nascimento https://pele.prostoprosport-br.com Brazilian footballer, forward (attacking midfielder. Played for Santos clubs) and New York Cosmos. Played 92 matches and scored 77 goals for the Brazilian national team.
Mohamed Salah https://mohamed-salah.prostoprosport-cz.org je egyptsky fotbalista, ktery hraje jako utocnik za anglictinu. klub Liverpool a egyptsky narodni tym. Povazovan za jednoho z nejlepsich fotbalistu na svete.
Kevin De Bruyne https://kevin-de-bruyne.prostoprosport-cz.org Belgicky fotbalista, zaloznik Manchesteru klub City” a belgicky narodni tym. Absolvent fotbalovych klubu „Ghent” a „Genk”. V roce 2008 zahajil svou karieru dospelych, debutoval v Genku.
Lionel Messi https://lionel-messi.prostoprosport-cz.org je argentinsky fotbalista, utocnik a kapitan klubu MLS Inter Miami. , kapitan argentinske reprezentace. Mistr sveta, vitez Jizni Ameriky, vitez finale, olympijsky vitez. Povazovan za jednoho z nejlepsich fotbalistu vsech dob.
Antoine Griezmann https://antoine-griezmann.prostoprosport-cz.org Francouzsky fotbalista, utocnik a zaloznik za Atletico de Madrid. Hrac a vicekapitan francouzskeho narodniho tymu, clen tymu – mistr sveta 2018 Stribrny medailista z mistrovstvi Evropy 2016 a mistrovstvi sveta 2022.
Pablo Martin Paez Gavira https://gavi.prostoprosport-cz.org Spanelsky fotbalista, zaloznik barcelonskeho klubu a spanelske reprezentace. Povazovan za jednoho z nejtalentovanejsich hracu sve generace. Ucastnik mistrovstvi sveta 2022. Vitez Ligy narodu UEFA 2022/23
Pedro Gonzalez Lopez https://pedri.prostoprosport-cz.org lepe znamy jako Pedri, je spanelsky fotbalista, ktery hraje jako utocny zaloznik. za Barcelonu a spanelskou reprezentaci. Bronzovy medailista z mistrovstvi Evropy 2020 a zaroven nejlepsi mlady hrac tohoto turnaje.
Karim Benzema https://karim-benzema.prostoprosport-cz.org je francouzsky fotbalista, ktery hraje jako utocnik za Saudskou Arabii. Arabsky klub Al-Ittihad. Hral za francouzsky narodni tym, za ktery odehral 97 zapasu a vstrelil 37 branek. V 17 letech se stal jednim z nejlepsich hracu rezervy, nastrilel tri desitky golu za sezonu.
Bruno Guimaraes Rodriguez Moura https://bruno-guimaraes.prostoprosport-cz.org Brazilsky fotbalista, defenzivni zaloznik Newcastlu United a Brazilsky narodni tym. Vitez olympijskych her 2020 v Tokiu.
Darwin Gabriel Nunez Ribeiro https://darwin-nunez.prostoprosport-cz.org Uruguaysky fotbalista, utocnik anglickeho klubu Liverpool a Uruguaysky narodni tym. Bronzovy medailista mistrovstvi Jizni Ameriky mezi mladeznickymi tymy.
Romelu Menama Lukaku Bolingoli https://romelu-lukaku.prostoprosport-cz.org Belgicky fotbalista, utocnik anglickeho klubu Chelsea a Belgican vyber. Na hostovani hraje za italsky klub Roma.
Well I truly liked reading it. This information offered by you is very useful for proper planning.
I’m not sure why but this blog is loading very slow for me. Is anyone else having this problem or is it a problem on my end? I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
Hiya very cool web site!! Guy .. Excellent .. Wonderful .. I will bookmark your site and take the feeds additionally?KI’m happy to find numerous useful info here within the submit, we need work out extra techniques on this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
номер телефона проститутки https://prostitutki-213.ru
отчаянные домохозяйки 7 сезон отчаянные домохозяйки смотреть в хорошем качестве
https://businka74.ru регистрация рио бет казино
Dragon Money Casino регистрация Dragon Money Casino
Качественная и недорогая https://mebelvam-nn.ru/catalog/myagkaya-mebel/ лучшие цены, доставка и сборка.
Hey There. I found your blog using msn. This is an extremely well written article. I will make sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful info. Thanks for the post. I will definitely return.
Pin Up casino https://pin-up.salexy.kz official website, Pin Up slot machines play for money online, Pin Up mirror working for today.
Sports in Azerbaijan https://idman-xeberleri.com.az development and popular sports Azerbaijan is a country with rich sports traditions and outstanding achievements on the international stage.
Howdy! I know this is kinda off topic however I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest authoring a blog post or vice-versa? My blog goes over a lot of the same subjects as yours and I feel we could greatly benefit from each other. If you happen to be interested feel free to shoot me an e-mail. I look forward to hearing from you! Wonderful blog by the way!
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
World of Games https://onlayn-oyunlar.com.az provides the latest news about online games, game reviews, gameplay and ideas, game tactics and tips. The most popular and spectacular
NHL (National Hockey League) News https://nhl.com.az the latest and greatest NHL news for today. Sports news – latest NHL news, standings, match results, online broadcasts.
hello!,I like your writing so much! percentage we keep up a correspondence more about your post on AOL? I require a specialist in this house to unravel my problem. Maybe that’s you! Taking a look ahead to look you.
Latest news and details about the NBA in Azerbaijan https://nba.com.az. Hot events, player transfers and the most interesting events. Explore the world of the NBA with us.
Very nice post and right to the point. I don’t know if this is really the best place to ask but do you guys have any ideea where to get some professional writers? Thanks in advance :)
Latest news about games for Android https://android-games.com.az, reviews and daily updates. Read now and get the latest information on the most exciting games
The most popular sports site https://sports.com.az of Azerbaijan, where the latest sports news, forecasts and analysis are collected.
Хотите сделать в квартире ремонт? Тогда советуем вам посетить сайт https://stroyka-gid.ru, где вы найдете всю необходимую информацию по строительству и ремонту.
1xbet https://1xbet.best-casino-ar.com with withdrawal without commission. Register online in a few clicks. A large selection of slot machines in mobile applications and convenient transfers in just a few minutes.
Hello, Neat post. There’s an issue together with your web site in web explorer, may check thisK IE nonetheless is the market chief and a huge section of people will pass over your great writing due to this problem.
Pin-up casino https://pin-up.jes-design.ru популярное онлайн-казино и ставки на спорт. Официальный сайт казино для доступа к играм и другим функциям казино для игры на деньги.
I like what you guys tend to be up too. This kind of clever work and exposure! Keep up the very good works guys I’ve included you guys to blogroll.
Paul Labille Pogba https://pogba.com.az French footballer, central midfielder of the Italian club Juventus. Currently suspended for doping and unable to play. World champion 2018.
Kevin De Bruyne https://kevin-de-bruyne.liverpool-fr.com Belgian footballer, born 28 June 1991 years in Ghent. He has had a brilliant club career and also plays for the Belgium national team. De Bruyne is known for his spectacular goals and brilliant assists.
I’ve recently started a site, the information you offer on this web site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
Pues con Ruven Ignacio Moreira encontramos grandes resultados en Cerralvo, nos gusta su estilo sencillo y humilde de trabajar.
Greetings I am so delighted I found your web site, I really found you by accident, while I was looking on Aol for something else, Regardless I am here now and would just like to say thank you for a fantastic post and a all round enjoyable blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to go through it all at the minute but I have book-marked it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a lot more, Please do keep up the great job.
Kylian Mbappe https://kylian-mbappe.psg-fr.com Footballeur, attaquant francais. Il joue pour le PSG et l’equipe de France. Ne le 20 decembre 1998 a Paris. Mbappe est francais de nationalite. La taille de l’athlete est de 178 cm.
Paul Pogba https://psg.paul-pogba-fr.com is a world-famous football player who plays as a central midfielder. The player’s career had its share of ups and downs, but he was always distinguished by his perseverance and desire to win.
Enjoyed studying this, very good stuff, regards. “Curiosity killed the cat, but for a while I was a suspect.” by Steven Wright.
Jude Victor William Bellingham https://jude-bellingham.real-madrid-ar.com English footballer, midfielder of the Spanish club Real Madrid and the England national team. In April 2024, he won the Breakthrough of the Year award from the Laureus World Sports Awards.
Vinicius Junior https://vinisius-junior.com.az player news, fresh current and latest events for today about the player of the 2024 season
Welcome to our official site! Get to know the history, players and latest news of Inter Miami Football Club https://inter-miami.com.az. Discover with us the successes and great performances of America’s newest and most exciting soccer club.
Оперативный вывод из запоя https://www.liveinternet.ru/users/laralim/post505923855/ на дому. Срочный выезд частного опытного нарколога круглосуточно. При необходимости больного госпитализируют в стационар.
Welcome to the site dedicated to Michael Jordan https://michael-jordan.com.az, a basketball legend and symbol of world sports culture. Here you will find highlights, career, family and news about one of the greatest athletes of all time.
LeanBiome is a dietary supplement designed to promote weight loss and improve overall health. It is formulated with a unique blend of probiotics, prebiotics, and natural ingredients that work together to support a healthy gut microbiome. The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in digestion, metabolism, and the immune system. By optimizing the gut microbiome, LeanBiome aims to help individuals achieve their weight loss goals more effectively and sustainably. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/leanbiome/
Tonic Greens has gained popularity as a health supplement known for its rich blend of vitamins, minerals, and plant extracts. This article explores its composition, potential health benefits, usage instructions, and possible side effects. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/tonicgreens/
SightCare is a revolutionary dietary supplement designed to support and maintain optimal eye health. In today’s digital age, where screens dominate our daily lives, the need for effective eye care solutions has never been greater. SightCare aims to meet this need with its scientifically formulated blend of essential nutrients and antioxidants. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/sightcare/
Boostaro stands out as a natural solution for boosting energy levels and supporting overall vitality. Its blend of caffeine, adaptogens, and essential nutrients offers a balanced approach to enhancing physical and mental energy. As with any supplement, consult with a healthcare professional before starting, especially if you have any health concerns or sensitivities. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/boostaro/
Prostadine is a dietary supplement formulated to support prostate health, particularly in men experiencing symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or other prostate-related issues. As men age, maintaining prostate health becomes increasingly important to avoid urinary discomfort and other related problems. Prostadine aims to provide a natural solution through a blend of ingredients known for their beneficial effects on the prostate. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/prostadine/
Glucotil is a dietary supplement designed to support healthy blood sugar levels and overall metabolic health. Managing blood sugar is crucial for individuals with diabetes or pre-diabetes, as well as for those looking to maintain healthy energy levels and prevent future metabolic issues. Glucotil combines natural ingredients that have been shown to positively affect blood glucose regulation and insulin sensitivity.
https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/glucotil/
The latest top football news https://football-kz.kz today. Interviews with football players, online broadcasts and match results, analytics and football forecasts, photos and videos.
Latest news about games for Android https://android-games.kz, reviews and daily updates. Read now and get the latest information about the most exciting games
Latest news and analysis of the Premier League https://premier-league.kz. Full descriptions of matches, team statistics and the most interesting football events. Premier Kazakhstan is the best place for football fans.
Купить зеркала https://zerkala-m.ru по низким ценам. Более 1980 моделей, купить недорого в интернет-магазине в Москве с доставкой по России. Удобный каталог, низкие цены, качественные фото.
The latest top football news https://football.sport-news-eg.com today. Interviews with football players, online broadcasts and match results, analytics and football forecasts, photos and videos.
Интернет магазин электроники и цифровой техники по доступным ценам. Доставка мобильной электроники по Москве и Московской области.
NHL news https://nhl-ar.com (National Hockey League) – the latest and most up-to-date NHL news for today.
News and events of the American Basketball League https://basketball-eg.com in Egypt. Hot events, player transfers and the most interesting events. Explore the world of the NBA with us.
ZenCortex is a nootropic supplement designed to enhance cognitive function, support brain health, and improve mental clarity. By combining a blend of natural ingredients known for their neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties, ZenCortex aims to boost memory, focus, and overall brain performance. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/zencortex/
mexican rx online
http://cmqpharma.com/# best online pharmacies in mexico
mexico drug stores pharmacies
Latest news https://android-games-ar.com about Android games, reviews and daily updates. The latest information about the most exciting games.
mexican rx online: cmq mexican pharmacy online – purple pharmacy mexico price list
Pineal XT is a dietary supplement formulated to enhance sleep quality and support sleep patterns. Known for its natural ingredients, Pineal XT particularly focuses on boosting melatonin production, aiding individuals in managing sleep-related issues effectively. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/pinealxt/
Prodentim offers a range of innovative dental care products designed to promote optimal oral health. From toothpaste to oral rinses, Prodentim products are formulated with advanced ingredients to address various dental concerns and enhance overall oral hygiene. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/prodentim/
Puravive is a dietary supplement designed to support weight loss and overall metabolic health. By leveraging a blend of natural ingredients known for their fat-burning and metabolism-boosting properties, Puravive aims to help individuals achieve their weight management goals and enhance their overall well-being. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/puravive-web/
The site is dedicated to football https://fooball-egypt.com, football history and news. Latest news and fresh reviews of the world of football
Открытие для себя Ерлинг Хааланда https://manchestercity.erling-haaland-cz.com, a talented player of «Manchester City». Learn more about his skills, achievements and career growth.
The fascinating story of the rise of Brazilian prodigy Vinicius Junior https://realmadrid.vinicius-junior-cz.com to the heights of glory as part of the legendary Madrid “Real”
Mohamed Salah https://liverpool.mohamed-salah-cz.com, who grew up in a small town in Egypt, conquered Europe and became Liverpool star and one of the best players in the world.
Useful information. Fortunate me I discovered your website by accident, and I am shocked why this accident didn’t happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Полезные советы и пошаговые инструкции по строительству https://syndyk.by, ремонту и дизайну домов и квартир, выбору материалов, монтажу и установке своими руками.
The inspiring story of how talented Kevin De Bruyne https://manchestercity.kevin-de-bruyne-cz.com became the best player of Manchester City and the Belgium national team. From humble origins to the leader of a top club.
Антиотмывочная проверка: Каким образом избежать ограничение фондов на платформах обмена криптовалют
Для чего нужна антиотмывочные меры?
Проверка по борьбе с отмыванием денег (Противодействие легализации доходов) – подразумевает набор инструментов, направленных для борьбы отбеливания денег. Данная процедура способствует оберегать криптовалютные активы участников и не допускать вовлечение сервисов противоправных операций. AML-проверка необходима в интересах обеспечения сохранности ваших активов наряду с соблюдением юридических правил.
Базовые подходы верификации
Криптобиржи помимо прочего транзакционные сервисы внедряют ряд ключевых методов для проверки участников:
“Знай своего клиента”: Данный подход включает базовые процедуры для идентификации личности пользователя, например подтверждение удостоверений местонахождения. Идентификация личности позволяет быть уверенным, в надежности владельца является законным.
Противодействие финансированию терроризма: Сфокусирована для предотвращения обеспечения террористических актов. Инструментарий контролирует сомнительные транзакции в случае необходимости замораживает учетные записи в рамках проведения внутриорганизационной экспертизы.
Выгоды проверки по борьбе с отмыванием денег
Антиотмывочные меры дает возможность платформам обмена криптовалют:
Выполнять глобальные и местные законодательные стандарты.
Оберегать участников недобросовестных действий.
Наращивать степень надежности со стороны владельцев госорганов.
Каким образом обезопасить свои активы при взаимодействии с криптовалютой
С целью ограничить риски замораживания ресурсов, придерживайтесь данным подсказкам:
Используйте проверенные платформы: Используйте единственно к сервисам с хорошей репутацией наряду с высоким степенью надежности.
Анализируйте участников: Прибегайте к услуги по противодействию отмыванию с целью проверки цифровых кошельков получателей непосредственно перед совершением операций.
Регулярно трансформируйте виртуальные счета: Данное действие поможет предотвратить потенциальных ограничений, в ситуации когда Ваши партнеры партнеры будут внесены под внимание.
Сохраняйте доказательства переводов: Когда потребуется необходимости будете в состоянии подтвердить легитимность принятых средств.
Резюме
AML-проверка – выступает в качестве ключевой способ с целью обеспечения безопасности операций на криптовалютном рынке. Данная процедура помогает не допустить легализацию ресурсов, поддержку терроризма а также иные незаконные активности. Следуя рекомендациям по безопасности а также выбирая безопасные обменники, будете в состоянии снизить опасности ограничения активов работать безопасной работой с цифровой валютой.
Antoine Griezmann https://atlticomadrid-dhb.antoine-griezmann-cz.com Atletico Madrid star whose talent and decisive goals helped the club reach the top of La Liga and the UEFA Champions League.
Son Heung-min’s https://tottenhamhotspur.son-heung-min-cz.com success story at Tottenham Hotspur and his influence on the South Korean football, youth inspiration and changing the perception of Asian players.
The story of Robert Lewandowski https://barcelona.robert-lewandowski-cz.com, his impressive journey from Poland to Barcelona, ??where he became not only a leader on the field, but also a source of inspiration for young players.
Rattling excellent visual appeal on this website , I’d rate it 10 10.
Puravive is a dietary supplement designed to support weight loss and overall metabolic health. By leveraging a blend of natural ingredients known for their fat-burning and metabolism-boosting properties, Puravive aims to help individuals achieve their weight management goals and enhance their overall well-being. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/puravive-web/
Sugar Balance is a dietary supplement designed to support healthy blood sugar levels. Utilizing a blend of natural ingredients, Sugar Balance aims to help individuals manage their blood sugar more effectively, offering a holistic approach to maintaining metabolic health and preventing complications associated with high blood sugar levels. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/sugarbalance
Kerassentials is a skincare and nail care product designed to promote healthy, strong nails and improve the overall condition of the skin. Combining natural and scientifically-backed ingredients, Kerassentials targets common issues such as fungal infections, brittle nails, and dry skin, providing a comprehensive solution for maintaining nail and skin health. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/kerassentials-try/
EyeFortin is an all-natural eye-health supplement that helps to keep your eyes healthy even as you age. It prevents infections and detoxifies your eyes while also being stimulant-free. This makes it a great choice for those who are looking for a natural way to improve their eye health. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/eyefortin/
Burn Boost is a dietary supplement designed to aid in weight management and fat loss. Combining a blend of natural ingredients, Burn Boost aims to increase metabolism, enhance energy levels, and support overall weight loss efforts. This article explores the composition, benefits, clinical evidence, and user experiences related to Burn Boost. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/burnboost/
GlucoTrust is a dietary supplement designed to support healthy blood sugar levels and improve overall metabolic health. Combining a blend of natural ingredients known for their beneficial effects on blood sugar regulation, GlucoTrust aims to provide a comprehensive solution for individuals looking to manage their blood sugar levels naturally. This article explores the composition, benefits, clinical evidence, and user experiences related to GlucoTrust. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/glucotrust/
Alpha Tonic is a dietary supplement designed to support male vitality, energy, and overall performance. Combining a blend of natural ingredients known for their beneficial effects on male health, Alpha Tonic aims to provide a comprehensive solution for men looking to enhance their physical and mental well-being. This article explores the composition, benefits, clinical evidence, and user experiences related to Alpha Tonic. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/alphatonic/
A study of the influence of Rodrigo https://realmadrid.rodrygo-cz.com on the success and marketing strategy of Real Madrid: analysis of technical skills, popularity in Media and commercial success.
Find out about Alisson https://liverpool.alisson-becker-cz.com‘s influence on Liverpool’s success, from his defense to personal achievements that made him one of the best goalkeepers in the world.
Red Boost is a dietary supplement formulated to support male vitality, enhance physical performance, and improve overall well-being. With a blend of potent natural ingredients, Red Boost aims to address common issues related to male health, such as low energy, reduced libido, and decreased stamina. This article delves into the composition, benefits, clinical evidence, and user experiences of Red Boost. https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/redboost/
I just could not depart your web site before suggesting that I actually enjoyed the standard info a person provide for your visitors? Is gonna be back often in order to check up on new posts
PotentStream is a dietary supplement designed to enhance male vitality, energy levels, and overall performance. Combining a blend of potent natural ingredients, PotentStream aims to provide a comprehensive solution for men experiencing issues related to low energy, reduced libido, and decreased stamina. This article explores the composition, benefits, clinical evidence, and user experiences of PotentStream.
https://sites.google.com/spsw.edu.pl/potentstream/
r7 casino онлайн https://mabiclub.ru
Thibaut Courtois https://realmadrid.thibaut-courtois-cz.com the indispensable goalkeeper of “Real”, whose reliability, leadership and outstanding The game made him a key figure in the club.
вавада бонусы вавада
Find out how Virgil van Dijk https://liverpool.virgil-van-dijk-cz.com became an integral part of style игры «Liverpool», ensuring the stability and success of the team.
Star Brazilian striker Gabriel Jesus https://arsenal.gabriel-jesus-cz.com put in a superb performance to lead Arsenal to new heights after moving from Manchester City.
Hello very cool site!! Man .. Excellent .. Amazing .. I’ll bookmark your website and take the feeds additionallyKI’m satisfied to seek out numerous helpful information here within the publish, we need work out extra strategies on this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
The fascinating story of Marcus Rashford’s ascent https://manchester-united.marcus-rashford-cz.com to glory in the Red Devils: from a young talent to one of the key players of the team.
WONDERFUL Post.thanks for share..more wait .. …
Try to make a fascinating actor Johnny Depp https://secret-window.johnny-depp.cz, who will become the slave of his strong hero Moudriho Creeps in the thriller “Secret Window”.
Fascinating event related to this Keanu Reeves helped him in the role of the iconic John Wick characters https://john-wick.keanu-reeves.cz, among which there is another talent who has combat smarts with inappropriate charisma.
Jackie Chan https://peakhour.jackie-chan.cz from a poor boy from Hong Kong to a world famous Hollywood stuntman. The incredible success story of Jackie Chan.
The inspiring story of the ascent of the young actress Anya Taylor https://queensmove.anya-taylor-joy.cz to fame after her breakthrough performance in the TV series “The Queen’s Move”. Conquering new peaks.
Witness the thrilling story of Jiri Prochazka’s https://ufc.jiri-prochazka-ufc.cz rapid rise to the top of the UFC’s light heavyweight division, marked by his dynamic fighting style and relentless determination.
It is in reality a great and helpful piece of information. I am happy that you shared this helpful information with us. Please stay us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
Jon Jones https://ufc.jon-jones.cz a dominant fighter with unrivaled skill, technique and physique who has conquered the light heavyweight division.
An article about the triumphant 2023 Ferrari https://ferrari.charles-leclerc.cz and their star driver Charles Leclerc, who became the Formula world champion 1.
Young Briton Lando Norris https://mclaren.lando-norris.cz is at the heart of McLaren’s Formula 1 renaissance, regularly achieving podium finishes and winning.
Activision and Call of Duty https://activision.call-of-duty.cz leading video game publisher and iconic shooter with a long history market dominance.
Free movies https://www.moviesjoy.cc and TV streaming online, watch movies online in HD 1080p.
Latest Diablo news https://diablo-ar.com, detailed game descriptions and guides. Diablo.az – The largest Diablo information portal in Arabic.
purple pharmacy mexico price list
https://cmqpharma.online/# buying from online mexican pharmacy
buying prescription drugs in mexico
Discover the wonderful world of online games https://onlayn-oyinlar.com with GameHub. Get the latest news, reviews and tips for your favorite games. Join our gaming community today!
Sports news https://gta-uzbek.com the most respected sports site in Uzbekistan, which contains the latest sports news, forecasts and analysis.
Latest news from the world of boxing https://boks-uz.com, achievements of Resul Abbasov, Tyson Fury’s fights and much more. Everything Boxing Ambassador has.
Latest GTA game news https://gta-uzbek.com, tournaments, guides and strategies. Stay tuned for the best GTA gaming experience
medication from mexico pharmacy: cmq pharma – mexican pharmacy
Explore the extraordinary journey of Kylian Mbappe https://mbappe-real-madrid.com, from his humble beginnings to global stardom.
Latest news about Pele https://mesut-ozil-uz.com, statistics, photos and much more. Get the latest news and information about football legend Pele.
Get the latest https://mesut-ozil-uz.com Mesut Ozil news, stats, photos and more.
Официальный сайт онлайн-казино Vavada https://vavada-kz-game.kz это новый адрес лучших слотов и джекпотов. Ознакомьтесь с бонусами и играйте на реальные деньги из Казахстана.
Marcus Lilian Thuram-Julien https://internationale.marcus-thuram-fr.com French footballer, forward for the Internazionale club and French national team.
Legendary striker Cristiano Ronaldo https://an-nasr.cristiano-ronaldo-fr.com signed a contract with the Saudi club ” An-Nasr”, opening a new chapter in his illustrious career in the Middle East.
外送茶
外送茶是什麼?禁忌、價格、茶妹等級、術語等..老司機告訴你!
外送茶是什麼?
外送茶、外約、叫小姐是一樣的東西。簡單來說就是在通訊軟體與茶莊聯絡,選好自己喜歡的妹子後,茶莊會像送飲料這樣把妹子派送到您指定的汽車旅館、酒店、飯店等交易地點。您只需要在您指定的地點等待,妹妹到達後,就可以開心的開始一場美麗的約會。
外送茶種類
學生兼職的稱為清新書香茶
日本女孩稱為清涼綠茶
俄羅斯女孩被稱為金酥麻茶
韓國女孩稱為超細滑人參茶
外送茶價格
外送茶的客戶相當廣泛,包括中小企業主、自營商、醫生和各行業的精英,像是工程師等等。在台北和新北地區,他們的消費指數大約在 7000 到 10000 元之間,而在中南部則通常在 4000 到 8000 元之間。
對於一般上班族和藍領階層的客人來說,建議可以考慮稍微低消一點,比如在北部約 6000 元左右,中南部約 4000 元左右。這個價位的茶妹大多是新手兼職,但有潛力。
不同地區的客人可以根據自己的經濟能力和喜好選擇適合自己的價位範圍,以免感到不滿意。物價上漲是一個普遍現象,受到地區和經濟情況等因素的影響,茶莊的成本也在上升,因此價格調整是合理的。
外送茶外約流程
加入LINE:加入外送茶官方LINE,客服隨時為你服務。茶莊一般在中午 12 點到凌晨 3 點營業。
告知所在地區:聯絡客服後,告訴他們約會地點,他們會幫你快速找到附近的茶妹。
溝通閒聊:有任何約妹問題或需要查看妹妹資訊,都能得到詳盡的幫助。
提供預算:告訴客服你的預算,他們會找到最適合你的茶妹。
提早預約:提早預約比較好配合你的空檔時間,也不用怕到時候約不到你想要的茶妹。
外送茶術語
喝茶術語就像是進入茶道的第一步,就像是蓋房子打地基一樣。在這裡,我們將這些外送茶入門術語分類,讓大家能夠清楚地理解,讓喝茶變得更加容易上手。
魚:指的自行接客的小姐,不屬於任何茶莊。
茶:就是指「小姐」的意思,由茶莊安排接客。
定點茶:指由茶莊提供地點,客人再前往指定地點與小姐交易。
外送茶:指的是到小姐到客人指定地點接客。
個工:指的是有專屬工作室自己接客的小姐。
GTO:指雞頭也就是飯店大姊三七茶莊的意思。
摳客妹:只負責找客人請茶莊或代調找美眉。
內機:盤商應召站提供茶園的人。
經紀人:幫內機找美眉的人。
馬伕:外送茶司機又稱教練。
代調:收取固定代調費用的人(只針對同業)。
阿六茶:中國籍女子,賣春的大陸妹。
熱茶、熟茶:年齡比較大、年長、熟女級賣春者(或稱阿姨)。
燙口 / 高溫茶:賣春者年齡過高。
台茶:從事此職業的台灣小姐。
本妹:從事此職業的日本籍小姐。
金絲貓:西方國家的小姐(歐美的、金髮碧眼的那種)。
青茶、青魚:20 歲以下的賣春者。
乳牛:胸部很大的小姐(D 罩杯以上)。
龍、小叮噹、小叮鈴:體型比較肥、胖、臃腫、大隻的小姐。
Magnificent website. Plenty of helpful info here. I am sending it to several buddies ans also sharing in delicious. And naturally, thank you in your effort!
Coffeeroom https://coffeeroom.by – магазин кофе, чая, кофетехники, посуды, химии и аксессуаров в Минске для дома и офиса.
Latest news and information about Marcelo https://marselo-uz.com on this site! Find Marcelo’s biography, career, game stats and more.
What are Ageless Knees? Ageless Knees is a knee pain relieving program. Chris Ohocinski, a State-Licensed and Nationally Certified Athletic Trainer, came up with this program.
A site dedicated to Michael Jordan https://michael-jordan.uz, a basketball legend and symbol of world sports culture. Here you will find highlights, career, family and news about one of the greatest athletes of all time.
Get to know the history, players and latest news of the Inter Miami football club https://inter-miami.uz. Join us to learn about the successes and great performances of America’s newest and most exciting soccer club.
Explore the dynamic world of sports https://noticias-esportivas-br.org through the lens of a sports reporter. Your source for breaking news, exclusive interviews, in-depth analysis and live coverage of all sports.
The latest top football news https://futebol-ao-vivo.net today. Interviews with football players, online broadcasts and match results, analytics and football forecasts
Site with the latest news, statistics, photos of Pele https://edson-arantes-do-nascimento.com and much more. Get the latest news and information about football legend Pele.
The best site dedicated to the football player Paul Pogba https://pogba.org. Latest news from the world of football.
Vinicius Junior https://vinicius-junior.org all the latest current and latest news for today about the player of the 2024 season
Gavi’s success story https://barcelona.gavi-fr.com at Barcelona: from his debut at 16 to a key role in club and national team of Spain, his talent inspires the world of football.
Pedri’s story https://barcelona.pedri-fr.com from his youth in the Canary Islands to becoming a world-class star in Barcelona, ??with international success and recognition.
Геракл24: Квалифицированная Замена Основания, Венцов, Настилов и Перемещение Строений
Фирма Геракл24 профессионально занимается на оказании комплексных работ по смене основания, венцов, полов и передвижению домов в городе Красноярском регионе и за пределами города. Наша группа квалифицированных экспертов обещает отличное качество исполнения всех типов восстановительных работ, будь то деревянные, с каркасом, из кирпича или бетонные здания.
Преимущества работы с Геракл24
Профессионализм и опыт:
Все работы осуществляются лишь профессиональными экспертами, имеющими долгий практику в области создания и ремонта зданий. Наши мастера профессионалы в своем деле и осуществляют задачи с высочайшей точностью и вниманием к мелочам.
Всесторонний подход:
Мы осуществляем полный спектр услуг по восстановлению и восстановлению зданий:
Реставрация фундамента: замена и укрепление фундамента, что позволяет продлить срок службы вашего строения и устранить проблемы, связанные с оседанием и деформацией строения.
Смена венцов: реставрация нижних венцов из дерева, которые чаще всего гниют и разрушаются.
Замена полов: замена старых полов, что значительно улучшает визуальное восприятие и практическую полезность.
Передвижение домов: безопасное и надежное перемещение зданий на новые места, что позволяет сохранить ваше строение и избежать дополнительных затрат на создание нового.
Работа с различными типами строений:
Дома из дерева: восстановление и укрепление деревянных конструкций, обработка от гниения и насекомых.
Дома с каркасом: укрепление каркасов и реставрация поврежденных элементов.
Кирпичные строения: восстановление кирпичной кладки и укрепление стен.
Дома из бетона: ремонт и укрепление бетонных конструкций, устранение трещин и повреждений.
Качество и прочность:
Мы применяем только высококачественные материалы и новейшее оборудование, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы и прочность всех выполненных задач. Каждый наш проект подвергаются строгому контролю качества на каждом этапе выполнения.
Личный подход:
Мы предлагаем каждому клиенту подходящие решения, с учетом всех особенностей и пожеланий. Наша цель – чтобы конечный результат полностью соответствовал ваши ожидания и требования.
Почему выбирают Геракл24?
Сотрудничая с нами, вы приобретете надежного партнера, который возьмет на себя все хлопоты по ремонту и реконструкции вашего строения. Мы гарантируем выполнение всех задач в установленные сроки и с соблюдением всех строительных норм и стандартов. Связавшись с Геракл24, вы можете быть спокойны, что ваше здание в надежных руках.
Мы предлагаем консультацию и дать ответы на все вопросы. Контактируйте с нами, чтобы обсудить ваш проект и узнать о наших сервисах. Мы поможем вам сохранить и улучшить ваш дом, сделав его безопасным и комфортным для проживания на долгие годы.
Gerakl24 – ваш выбор для реставрации и ремонта домов в Красноярске и области.
Discover Pierre Gasly’s https://alpine.pierre-gasly.com journey through the world of Formula 1, from his beginnings with Toro Rosso to his extraordinary achievements with Alpine.
Victor Wembanyama’s travel postcard https://san-antonio-spurs.victor-wembanyama.biz from his career in France to his impact in the NBA with the San Antonio Spurs.
Golden State Warriors success story https://golden-state-warriors.stephen-curry-fr.com Stephen Curry: From becoming a leader to creating a basketball dynasty that redefined the game.
Discover Casper Ruud’s https://tennis.casper-ruud-fr.com journey from his Challenger debut to the top 10 of the world tennis rankings. A unique success.
Hey there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my old room mate! He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this article to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
You are my inhalation, I have few web logs and rarely run out from to post : (.
NetTruyen ZZZ: Nền tảng đọc truyện tranh trực tuyến dành cho mọi lứa tuổi
NetTruyen ZZZ là nền tảng đọc truyện tranh trực tuyến miễn phí với số lượng truyện tranh lên đến hơn 30.000 đầu truyện với chất lượng hình ảnh và tốc độ tải cao. Nền tảng được xây dựng với mục tiêu mang đến cho người đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện tranh tốt nhất, đồng thời tạo dựng cộng đồng yêu thích truyện tranh sôi động và gắn kết với hơn 11 triệu thành viên (tính đến tháng 7 năm 2024).
NetTruyen ZZZ – Kho tàng truyện tranh phong phú:
NetTruyen ZZZ sở hữu kho tàng truyện tranh khổng lồ với hơn 30.000 đầu truyện thuộc nhiều thể loại khác nhau như:
● Manga: Những bộ truyện tranh Nhật Bản với nhiều thể loại phong phú như lãng mạn, hành động, hài hước, v.v.
● NetTruyen anime: Hàng ngàn bộ truyện tranh anime chọn lọc được đăng tải đều đặn trên NetTruyen ZZZ được chuyển thể từ phim hoạt hình Nhật Bản với nội dung hấp dẫn và hình ảnh đẹp mắt.
● Truyện manga: Hơn 10.000 bộ truyện tranh manga hay nhất được đăng tải đầy đủ trên NetTruyen ZZZ.
● Truyện manhua: Hơn 5000 bộ truyện tranh manhua được đăng tải trọn bộ đầy đủ trên NetTruyen ZZZ.
● Truyện manhwa: Những bộ truyện tranh manhwa Hàn Quốc được yêu thích nhất có đầy đủ trên NetTruyen với cốt truyện lôi cuốn và hình ảnh bắt mắt cùng với nét vẽ độc đáo và nội dung đa dạng.
● Truyện ngôn tình: Những câu chuyện tình yêu lãng mạn, ngọt ngào và đầy cảm xúc.
● Truyện trinh thám: Những câu chuyện ly kỳ, bí ẩn và đầy lôi cuốn xoay quanh các vụ án và quá trình phá án.
● Truyện tranh xuyên không: Những câu chuyện về những nhân vật du hành thời gian hoặc không gian đến một thế giới khác.
NetTruyen ZZZ không ngừng cập nhật những bộ truyện tranh mới nhất và hot nhất trên thị trường, đảm bảo mang đến cho bạn đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện mới mẻ và thú vị nhất.
Chất lượng hình ảnh và nội dung đỉnh cao tại NetTruyenZZZ:
Với hơn 30 triệu lượt truy cập hằng tháng, NetTruyen ZZZ luôn chú trọng vào chất lượng hình ảnh và nội dung của các bộ truyện tranh được đăng tải trên nền tảng. Hình ảnh được hiển thị sắc nét, rõ ràng, không bị mờ hay vỡ ảnh. Nội dung được dịch thuật chính xác, dễ hiểu và giữ nguyên vẹn ý nghĩa của tác phẩm gốc.
NetTruyen ZZZ hợp tác với đội ngũ dịch giả và biên tập viên chuyên nghiệp, giàu kinh nghiệm để đảm bảo chất lượng bản dịch tốt nhất. Nền tảng cũng có hệ thống kiểm duyệt nội dung nghiêm ngặt để đảm bảo nội dung lành mạnh, phù hợp với mọi lứa tuổi.
Trải nghiệm đọc truyện mượt mà, tiện lợi:
NetTruyen ZZZ được thiết kế với giao diện đẹp mắt, thân thiện với người dùng và dễ dàng sử dụng. Bạn đọc có thể đọc truyện tranh trên mọi thiết bị, từ máy tính, điện thoại thông minh đến máy tính bảng. Nền tảng cũng cung cấp nhiều tính năng tiện lợi như:
● Tìm kiếm truyện tranh theo tên, tác giả, thể loại, v.v.
● Lưu truyện tranh yêu thích để đọc sau.
● Đánh dấu trang để dễ dàng quay lại vị trí đang đọc.
● Chia sẻ truyện tranh với bạn bè.
● Tham gia bình luận và thảo luận về truyện tranh.
NetTruyen ZZZ luôn nỗ lực để mang đến cho bạn đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện mượt mà, tiện lợi và thú vị nhất.
Định hướng phát triển:
NetTruyen ZZZ cam kết không ngừng phát triển và hoàn thiện để trở thành nền tảng đọc truyện tranh trực tuyến tốt nhất dành cho bạn đọc tại Việt Nam. Nền tảng sẽ tiếp tục cập nhật những bộ truyện tranh mới nhất và hot nhất trên thị trường thế giới, đồng thời nâng cao chất lượng hình ảnh và nội dung. NetTruyen ZZZ cũng sẽ phát triển thêm nhiều tính năng mới để mang đến cho bạn đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện tốt nhất.
NetTruyen ZZZ luôn đặt lợi ích của bạn đọc lên hàng đầu. Nền tảng cam kết:
● Cung cấp kho tàng truyện tranh khổng lồ và đa dạng với chất lượng hình ảnh và nội dung đỉnh cao.
● Mang đến cho bạn đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện mượt mà, tiện lợi và thú vị nhất.
● Luôn lắng nghe ý kiến phản hồi của bạn đọc và không ngừng cải thiện để mang đến dịch vụ tốt nhất.
NetTruyen ZZZ hy vọng sẽ trở thành người bạn đồng hành không thể thiếu của bạn trong hành trình khám phá thế giới truyện tranh đầy màu sắc.
Kết nối với NetTruyen ZZZ ngay hôm nay để tận hưởng những trải nghiệm đọc truyện tuyệt vời.
Hello there, just became alert to your blog through Google, and found that it’s truly informative. I’m going to watch out for brussels. I’ll be grateful if you continue this in future. A lot of people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
The story of Fernando Alonso https://formula-1.fernando-alonso-fr.com in Formula 1: a unique path to success through talent, tenacity and strategic decisions, inspiring and exciting.
The fascinating story of the creation and rapid growth of Facebook https://facebook.mark-zuckerberg-fr.biz under the leadership of Mark Zuckerberg, who became one of the most influential technology entrepreneurs of our time.
Max Verstappen and Red Bull Racing’s https://red-bull-racing.max-verstappen-fr.com path to success in Formula 1. A story of talent, determination and team support leading to a championship title.
The astonishing story of Emmanuel Macron’s https://president-of-france.emmanuel-macron-fr.com political rise from bank director to the highest office in France.
Une ascension fulgurante au pouvoir Donald Trump https://usa.donald-trump-fr.com et son empire commercial
The fascinating story of the creation and meteoric rise of Amazon https://amazon.jeff-bezos-fr.com from its humble beginnings as an online bookstore to its dominant force in the world of e-commerce.
A fascinating story about how Elon Musk https://spacex.elon-musk-fr.com and his company SpaceX revolutionized space exploration, opening new horizons for humanity.
An exploration of Nicole Kidman’s https://watch.nicole-kidman-fr.com career, her notable roles, and her continued quest for excellence as an actress.
How Taylor Swift https://midnights.taylor-swift-fr.com reinvented her sound and image on the intimate and reflective album “Midnights,” revealing new dimensions of her talent.
Explore the rich history and unrivaled atmosphere of the iconic Old Trafford Stadium https://old-trafford.manchester-united-fr.com, home of one of the world’s most decorated football clubs, Manchester United.
is montenegro in the eu Montenegro
The iconic Anfield https://enfield.liverpool-fr.com stadium and the passionate Liverpool fans are an integral part of English football culture.
The new Premier League https://premier-league.chelsea-fr.com season has gotten off to an intriguing start, with a new-look Chelsea looking to return to the Champions League, but serious challenges lie ahead.
Hey! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and say I genuinely enjoy reading your blog posts. Can you suggest any other blogs/websites/forums that go over the same topics? Thanks!
The story of Kanye West https://the-college-dropout.kanye-west-fr.com, starting with his debut album “The College Dropout,” which changed hip-hop and became his cultural legacy.
The fascinating story of the phenomenal rise and meteoric fall of Diego Maradona https://napoli.diegomaradona.biz, who became a cult figure at Napoli in the 1980s.
A fascinating story about Brazilian veteran Thiago Silva’s https://chelsea.thiago-silva.net difficult path to the top of European football as part of Chelsea London.
The story of Luka Modric’s rise https://real-madrid.lukamodric-br.com from young talent to one of the greatest midfielders of his generation and a key player for the Royals.
From academy product to captain and leader of Real Madrid https://real-madrid.ikercasillas-br.com Casillas became one of the greatest players in the history of Real Madrid.
nettruyen
NetTruyen ZZZ: Nền tảng đọc truyện tranh trực tuyến dành cho mọi lứa tuổi
NetTruyen ZZZ là nền tảng đọc truyện tranh trực tuyến miễn phí với số lượng truyện tranh lên đến hơn 30.000 đầu truyện với chất lượng hình ảnh và tốc độ tải cao. Nền tảng được xây dựng với mục tiêu mang đến cho người đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện tranh tốt nhất, đồng thời tạo dựng cộng đồng yêu thích truyện tranh sôi động và gắn kết với hơn 11 triệu thành viên (tính đến tháng 7 năm 2024).
NetTruyen ZZZ – Kho tàng truyện tranh phong phú:
NetTruyen ZZZ sở hữu kho tàng truyện tranh khổng lồ với hơn 30.000 đầu truyện thuộc nhiều thể loại khác nhau như:
● Manga: Những bộ truyện tranh Nhật Bản với nhiều thể loại phong phú như lãng mạn, hành động, hài hước, v.v.
● NetTruyen anime: Hàng ngàn bộ truyện tranh anime chọn lọc được đăng tải đều đặn trên NetTruyen ZZZ được chuyển thể từ phim hoạt hình Nhật Bản với nội dung hấp dẫn và hình ảnh đẹp mắt.
● Truyện manga: Hơn 10.000 bộ truyện tranh manga hay nhất được đăng tải đầy đủ trên NetTruyen ZZZ.
● Truyện manhua: Hơn 5000 bộ truyện tranh manhua được đăng tải trọn bộ đầy đủ trên NetTruyen ZZZ.
● Truyện manhwa: Những bộ truyện tranh manhwa Hàn Quốc được yêu thích nhất có đầy đủ trên NetTruyen với cốt truyện lôi cuốn và hình ảnh bắt mắt cùng với nét vẽ độc đáo và nội dung đa dạng.
● Truyện ngôn tình: Những câu chuyện tình yêu lãng mạn, ngọt ngào và đầy cảm xúc.
● Truyện trinh thám: Những câu chuyện ly kỳ, bí ẩn và đầy lôi cuốn xoay quanh các vụ án và quá trình phá án.
● Truyện tranh xuyên không: Những câu chuyện về những nhân vật du hành thời gian hoặc không gian đến một thế giới khác.
NetTruyen ZZZ không ngừng cập nhật những bộ truyện tranh mới nhất và hot nhất trên thị trường, đảm bảo mang đến cho bạn đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện mới mẻ và thú vị nhất.
Chất lượng hình ảnh và nội dung đỉnh cao tại NetTruyenZZZ:
Với hơn 30 triệu lượt truy cập hằng tháng, NetTruyen ZZZ luôn chú trọng vào chất lượng hình ảnh và nội dung của các bộ truyện tranh được đăng tải trên nền tảng. Hình ảnh được hiển thị sắc nét, rõ ràng, không bị mờ hay vỡ ảnh. Nội dung được dịch thuật chính xác, dễ hiểu và giữ nguyên vẹn ý nghĩa của tác phẩm gốc.
NetTruyen ZZZ hợp tác với đội ngũ dịch giả và biên tập viên chuyên nghiệp, giàu kinh nghiệm để đảm bảo chất lượng bản dịch tốt nhất. Nền tảng cũng có hệ thống kiểm duyệt nội dung nghiêm ngặt để đảm bảo nội dung lành mạnh, phù hợp với mọi lứa tuổi.
Trải nghiệm đọc truyện mượt mà, tiện lợi:
NetTruyen ZZZ được thiết kế với giao diện đẹp mắt, thân thiện với người dùng và dễ dàng sử dụng. Bạn đọc có thể đọc truyện tranh trên mọi thiết bị, từ máy tính, điện thoại thông minh đến máy tính bảng. Nền tảng cũng cung cấp nhiều tính năng tiện lợi như:
● Tìm kiếm truyện tranh theo tên, tác giả, thể loại, v.v.
● Lưu truyện tranh yêu thích để đọc sau.
● Đánh dấu trang để dễ dàng quay lại vị trí đang đọc.
● Chia sẻ truyện tranh với bạn bè.
● Tham gia bình luận và thảo luận về truyện tranh.
NetTruyen ZZZ luôn nỗ lực để mang đến cho bạn đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện mượt mà, tiện lợi và thú vị nhất.
Định hướng phát triển:
NetTruyen ZZZ cam kết không ngừng phát triển và hoàn thiện để trở thành nền tảng đọc truyện tranh trực tuyến tốt nhất dành cho bạn đọc tại Việt Nam. Nền tảng sẽ tiếp tục cập nhật những bộ truyện tranh mới nhất và hot nhất trên thị trường thế giới, đồng thời nâng cao chất lượng hình ảnh và nội dung. NetTruyen ZZZ cũng sẽ phát triển thêm nhiều tính năng mới để mang đến cho bạn đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện tốt nhất.
NetTruyen ZZZ luôn đặt lợi ích của bạn đọc lên hàng đầu. Nền tảng cam kết:
● Cung cấp kho tàng truyện tranh khổng lồ và đa dạng với chất lượng hình ảnh và nội dung đỉnh cao.
● Mang đến cho bạn đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện mượt mà, tiện lợi và thú vị nhất.
● Luôn lắng nghe ý kiến phản hồi của bạn đọc và không ngừng cải thiện để mang đến dịch vụ tốt nhất.
NetTruyen ZZZ hy vọng sẽ trở thành người bạn đồng hành không thể thiếu của bạn trong hành trình khám phá thế giới truyện tranh đầy màu sắc.
Kết nối với NetTruyen ZZZ ngay hôm nay để tận hưởng những trải nghiệm đọc truyện tuyệt vời.
сайт казино рио бет Rio Bet
Dragon Money Casino официальный сайт Dragon Money
Hey there are using WordPress for your blog platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you require any html coding knowledge to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Лучшие пансионаты для пожилых людей https://ernst-neizvestniy.ru в Самаре – недорогие дома для престарелых в Самарской области
The fascinating story of Sergio Ramos’ https://seville.sergioramos.net rise from Sevilla graduate to one of Real Madrid and Spain’s greatest defenders.
Hey there! I know this is kinda off topic however , I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest writing a blog post or vice-versa? My website goes over a lot of the same topics as yours and I feel we could greatly benefit from each other. If you happen to be interested feel free to shoot me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Terrific blog by the way!
The incredible success story of 20-year-old Florian Wirtz https://bayer-04.florianwirtz-br.com, who quickly joined the Bayer team and became one of the best young talents in the world.
The incredible story https://napoli.khvichakvaratskhelia-br.com of a young Georgian talent’s transformation into an Italian Serie A star. Khvicha Kvaraeshvili is a rising phenomenon in European football.
O meio-campista Rafael Veiga leva https://palmeiras.raphaelveiga-br.com o Palmeiras ao sucesso – o campeonato brasileiro e a vitoria na Copa Libertadores aos 24 anos.
Midfielder Rafael Veiga leads https://manchester-city.philfoden-br.com Palmeiras to success – the championship Brazilian and victory in the Copa Libertadores at the age of 24.
The rise of 20-year-old midfielder Jamal Musiala https://bavaria.jamalmusiala-br.com to the status of a winger in the Bayern Munich team. A story of incredible talent.
A historia da jornada triunfante de Anitta https://veneno.anitta-br.com de aspirante a cantora a uma das interpretes mais influentes da musica moderna, incluindo sua participacao na serie de TV “Veneno”.
Fabrizio Moretti https://the-strokes.fabriziomoretti-br.com the influential drummer of The Strokes, and his unique sound revolutionized the music scene, remaining icons of modern rock.
Selena Gomez https://calm-down.selenagomez-br.net the story from child star to global musical influence, summarized in hit “Calm Down”, with Rema.
you might have a terrific blog here! would you like to make some invite posts on my blog?
Bieber’s https://baby.justinbieber-br.com path to global fame began with his breakthrough success Baby, which became his signature song and one of the most popular music videos of all time.
In the world of professional tennis, the name of Gustavo Kuerten https://roland-garros.gustavokuerten.com is closely linked to one of the most prestigious Grand Slam tournaments – Roland Garros.
Daniel Alves https://paris-saint-germain.danielalves.net is a name that symbolizes the greatness of the world of football.
Bruno Miguel Borges Fernandes https://manchester-united.brunofernandes-br.com was born on September 8, 1994 in Maia, Portugal.
Rodrygo Silva de Goes https://real-madrid.rodrygo-br.com, known simply as Rodrygo, emerged as one of the the brightest young talents in world football.
I went over this web site and I believe you have a lot of superb info , saved to my bookmarks (:.
Thank you for sharing excellent informations. Your web site is very cool. I’m impressed by the details that you have on this site. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for more articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the info I already searched everywhere and simply could not come across. What a great website.
Toni Kroos https://real-madrid.tonikroos-ar.com the German midfielder known for his accurate passes and calmness on the field, has achieved remarkable success at one of the most prestigious football clubs in the world.
Robert Lewandowski https://barcelona.robertlewandowski-ar.com is one of the most prominent footballers of our time, and his move to Barcelona has become one of the most talked about topics in world football.
Keep functioning ,impressive job!
Pedro Gonzalez Lopez https://barcelona.pedri-ar.com known as Pedri, was born on November 25, 2002 in the small town of Tegeste, located on Tenerife, one of the Canary Islands.
Andreson Souza Conceicao https://al-nassr.talisca-ar.com known as Talisca, is one of the brightest stars of modern football.
very nice post, i certainly love this website, carry on it
Brazilian footballer Neymar https://al-hilal.neymar-ar.com known for his unique playing style and outstanding achievements in world football, has made a surprise move to Al Hilal Football Club.
Luka Modric https://real-madrid.lukamodric-ar.com can certainly be called one of the outstanding midfielders in modern football.
Football in Saudi Arabia https://al-hilal.ali-al-bulaihi-ar.com has long been one of the main sports, attracting millions of fans. In recent years, one of the brightest stars in Saudi football has been Ali Al-Bulaihi, defender of Al-Hilal Football Club.
visit my website https://currencyconvert.net
Сайт https://ps-likers.ru предлагает уроки по фотошоп для начинающих. На страницах сайта можно найти пошаговые руководства по анимации, созданию графики для сайтов, дизайну, работе с текстом и фотографиями, а также различные эффекты.
RDBox.de https://rdbox.de bietet schallgedammte Gehause fur 3D-Drucker, die eine sehr leise Druckumgebung schaffen – nicht lauter als ein Kuhlschrank. Unsere Losungen sorgen fur stabile Drucktemperatur, Vibrationsisolierung, Luftreinigung und mobile App-Steuerung.
Karim Benzema https://al-ittihad.karimbenzema.ae is a name worthy of admiration and respect in the world of football.
Maria Sharapova https://tennis.maria-sharapova-ar.com was born on April 19, 1987 in Nyagan, Russia. When Masha was 7 years old, her family moved to Florida, where she started playing tennis.
Roberto Firmino https://al-ahli.roberto-firmino-ar.com one of the most talented and famous Brazilian footballers of our time, has paved his way to success in different leagues and teams.
Angel Di Maria https://benfica.angel-di-maria-ar.com is a name that will forever remain in the memories of Benfica fans.
Khvicha Kvaratskhelia https://napoli.khvicha-kvaratskhelia-ar.com is a name that in recent years has become a symbol of Georgian football talent and ambition.
Казахский национальный технический университет https://satbayev.university им. К.Сатпаева
Продажа новых автомобилей Hongqi
https://hongqi-krasnoyarsk.ru/buyers/credit-form в Красноярске у официального дилера Хончи. Весь модельный ряд, все комплектации, выгодные цены, кредит, лизинг, трейд-ин
online shopping pharmacy india: cheapest online pharmacy india – top online pharmacy india
https://foruspharma.com/# mexican drugstore online
canadian world pharmacy: medication canadian pharmacy – escrow pharmacy canada
canadian pharmacy world [url=https://canadapharmast.online/#]canadian pharmacies that deliver to the us[/url] canadianpharmacy com
medicine in mexico pharmacies: pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa – pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa
Sadio Mane https://al-nassr.sadio-mane-ar.com the Senegalese footballer best known for his performances at clubs such as Southampton and Liverpool, has become a prominent figure in Al Nassr.
Brazilian footballer Ricardo Escarson https://orlando-city.kaka-ar.com dos Santos Leite, better known as Kaka, is one of the most famous and successful players in football history.
Zinedine Zidane https://real-madrid.zinedine-zidane-ar.com the legendary French footballer, entered the annals of football history as a player and coach.
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs: mexican pharmacy – mexico drug stores pharmacies
Brazilian footballer Malcom https://al-hilal.malcom-ar.com (full name Malcom Felipe Silva de Oliveira) achieved great success in Al Hilal, one of the leading football teams in Saudi Arabia and the entire Middle East.
Monica Bellucci https://dracula.monica-bellucci-ar.com one of the most famous Italian actresses of our time, has a distinguished artistic career spanning many decades. Her talent, charisma, and stunning beauty made her an icon of world cinema.
medication from mexico pharmacy: pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa – mexico drug stores pharmacies
https://canadapharmast.online/# canadian online drugs
reputable canadian pharmacy: canadian pharmacy ltd – canadian pharmacy sarasota
Jackie Chan https://karate-kid.jackiechan-ar.com was born in 1954 in Hong Kong under the name Chan Kong San.
mexican mail order pharmacies: buying prescription drugs in mexico – best online pharmacies in mexico
best online pharmacy india: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – top online pharmacy india
mexico pharmacy [url=https://foruspharma.com/#]mexican mail order pharmacies[/url] mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
http://indiapharmast.com/# Online medicine order
indian pharmacy online: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
indian pharmacy paypal: india pharmacy mail order – п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
mexican pharmaceuticals online: mexican pharmaceuticals online – mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
https://clomiddelivery.pro/# get clomid
amoxicillin 500mg capsules price: buy amoxicillin 500mg online – buy amoxicillin 250mg
https://ciprodelivery.pro/# cipro online no prescription in the usa
buy ciprofloxacin over the counter [url=https://ciprodelivery.pro/#]buy ciprofloxacin[/url] cipro ciprofloxacin
https://paxloviddelivery.pro/# Paxlovid over the counter
Travis Scott https://astroworld.travis-scott-ar.com is one of the brightest stars in the modern hip-hop industry.
The history of one of France’s https://france.paris-saint-germain-ar.com most famous football clubs, Paris Saint-Germain, began in 1970, when capitalist businessmen Henri Delaunay and Jean-Auguste Delbave founded the club in the Paris Saint-Germain-en-Laye area.
Juventus Football Club https://italy.juventus-ar.com is one of the most successful and decorated clubs in the history of Italian and world football.
Chelsea https://england.chelsea-ar.com is one of the most successful English football clubs of our time.
paxlovid buy: paxlovid price – п»їpaxlovid
https://paxloviddelivery.pro/# п»їpaxlovid
paxlovid pharmacy [url=https://paxloviddelivery.pro/#]paxlovid buy[/url] buy paxlovid online
http://amoxildelivery.pro/# amoxicillin 500mg tablets price in india
Автомобили Hongqi https://hongqi-krasnoyarsk.ru в наличии – официальный дилер Hongqi Красноярск
Liverpool https://england.liverpool-ar.com holds a special place in the history of football in England.
Priyanka Chopra https://baywatch.priyankachopra-ar.com is an Indian actress, singer, film producer and model who has achieved global success.
After some difficult years in the late 2010s, Manchester United https://england.manchester-united-ar.com returned to greatness in English football by 2024.
The Formula One World Championship https://world-circuit-racing-championship.formula-1-ar.com, known as the Formula Championship in motor racing, is the highest tier of professional motor racing.
Wonderful paintings! That is the type of info that are supposed to be shared across the internet. Shame on the seek engines for not positioning this put up higher! Come on over and consult with my site . Thank you =)
http://doxycyclinedelivery.pro/# doxycycline 100mg for sale
http://doxycyclinedelivery.pro/# doxycycline no prescription
where to get amoxicillin over the counter [url=http://amoxildelivery.pro/#]amoxicillin canada price[/url] can we buy amoxcillin 500mg on ebay without prescription
You made some clear points there. I looked on the internet for the subject and found most guys will agree with your website.
doxycycline order: doxycycline 100 mg cap over the counter – doxycycline uk
Does your site have a contact page? I’m having trouble locating it but, I’d like to shoot you an email. I’ve got some recommendations for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great site and I look forward to seeing it expand over time.
Muhammad Ali https://american-boxer.muhammad-ali-ar.com is perhaps one of the most famous and greatest athletes in the history of boxing.
Thanks for this post, I am a big fan of this web site would like to continue updated.
http://amoxildelivery.pro/# how to get amoxicillin over the counter
https://doxycyclinedelivery.pro/# doxycycline 100mg best price
cipro online no prescription in the usa [url=https://ciprodelivery.pro/#]ciprofloxacin 500 mg tablet price[/url] buy cipro cheap
Have you ever considered creating an ebook or guest authoring on other websites? I have a blog centered on the same ideas you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my subscribers would appreciate your work. If you’re even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an email.
The road to the Premier League https://english-championship.premier-league-ar.com begins long before a team gets promoted to the English Premier League for the first time
The Italian football championship https://italian-championship.serie-a-ar.com known as Serie A, has seen an impressive revival in recent years.
In the German football https://german-championship.bundesliga-football-ar.com championship known as the Bundesliga, rivalries between clubs have always been intense.
cost cheap clomid price: can you get cheap clomid without a prescription – can i get generic clomid prices
https://doxycyclinedelivery.pro/# doxycycline capsule 100mg price
The Saudi Football League https://saudi-arabian-championship.saudi-pro-league-ar.com known as the Saudi Professional League, is one of the most competitive and dynamic leagues in the world.
Rodrigo Goes https://real-madrid.rodrygo-ar.com better known as Rodrigo, is one of the brightest young talents in modern football.
Arsenal https://arsenal.mesut-ozil-ar.com made a high-profile signing in 2013, signing star midfielder Mesut Ozil from Real Madrid.
https://paxloviddelivery.pro/# paxlovid generic
how can i get cheap clomid without prescription [url=https://clomiddelivery.pro/#]cost of clomid without insurance[/url] can i order cheap clomid no prescription
Bayern Munich’s https://bayern.jamal-musiala-ar.com young midfielder, Jamal Musiala, has become one of the brightest talents in European football.
https://paxloviddelivery.pro/# buy paxlovid online
подъемное оборудование подъемное оборудование лифты
amoxicillin 775 mg: amoxicillin 250 mg – buy amoxicillin 250mg
Al-Nasr Club https://saudi.al-hilal-ar.com from Riyadh has a rich history of success, but its growth has been particularly impressive in recent years.
FC Barcelona https://spain.fc-barcelona-ar.com is undoubtedly one of the most famous and well-known football clubs in the world.
http://clomiddelivery.pro/# cost of clomid no prescription
http://ciprodelivery.pro/# ciprofloxacin 500 mg tablet price
doxycycline brand [url=https://doxycyclinedelivery.pro/#]doxycycline 100 mg cost generic[/url] buy doxycycline 100 mg tablet
When I initially commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get 4 emails with the identical comment. Is there any means you’ll be able to take away me from that service? Thanks!
https://paxloviddelivery.pro/# paxlovid india
split to Montenegro rent a yacht Montenegro
Arsenal https://england.arsenal-ar.com is one of the most famous and successful football clubs in the history of English football.
purchase cipro: ciprofloxacin over the counter – buy cipro cheap
Ремонт плоской кровли https://remontiruem-krovly.ru в Москве, цена работы за 1 м?. Прайс лист на работы под ключ, отзывы и фото.
The future football star Shabab Al-Ahly https://dubai.shabab-al-ahli-ar.com was born in Dubai in 2000. From a young age, he showed exceptional football abilities and joined the youth academy of one of the UAE’s leading clubs, Shabab Al-Ahly.
coindarwin price analysis
The Story Behind Solana’s Originator Toly’s Triumph
Subsequent to A Pair of Portions of Espresso and a Beer
Yakovenko, the visionary the innovator behind Solana, started his path with a modest ritual – a couple of coffees and an ale. Little did he know, these moments would trigger the machinery of his destiny. At present, Solana exists as an influential participant in the blockchain sphere, having a market cap in the billions.
Ethereum ETF First Sales
The Ethereum ETF newly launched with a substantial volume of trades. This landmark occasion observed multiple spot Ethereum ETFs from various issuers be listed in the U.S., bringing unseen activity into the typically steady ETF trading space.
SEC Sanctions Ethereum ETF
The Securities and Exchange Commission has officially approved the spot Ethereum ETF to trade. As a cryptographic asset that includes smart contracts, it is expected that Ethereum to majorly affect the crypto industry due to this approval.
Trump’s Bitcoin Tactics
As the election approaches, Trump presents himself as the “Crypto President,” constantly highlighting his backing of the crypto sector to garner votes. His strategy differs from Biden’s tactic, aiming to capture the support of the crypto community.
Elon Musk’s Crypto Moves
Musk, a well-known figure in the crypto community and an advocate of Trump, shook things up again, propelling a meme coin linked to his antics. His participation keeps influencing market trends.
Binance Developments
Binance’s unit, BAM, has been permitted to use customer funds into U.S. Treasury instruments. Moreover, Binance noted its 7th anniversary, underscoring its progress and obtaining various compliance licenses. Meanwhile, Binance also announced plans to delist several major crypto trading pairs, influencing multiple market entities.
Artificial Intelligence and Economic Outlook
The chief stock analyst at Goldman Sachs recently commented that artificial intelligence won’t trigger a major economic changeHere’s the spintax version of the provided text with possible synonyms
купить новостройку с отделкой купить новостройку от застройщика
купить новостройку цены застройщика новые квартиры от застройщиков
купить однокомнатную квартиру в новостройке купить новостройку недорого
azithromycin amoxicillin: where can i buy amoxicillin over the counter – can i buy amoxicillin over the counter
квартиры от застройщика цены купить 2 квартиру новостройке
квартиры от застройщика цены жк https://novyekvartiry2.ru
Please let me know if you’re looking for a article author for your weblog. You have some really great posts and I think I would be a good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d really like to write some content for your blog in exchange for a link back to mine. Please send me an e-mail if interested. Kudos!
недвижимость новостройки купить купить квартиру от застройщика
купить квартиру в новостройке https://kvartiranovostroi2.ru
Красивая музыка https://melodia.space для души слушать онлайн.
seo продвижение и раскрутка сайта раскрутка сайта цена казань
Новинний ресурс https://actualnews.kyiv.ua про всі важливі події в Україні та світі.
Україна свіжі новини https://kiev-pravda.kiev.ua останні події на сьогодні
Головні новини https://mediashare.com.ua про регіон України. Будьте в курсі останніх новин
Новини та аналітика https://newsportal.kyiv.ua ситуація в Україні.
Головні новини https://pto-kyiv.com.ua України та світу
Новини України https://sensus.org.ua та світу сьогодні. Головні та останні новини дня
Новини, останні події https://prp.org.ua в Україні та світі, новини політики, бізнесу та економіки, законодавства
Останні новини світу https://uamc.com.ua про Україну від порталу новин Ukraine Today
paxlovid price: buy paxlovid online – п»їpaxlovid